Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. The economic essence of the financial condition of the enterprise
- 2. Methods of analysis and forecasting
- 3. Conceptual approaches to the diagnosis and forecasting of the financial condition of the enterprise
- Conclusions
- Source list
Introduction
In order to function within the framework of a market economy, business entities need to ensure the condition of available financial resources, which would ensure the uninterrupted fulfillment of financial obligations to business partners, the country, owners and employees.
The financial condition of the enterprise characterized by the financial resources required for the implementation of normal production and commercial activities, the appropriateness and effectiveness of their placement and use, the level of relations in the financial sphere with other business entities, the degree of solvency and financial stability. The financial condition of the enterprise, in turn, depends on the results of its production, commercial and financial activities.
Issues of economic evaluation and analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise are widely studied in the works of domestic scientists – V. G. Artemenko, M. I. Bakanov, I. T Balabanov, S. B. Bargolts, I. A. Blanc, T. B. Berdnikova, N. V. Voitlovsky, L. S. Vasilyeva, A. I. Ginsburg, E. V. Efimova, A. P. Kalinina, I. I. Karakoza, V. V. Kovalev, I. V. Lipsits, N. P. Lyubushin, V. I. Makaryeva, D. A. Pankov, L. V. Prykina, G. V. Savitskaya, E. S. Stoyanov, N. A. Rusak, S. K. Tatura, A. D. Sheremet, G. A. Shtofer and many others. [13].
A foreign school for studying the financial condition of an enterprise closely associates this concept with an assessment of the probability of bankruptcy of a business entity in order to predict a crisis situation in advance, before its signs appear, as well as the possible prevention of this situation in the future. A large number of studies conducted in the crisis of 60-70 years of the last century in the United States. Foreign economists W. Beaver, E. Altman, D. Duran, L. Korobou, O. Stur, D. Martin, M. Brown, D. Stone, C. Hitching, J. K. Van Horne, R. Tuffler, G Springgate, D. Fulmer, and others analyzed the financial performance of large samples of various enterprises that ceased to exist due to bankruptcy. [14].
The aim of this work is to study innovations in the analysis of the activities of several food industry enterprises and develop practical recommendations for improving their financial condition.
The object of study is a system of indicators for analyzing and forecasting the financial activities of the organization.
The subject of the study is the methodology for assessing and forecasting the financial condition of an enterprise.
To achieve the goal, the following tasks were set and solved:
- analyzed the essence of the financial analysis of the enterprise;
- investigated financial condition as an object of management;
- studied methods of analysis and forecasting the financial condition of the enterprise;
- considered innovations in the diagnosis and forecasting of the financial situation of enterprises;
- the analysis of the financial condition of food industry enterprises;
- developed guidelines for improving financial condition.
The instrumental apparatus includes the following: systemic, logical, comparative-analytical, statistical, groupings, analysis and synthesis.
The research information base is official reporting data, publications on selected issues in periodicals, materials of scientific and practical conferences and seminars, computer publications and Internet sites. In the course of this work, data from technical and economic indicators, the 1st and 2nd reporting forms are used.
Based on the study of the theoretical foundations of the financial condition, one work published that took part in the conference International forum for Multiple Academic Disciplines
in Germany, Dresden on May 15, 2017.
1. The economic essence of the financial condition of the enterprise
The financial condition of the enterprise characterized by a combination of financial indicators and is the result of a capital circulation or movement of assets and sources of their formation [5].
The opinions of domestic authors characterize the financial condition as a combination of certain categories.
R. S. Sayfulin, T. V. Afanasyeva, T. N. Kutaeva, emphasize in the essence of the financial condition the need for financial resources, the rationality of the allocation of such (profitability).
M. I. Bakanov, A. D. Sheremet, G. I. Melnikov, without entering into a discussion with previous economists, also emphasizes in determining the financial condition the importance of current and long-term liquidity and solvency of the enterprise.
G. V. Savitskaya, E. Nosova, emphasize the inherent financial stability for the stability of the enterprise, with the same financial security of the enterprise and the rational use of resources.
I. L. Buzova, V. V. Kolmakov, S. Y. Korovin, L. G. Simonenko, bring to the fore the determination of the financial condition of his ability, based on the results of his economic activity, to occupy a stable position in the competitive market (business activity).
