Abstract on the topic of graduation workContentIntroductionMany years of experience in implementing ISO 9000 standards by enterprises have confirmed their effectiveness in business management. However, in order to solve a number of tasks related to increasing operational efficiency that arise in manufacturing enterprises, it is necessary to use additional tools, which are innovative methods of quality management. 1. Formulation of the problemAn in-depth analysis of innovative quality management methods allows us to make sure that they are based on similar principles introduced by the concept of Total Quality Management. These principles are fundamental to quality management and form the foundation of any QMS. Thus, the considered innovative methods of quality management have great potential for mutual integration and are considered as a tool for enterprise development. This is what the authors of the study of 2. GoalAnalysis of the scientific and methodological approach for the integration of innovative methods of quality management in industrial enterprises. 3. Main materialThe article discusses the methods widely used in the enterprises of economically leading countries. Lean manufacturing makes it possible to reduce the resources used to support the economy, which not only positively affects the cost of production, but also avoids many problems in the long term. For this, it is necessary to focus on a more rational use of resources, instead of increasing production capacity, accompanied by an increase in the consumption of raw materials[1]. Lean manufacturing (leanproduction) is a concept of managing a manufacturing enterprise based on a constant desire to eliminate all types of losses. The concept allows you to organize the production of products with minimal costs in the shortest possible time and at the same time achieve the level of quality that the client requires.To eliminate losses, as well as to prevent their occurrence in the framework of lean production, many methods of rational organization of production activities have been developed. Let's take a closer look at the most important methods, the use of which is a prerequisite for the successful implementation of the program for the introduction of lean production in the enterprise. Continuous improvement – The use of Kaizen is a combination of efforts of all employees of the enterprise in the direction of forming a special corporate culture and achieving common goals. Another important method of rational organization of production activities of the enterprise is the method of organization of workplaces 5s, which is an effective tool for improving the working environment. in conditions of a busy schedule of production activities, employees stop paying attention to such This system allows, practically without attracting capital costs, not only to increase productivity, reduce costs, reduce the level of rejects and injuries, but also create the necessary starting conditions for the implementation of complex and expensive production and organizational innovations, ensure their high efficiency, primarily due to radical changes, the attitude of personnel to your work. The mastery of the 5S system made it possible to improve the discipline of personnel, to keep the equipment and premises clean. At the same time, according to the specialists of the Japan Manufacturing Service Association (JIPM), without simultaneously deploying the TPM, the 5S system does not lead to a significant reduction in the number of breakdowns, equipment stops and product defects, because perfect equipment retention does not guarantee against malfunctions. These two systems work well with each other, and function much better together [2]. 
Figure 1 – Elements of the 5S system Figure 1 shows the 5 elements of the 5S system, which mean the following:
No less important method of implementing lean production is the universal productive maintenance of equipment (English – Total Productive Maintenance – TPM). The essence of which is to involve every employee of the company in the maintenance of the equipment, and not just specialists-technicians. The purpose of TRM is to increase the service life of the equipment and its efficiency. The positive effects of using this method: reduces the number of downtime, errors in working with equipment, accidents; increases the sense of responsibility for each employee. just-in-time is a technique that allows you to significantly reduce losses, both in production and in the warehouse. This technique works with one of the main losses of the production process – waiting. Waiting loss occurs when parts are released from the previous operation, but cannot be processed on the next operation, which eventually leads to other losses. In this regard, it is critically important to submit details for a subsequent operation only when it is necessary. In fact, just in time is a custom job for the next operation. like any Kanban-regulates the flow of manufactured products and raw materials inside and outside of production. The need for components or finished products is determined using signal cards.Usually, Kanban cards have a bright, attention-grabbing design, for example, the parties that need to be processed first are provided with red cards, and less urgent