E. I. Shokhin, N. V. Kolchina, S. A. Kamsha, M. G. Kudinov, describe the financial condition generally, using indicators that reflect the absolute and relative values of the availability, placement and use of financial assets of the enterprise.
According to Savitskaya, the most significant characteristics of the financial condition: creditworthiness, probability of bankruptcy, leverage, solvency, financial stability and, of course, the structure of assets and liabilities, business activity, turnover and efficiency of use of capital
[12].
The financial condition is characterized [3]: the provision of the enterprise with the financial resources necessary for the normal functioning of the enterprise, the appropriateness of their location, solvency and financial stability
.
Summarizing the opinion of domestic researchers, we came to the conclusion that the financial condition of an enterprise is a complex economic category that determines the ability of an enterprise to finance its activities and is characterized by a system of indicators for allocating funds (assets) and their effective use, as well as their formation sources (liabilities); solvency and financial stability.
Financial resources for the enterprise are: equity, profit, loans received and securities placed on the market. It must constantly take care of increasing the efficiency of the use of financial resources, since their increase will contribute to the expansion of the enterprise, its economic growth.
The main factors affecting the financial condition of an enterprise are:
- external – the general stability of the economy, in particular: inflation, changes in price levels, exchange rates, bankruptcy of debtors;
- internal %ndash; the state of the financial planning of the enterprise; organizational management of stocks, receivables and payables, cash flows; composition, size and structure of the organization’s property.
That is, the financial condition of the enterprise depends on the results of its production, commercial and financial activities. If the production and financial plans successfully implemented, then this positively affects the financial position of the company. And, on the contrary, as a result of the under fulfillment of the plan for the production and sale of products, there is an increase in its cost, a decrease in revenue and the amount of profit, and as a result, a deterioration in the financial condition of the enterprise and its solvency [4].
Thus, the financial condition of the enterprise is a complex economic category, which characterized by the placement and use of funds and sources of their occurrence. The optimality of capital structure, as well as the optimality of asset structure contribute to maintaining the financial condition at the proper level.
2. Methods of analysis and forecasting
Assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise is carried out in order to identify the main factors affecting the "financial well-being" of the company, as well as to forecast growth trends and develop business development strategies [10].
The result of assessing the financial condition of the enterprise is:
- Identified changes in financial condition in the spatio-temporal aspect.
- Identified key factors determining changes in financial condition.
- Conclusions and forecast on the main trends in the financial condition of the enterprise.
Since financial analysis is a comprehensive study of the financial condition in order to further evaluate the results and develop strategic and tactical measures aimed at improving the efficiency of functioning, it should be sufficiently deep and comprehensive, touching on many aspects and characteristics of the enterprise.
Domestic and foreign scientists have developed many methods for analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise. In addition, the analysis itself is carried out in many directions: assessment of property status, liquidity, solvency, financial stability, business activity, profitability, etc.
Methods of analysis of financial condition are presented in table. 2.1.
Analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise should be comprehensively and comprehensively, exploring all the characteristics of this complex economic category, namely [9]:
- Assess the property condition of the enterprise and the dynamics of its change. At this stage, the absolute and relative changes in the balance sheet items for a certain period are studied, their trends are monitored and the structure of the enterprise’s financial resources is determined.
- Analyze the financial results of the company. At this stage, we study the dynamics and structure of the financial results of the enterprise, determine the factors that influenced the formation of its net profit.
- Analyze the liquidity of the enterprise using balance sheet data, which allows you to determine its ability to pay off its current liabilities. To analyze the liquidity of the enterprise by domestic authors, it is recommended to calculate indicators.
- Analyze the business activity of the enterprise, i.e. analyze the effectiveness of its core business, which is characterized by the speed of circulation of financial resources.
- Analyze the solvency (financial stability) of the enterprise, which is carried out according to its balance sheet and characterizes the structure of sources of financing resources, the degree of financial stability and independence of the enterprise from external sources of financing activities. A deeper analysis of the financial stability of the enterprise involves the calculation of a larger number of indicators, for example, 3 absolute and 12 relative [8].
- Analyze the profitability of the enterprise, which allows to evaluate the effectiveness of investment and the rationality of their use.