parties are provided with green ones. The use of cards helps to eliminate losses on unnecessary movements, work exactly on time and improve the overall production culture. Quick Changeover (SMED) – prevents loss of time, reduces the time of one changeover to the minimum possible value. Readjustment is performed on the basis of two actions: internal and external. Internal actions involve stopping the equipment, and external actions can also be performed while the device is running. The SMED technique involves converting actions from internal to external.As a result, it becomes easier to produce small batches of products, and the useful operation time of the equipment increases. Error protection (Poka-Yoke) is the creation of methods that prevent errors from occurring in the production process. The main goal is to achieve Six Sigma is based on an approach of continuous improvement of processes and reduction of the number of defects. the organization should adopt a continuous improvement and performance improvement approach. Improvement can be achieved through radical changes (the process reengineering approach) or through minor permanent improvements (the kaizen approach). Improvements can be aimed at improving product safety, improving quality, shortening the production cycle, improving jobs, reducing costs, etc.the key elements of six sigma are: customer satisfaction; identification of processes, their indicators and methods of process management; teamwork and staff involvement. According to ISO 9001, when building the QMS, the organization forms a process management model, which becomes the logical basis for the introduction of innovative methods of Lean production. Among the most important elements of the formed and functioning system are: principles of efficiency, efficiency and continuity of process improvement; process monitoring and product monitoring; use of documented information. A successful QMS contains the organizational and cultural prerequisites necessary to connect the tools of The QMS structures the management system in the right way, gives it important characteristics of process, system, continuously improving and fact-based management, orients the organization to the needs of the consumer, leadership of management, staff involvement and mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers. Investigation of the principles underlying the All methods are aimed at improvement and improvement, they operate at different levels of management of the organization: so, the QMS covers the highest level of management, paying attention to all processes that directly or indirectly affect the quality of products, in their totality and interaction: 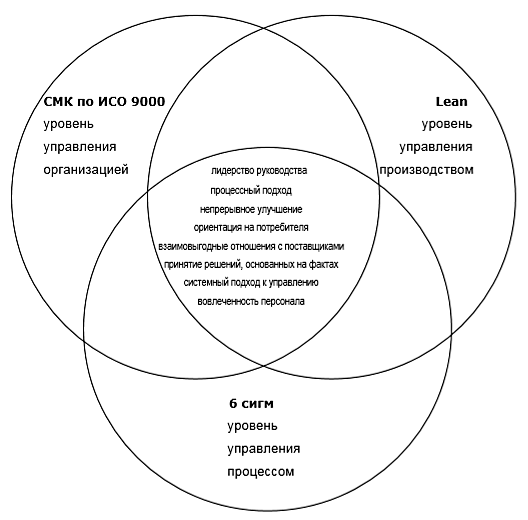
Figure 2 – Structure of mutual integration of innovative quality management methods Further study of the integration of these methods, the positive and negative aspects of the joint use of ConclusionSumming up, it is necessary to say that in the current economic situation, enterprises should keep a strict focus on meeting the requirements of the consumer at the lowest cost and more efficiently, which will allow them to maintain competitiveness. Each of the concepts can help in achieving these goals, as they are all aimed at reducing the number of product defects, improving the efficiency of processes and improving the production system. And in an integrated form, the methods can achieve significantly greater management efficiency than from using each system separately [8]. Implementation of integrated quality management is a transition to a new, more qualitative level, which implies the involvement of all employees. At the same time, active participation is provided by both material incentives, the introduction or approved proposals for implementation, and non-material ones, such as the opportunity to participate in the management of the enterprise, the implementation of one's own ideas, career growth, etc. Bibliography1. Виноградов В. Ю., Сайфуллин А. А., Виноградова Н. В., Гибадуллин Р. З. Роль бережливого производства в современном мире // Молодой ученый. – 2015. – №20. – С. 30–31. 2. Момот А. И. Менеджмент качества и элементы системы качества, – К.:Центр учебной литературы, 2007 – 368с. 3. Куприянова Т.М., Растимешин В.Е.: Упорядочение / 5S-система наведения порядка, чистоты и укрепления дисциплины с участием всего персонала // «Мясные технологии» №7, 8, 9 2007 г. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.orgresurs.ru 4. Растимешин В.Е., Куприянова Т.М. С чего начинается качество на рабочем месте // Методы менеджмента качества. – 2003. – № 5. – С. 4–10. 5. Растимешин В.Е., Куприянова Т.М. Как навести порядок в офисе // Методы менеджмента качества. – 2003. – № 7. – С. 12–15. 6. Дерябин П.М. Почему нужно внедрять систему Упорядочение // Методы менеджмента качества. – 2004. – № 2. – С. 14. 7. Давыдова Н.С., Клочков Ю.П. Бережливое производство на предприятиях машиностроения: теория и практика внедрения. Российская акад. естествознания. – Москва: Издательский дом Акад. естествознания, 2012. – 111 с. 8. Годунова А.О. Бережливое производство в контексте новейшей управленческой концепции управления производственной системы предприятия – Мордовский государственный университет имени Н. П. Огарёва, г. Саранск |