Table 2.1 – The main methods used in financial analysis
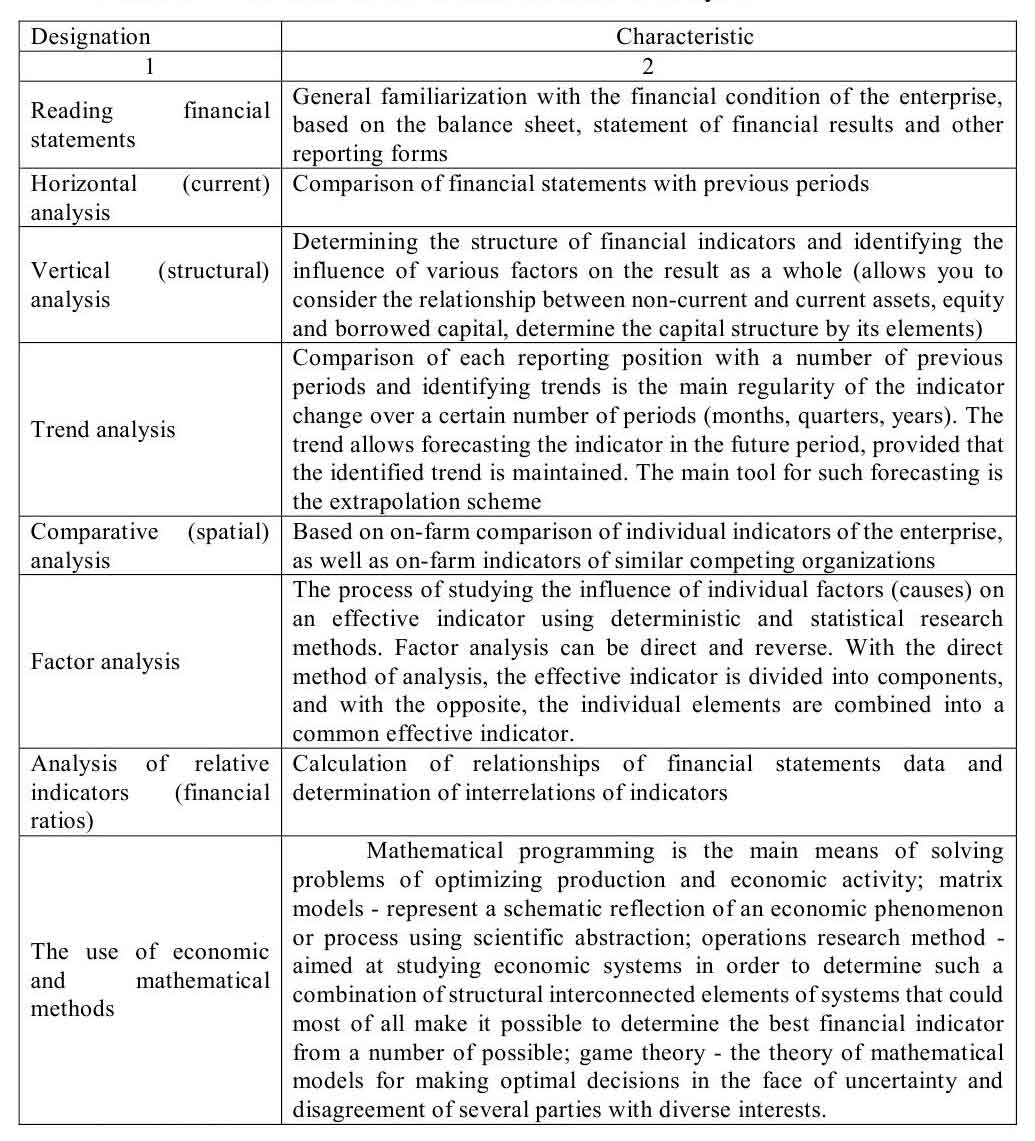
Compliteded based on [15], [7], [6]
On the basis of a deep, comprehensive analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise carried out in the above areas, a conclusion is prepared that includes a general assessment of the financial condition at the last reporting date and the dynamics of its change, as well as recommendations for its improvement in the future.
If an enterprise is unprofitable during the analyzed period and most indicators of financial condition do not meet regulatory requirements, and there is also a tendency to deteriorate, then the financial condition of the enterprise is considered unsatisfactory and it is necessary to develop measures to overcome the crisis.
The crisis will negatively affect the activities of the enterprise, irrelevant development of measures to bring the business entity out of the crisis will steadily direct him to bankruptcy. Optimal models for assessing bankruptcy can be considered Altman 2 and 5 factor models. 2-х и 5-ти факторные модели Альтмана.
Summarizing the foregoing, we dwell on the fact that the methodological approach to the content of the economic analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise, in our opinion, should be as follows: the analysis of financial results should be carried out in accordance with the logic of movement from general to particular and further, to determine the impact of particular on general.
In other words, first you need to evaluate the generalizing categories that characterize the financial results in their dynamics, consider the structure, determine the changes in the analyzed period in relation to the base period or to the business plan. Next, you need to identify the factors whose action entailed changes in these indicators. And only then you need to turn to a detailed analysis of financial results based on an in-depth analysis of private indicators and identification of profit margins.
In the West, about 50% of large and 18% of small and medium-sized firms rely on formalized quantitative methods in managing financial resources in analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise. The classification of quantitative forecasting methods is shown in figure 2.1. Forecasting the financial condition is based on the study of financial and economic activities in the past period and changes in the external and internal economic conditions in the future. The forecast of the further financial situation can be presented in the following two directions [11]:
- Forecast of a certain or several indicators of greatest interest and significance for the analyst, for example: sales revenue, profit, cost of production, etc.
- Forecast in the form of enterprise reporting tables in a standard or enlarged nomenclature of articles. Based on the analysis of historical data, each balance sheet item and the profit and loss statement are forecasted. A huge advantage of this form is that the forecast obtained allows you to comprehensively analyze the financial condition.

Figure 2.1 Basic forecasting methods
(animation: 6 frames, infinite repetitions, 154 kilobytes)
Methods of expert assessments provide for a multi-stage survey of experts on special schemes and processing of results using financial statistics tools. These methods in practice consist in using the experience and knowledge of the manager. This provides decision making in the simplest and fastest way. The disadvantage is the low accuracy of forecasting and the lack of responsibility for the forecast. Often, these methods are used in forecasting revenue, profit and market share.
Deterministic methods presuppose the presence of functional or rigidly determined relationships in which each value of a factor attribute corresponds to a well-defined nonrandom value of the resultant attribute. For example: to predict the cost of sales, based on the company's revenue for previous years. The balance model for predicting the economic potential of an enterprise is clear from its name. The balance sheet of the enterprise can be described at various levels, reflecting the relationship between the assets and liabilities of the enterprise. One of the simplest is the main balance equation, which has the form [11]:
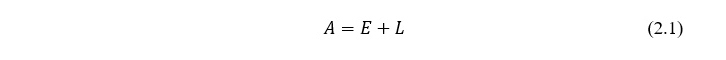
Where, А – assets, Е – equity, L – liability of enterprise.
The projected change in resource potential should be determined using:
- corresponding changes in sources of funds;
- possible changes in their ratio.
So, the balance model provides an opportunity to calculate the predicted value of one of the parameters of the equation: total assets, equity or borrowed funds when substituting the forecast values of two other factors.Стохастические методы предполагают наличие вероятностного характера как прогноза, так и самой связи между исследуемыми показателями. Вероятность получения точного прогноза возрастает при росте числа эмпирических данных.
The simple dynamic analysis method proceeds from the premise that the predicted indicator (Y) changes with direct (inverse) proportionality over time. To determine the predicted values of the indicator Y, a dependence is constructed similar to the following:
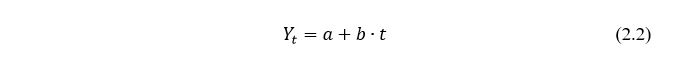
Where, t – sequence number of the period.
The parameters of the regression equation (a, b) are found using the least squares method. When you place the desired value of t in the formula, you can calculate the desired forecast. This method is most suitable for predicting the value of revenue, other income and expenses of the enterprise, since the change in these indicators over time often occurs in accordance with the historical
dynamics - a trend built using data from previous periods.
The autoregressive dependency method is based on a fairly obvious premise that economic processes are characterized by interdependence and a certain inertia. The latter means that the value of almost any financial indicator at time t depends in a certain way on the state of this indicator in previous periods. The equation of autoregressive dependence in the general form has the form:
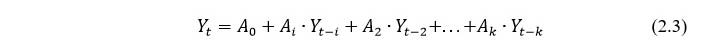
Where, Yt – the predicted value of the indicator Y at time t;
Y(t-1) – indicator value Y at time (t-i);
Ai – i-th regression coefficient.
Multivariate regression analysis can be used to build a forecast of any indicator, taking into account the existing relationships between it and other indicators. First, as a result of a qualitative analysis, k-number factors are distinguished (X1, X2, Xk), influencing, in the opinion of the analyst, on the change in the predicted indicator Y, and, as a rule, a linear regression dependence of the type is constructed:
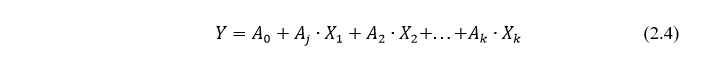
Where Aj – regression coefficients, i = 1, 2, … , k.
The value of the regression coefficients (A0, A1, A2, … , Ak) is determined as a result of mathematical calculations, which are usually carried out using standard statistical computer programs.
Thus, the main criteria in assessing the effectiveness of forecasting methods are the accuracy and completeness of the future financial condition of the enterprise. From the point of view of completeness, of course, the best methods are those that allow you to build predictive reporting forms. In this case, the future state of the enterprise will be analyzed no less detailed than its current position.
The forecast values of the main items of the balance sheet and the profit and loss statement obtained on the basis of the presented methods can be used to determine the future financial condition of the enterprise thanks to financial analysts, rating agencies, creditors, government agencies, etc.
3. Conceptual approaches to the diagnosis and forecasting of the financial condition of the enterprise
There are various approaches to prioritizing to improve the quality of financial decisions, however, most authors, in the current economic relations, focus on a priori assessment of decisions or on the diagnosis of the consequences of managerial decisions [16].
Based on the traditional approach, which is popular among domestic economists, we can conclude that financial diagnostics includes five main stages:
- The choice of a system of financial ratios. To assess the financial condition of the enterprise, its stability, a whole system of indicators is used. The number of financial ratios is very large, so it is advisable to choose only the main, most informative and significant ratios that reflect the following main aspects of the financial condition: property status; financial stability; solvency; business activity; profitability. The recommended number of financial ratios is not more than three to seven for each aspect of the financial condition. The specific set of indicators may vary depending on the specifics of the industry, business objectives and other factors.
- Express analysis. The purpose of the express analysis is a clear and simple assessment of financial well-being and the dynamics of the economic entity. In the process of analysis, it is possible to propose the calculation of various indicators and supplement it with methods based on the experience and qualifications of a specialist.
- Detailed analysis of financial condition. Its purpose is a more detailed description of the property and financial situation of an economic entity, the results of its activities in the past reporting period, as well as the prospects for the development of the entity in the future. It concretizes, supplements and expands individual express analysis procedures. The degree of detail depends on the desire of the analyst.
- Definition of the diagnosis. The results of the analysis make it possible to accurately assess the current financial situation and activities of the enterprise for previous years, identify vulnerabilities that require special attention, correctly diagnose with the goal of further improving the company's activities (if necessary).
- Development of draft management decisions. Depending on the comprehensive assessments of the financial condition and trends, based on the financial diagnostics, it is necessary not only to draw conclusions about the situation, but also to develop draft management decisions in order to further develop the enterprise. Similar work in enterprises is carried out using various methods of financial planning.
As for the global practice and foreign scientists of economists, in this case fairly stable approaches have been developed to diagnose the financial condition of enterprises and form conclusions and recommendations based on the results of the analysis. The techniques used in this process can be divided into four groups [1]:
- Transformational techniques.
- Quality techniques.
- Coefficient techniques.
- Integrated methods for diagnosing financial condition.
Transformational techniques. These methods of diagnosing financial condition are mainly aimed at converting statements into a more convenient form for perception:
- aggregation of articles, that is, a change in the composition of balance sheet items;
- balance supplement with indicators of structure, dynamics and structural dynamics;
- transformation into foreign reporting forms, that is, in accordance with IFRS, etc.
However, these methods, generally speaking, do not carry an analytical function and do not directly lead to any conclusions and recommendations. Reporting deflation methods using official inflation indices, foreign currencies and expert estimates are designed, first of all, to ensure comparability of data from different reporting periods, however, the adequacy of such methods limits a number of factors [2]:
- The movement of funds usually occurs unevenly during the period, while deflation is performed on separate reporting dates.
- Real inflation rates usually differ significantly for individual categories of assets and even for different types of assets in a group, while deflation is performed by a single averaged index.
- Accounting estimates are historical in nature, assets used for several periods without revaluation are expressed in units of purchasing power corresponding to the early reporting periods and, therefore, will be unreasonably deflated.
- Deflation does not take into account aspects of changes in the market value of assets under the influence of changing risk assessments associated with them. Thus, the block of transformational techniques is descriptive in nature and, generally speaking, cannot be considered as a set of methods for assessing the financial condition of an enterprise.
Qualitative methods for assessing the financial condition are divided into methods of vertical, horizontal analysis, balance sheet liquidity analysis and formalized questionnaire schemes.
It is hardly reasonable to consider the structure of the enterprise’s funds with respect to a single standard, since the specifics of the activity (even within the same industry with differences in technological processes) must inevitably leave an imprint on the structure of assets and liabilities.
Comparison with industry average indicators (databases on which in Russia are also not centrally maintained and published) can only show that the enterprise indicators deviate from the average, without specifying whether this trend is positive or not.
At the same time, the possibilities of the above-mentioned qualitative methods are limited under the condition of strong inflation, which is typical for post-Soviet countries at present.
The desire for such a detailed financial analysis led to the development, calculation and surface use of a clearly excessive amount of financial ratios, especially since most of them are functionally dependent on each other.
Integrated methods for assessing the financial condition involve the synthesis of financial indicators in complex designs in the following areas: regression models for assessing the probability of bankruptcy, bank credit ratings, industry ranking, fuzzy set analysis and summary rating models.
Despite the advantages of regression models for predicting bankruptcy, attempts to mechanically introduce them into the activities of Russian analysts are limited by a number of objective assumptions. Firstly, at the moment there are no models based on Russian financial statements. Secondly, Western integral indicators, which are used by many domestic analysts to assess the probability of bankruptcy of companies, are quite distant from Russian practice.
Thus, the use of such models requires great caution, since they are not entirely suitable for assessing the risk of bankruptcy of our business entities, since they do not take into account the specifics of the capital structure in various sectors.
Conclusions
The financial condition of an enterprise is a comprehensive economic category that determines the ability of an enterprise to finance its activities and is characterized by a system of indicators for allocating funds (assets) and their effective use, as well as their formation sources (liabilities); solvency and financial stability.
Financial analysis is a multi-purpose tool aimed at identifying various shortcomings in the activities of the enterprise that are potentially dangerous in terms of the possibility of bankruptcy.
The main objectives of financial analysis are:
- study of the theoretical foundations of financial analysis;
- general assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise;
- financial stability analysis;
- solvency and liquidity analysis;
- analysis of enterprise capital efficiency;
- analysis of the financial condition of insolvent enterprises, the search for ways to prevent bankruptcy.
Financial diagnostics is a process of assessing the state of an economic entity in relation to criteria established as optimal at the moment. Financial diagnosis involves:
- conclusions on the existing financial position of the object of diagnosis;
- study of the reasons for its change;
- analysis of the development prospects of the diagnostic object, in particular, from the point of view of the creditworthiness of the enterprise, organization.
Financial diagnostics allows you to answer a number of questions: about the degree of creditworthiness and ability of an enterprise (organization) to maintain its creditworthiness, about the development path
of an enterprise (organization) throughout the entire lending period, taking into account its financial situation, about the availability of financial potential to maintain creditworthiness and etc.
Summing up the analysis of methodological approaches of financial diagnostics and forecasting, it should be noted that the experience of conducting financial analysis of foreign enterprises suggests that most of the existing methods in their current form are not applicable to assessing the financial condition of domestic ones. It is necessary to conduct a series of relevant studies in order to optimize the existing approaches closer to the realities of the functioning of the business entity in the post-Soviet space.
In conclusion, the following should be said. With the development of the economy and financial analysis, its methodological basis should be improved and developed. The methodology of financial diagnostics, in general, having a rather universal structure, has a lot of nuances and subtleties that cannot be taken into account when creating any general documents. However, if the central government departments offer the society a certain system of criteria and standards, then they must be carefully verified, justified and consistent.
This master's thesis will contain recommendations for improving these methodological approaches for food industry enterprises, exploring the company Lacond
LLC.
Source list
- Баканов М. И. Теория анализа хозяйственной деятельности / М. И. Баканов. – Москва: Финансы и статистика, 2008. – 405 с.
- Балабанов И. Т. Основы финансового менеджмента: Учеб. пособие. – 3-е изд., перераб. и доп. – Москва: Финансы и статистика, 2001. – 528 с.
- Бородина Н. В. Анализ финансового предприятий Тамбовской области / Н. В Бородина, Т. Н. Черемсина // Социально-экономические явления и процессы. – Тамбов, 2013. – №3 (049). С. 24-31.
- Гиляровская Л. Т. Экономический анализ: учебник для вузов / Л. Т. Гиляровская. – Москва: ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, 2001. – 527 с.
- Евстигнеева О. А. Содержание понятия финансовое состояние коммерческой организации / О. А. Евстигнеева // Тольятти: Вектор науки Тольяттинского государственного университета, 2014. – № 2. – С. 100-103.
- Литвинюк А. С. Экономический анализ. Шпаргалки / А. С. Литвинюк. – Москва: Эксмо, 2009. – 32 с.
- Луппол Е. М. Методы прогнозирования инфляции / Е. М. Луппол, В. Д. Цуркан // Финансы, денежное обращение и кредит: фундаментальные и прикладные научные исследования: сб. науч. трудов по материалам I междунар. научно-практической конференции 31 мая 2016 г. – Нижний Новгород: НОО «Профессиональная наука», 2016. – С. 127-135.
- Научные ответы на вызовы современности: экономика. В 2 книгах. Кн. 2: монография / [авт.кол.: Загорная Т. О., Елкина О. С., Круглов В. Н. и др.]. – Одесса: КУПРИЕНКО СВ, 2016 – 185 с. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_26011044_80952126.pdf (дата обращения: 01.05.2017).
- Об утверждении Положения о порядке осуществления анализа финансового состояния. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://search.ligazakon.ua/l_doc2.nsf/link1/REG5312.html/ (дата обращения: 21.01.2017).
- Оценка финансового состояния предприятия [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.active-consult.ru/finsostoyanie.htm (дата обращения: 22.12.2017).
- Румянцев Э. О. Методы прогнозирования финансового состояния предприятия / Э. О. Румянцев // Москва: Российское предпринимательство, 2008. – №5 (2). – С. 64-68.
- Савицкая Г. В. Анализ хозяйственной деятельности предприятия / Г. В. Савицкая ; учебное пособие. ; 7.е издание. – Минск: Новое знание, 2002. – 607 с.
- Симоненко Н. Н. Управление финансовым состоянием предприятия / Н. Н. Симоненко, М. Ю. Пашковский // Комсомольск, КнАГУ: Фундаментальные исследования, 2015. - №2-16. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.fundamental-research.ru/ru/article/view?id=37823 (дата обращения: 22.01.2017).
- Хриплый Ф. П. Сравнительный анализ методов оценки состояния организации / Ф. П. Хриплый, А. Ф. Хриплый // Волжский: Политематический сетевой электронный научный журнал Кубанского государственного аграрного университета, 2012. – №81. – С. 1-22.
- Элитариум: центр дистанционного образования. Финансовый анализ для оценки деятельности предприятия: методы и формулы [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.elitarium.ru/finansovyj-analiz-kapital-pribyl-prodazhi-aktivy-objazatelstva-dejatelnost-balans-investicii-uchet/ (дата обращения: 22.01.2017).
- Юрзинова И. Л. Новые подходы к диагностике финансового состояния хозяйствующих субъектов / И. Л. Юрзинова // Экономический анализ: теория и практика, 2005. – № 14 (47). – С. 58-64.
