Abstract on the topic of graduation work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Theoretical aspects of the influence of corporate culture on the production efficiency of the enterprise
- 3.1 The essence of corporate culture in the enterprise
- 3.2 Factors affecting the corporate culture of the enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Numerous studies show that corporate culture has a decisive influence on the development of employee motivation.
First of all, it is necessary to define the concept of corporate culture, since according to many authors there is no clear boundary between organizational culture
and corporate culture
.
So, according to Bazarov T. Yu., corporate culture can be defined in the context of value-normative rules, within which interaction with other organizational structures is carried out, while organizational culture is still a common integral indicator that characterizes both values and methods of evaluating the results of activities and interaction with partners, and much more [6, p.199].
This definition does not specify the source from which the origin of corporate culture occurs, but clearly outlines the framework of interaction, which makes it possible to define corporate culture as a complex set of assumptions that are accepted by all members of the organization and set general rules of behavior. Thus, the corporate culture defines the ideology of management and shows the values, norms of employee behavior, regulates expectations, makes it possible to predict the behavior of a person, his reaction to critical situations [5, p. 157]. Corporate culture exists in a single symbolism, value orientations, through which there is a transfer of guidelines, rules of behavior (both vowels and non-vowels), a common understanding of acceptable and unacceptable relationships that underlie the creation of interaction both inside and outside the organization.
Effective corporate culture is the most effective way for an organization and its staff to interact today. It becomes better with the participation of the team, sets the long-term goal of the organization's existence, creates corporate standards that must be adhered to in order to effectively achieve this goal, convinces the employees of the organization of the correctness of these goals and standards, and finally introduces a mechanism for transferring corporate values to employees to optimize their work.
1. Theme urgency
Relevance of the research topic. The role of corporate culture, which has been formed and consolidated as one of the most important components of the subsystems of the personnel management system, continues to grow today. Its influence affects such aspects of activity as innovation, human resources and social policy, marketing, and sales. Each of these processes takes place within the framework of the corporate culture.
This direction became the foundation for the subsequent development of methodological aspects of conducting marketing research in working with personnel.
The degree of development of the scientific topic. The tools for familiarizing the author with the best practices in the field of personnel marketing were the theoretical and practical developments of Abryutin M. S., Grachev. A. V. Akulich V. A. Bakanov M I., Psychiatry A. D., belokrylova L. E. Rofe A. And Sklyarenko V. K., Bazaars Yu M. Genkin, B. M., Kozlov V. V. and others.
The study of foreign experience was based on the works of Liker D. K, Schlender P. E., Mayo E., Warner W., James Shuryevsky, Eccles R. J., Effron J. and others.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the final qualification work is to identify the specifics of corporate communications of the enterprise.
To achieve this goal, you need to solve the following tasks:
– Consider the theoretical basis for the formation of corporate culture
– To study the system of personnel involvement in the company's activities.
– Analyze the labor indicators of the enterprise.
– Develop recommendations for improving the corporate culture of the enterprise.
Research object : processes of formation of the corporate culture system of the organization.
Research subject : a set of theoretical, methodological and applied issues of improving the corporate culture of the enterprise.
Where the corporate culture is aimed at creating an atmosphere in which employees can create and develop their creativity, there was an opportunity to realize the potential of each employee. Given the fact that these companies have a huge staff and huge resources involved in their work, there is a structural division into small, dynamic groups, so that everyone understands that a lot depends on them. For example, in Microsoft, the generation of ideas takes place at the level of each individual employee, and the organization creates conditions under which these ideas are implemented and can be brought to the final result [18, p. 544].
Michael Dell, one of the most successful entrepreneurs of his generation, runs the company Another example of the fact that the traditional approach to management has become one of the reasons for the loss of competitiveness of many companies is the example of Thus, it became obvious that today, when forming a corporate culture, a strict hierarchy is not welcome, although it is not advisable to completely deny its significance, since such a system has the expediency of using in those industries where work is completely standardized, requires discipline, where there is no place for creativity [2, p. 121].
At the same time, according to some practitioners, providing a large amount of initiative can lead to chaos and, as a result, to a showdown between subordinates and management. Here, one of the tasks of senior managers is to find such an interaction between strict subordination and giving independence to lower-level managers.
Representatives of the company From the above, it follows that the issues of both the management style and the structure of the company are fairly well-developed components of the corporate culture. However, it should be noted that it is important to pay attention to the attitude of employees to such issues. The company structure may be far from perfect, and employees will still be treated with respect and pride, and vice versa, but with a low level of corporate culture, these achievements can be reduced to zero. When creating the structural and managerial elements of a corporate culture, it is important to take into account not only the economic feasibility, but also to pay attention to the attitude of employees to these issues.
An important part of corporate culture management is the HR strategy. Recruitment specialists note a tendency to increase interest in candidates along with professional requirements, such as psychological and behavioral characteristics, which is undoubtedly associated with the specifics of the corporate culture, which includes values, ethical norms, and sometimes national mentality [4, p. 54].
Drawing 1.3 – Corporate culture structure (animation: 5 frames, 10 repetition cycles, 37.2 kilobytes) British, German and American firms prefer recruitment through recruitment agencies or conduct their own selection based on the resumes sent. All foreigners, without exception, approach the interview procedure very carefully. In German companies, applicants pass three interviews, and it is also known that in an American firm, Requirements to the psychological type of employee this is not a fad firms because of the compliance of the applicant internal company standards in the areas of communication, established the firm can decide whether to adapt to this new corporate culture employee leaves his relations with colleagues and leadership, and how effectively, in the end, it will work.
Bringing the basic values of the company and its ethics to new employees should be a constant activity designed to unite all employees with a universal idea, instill in them a team spirit that contributes to the achievement of the tactical goals of the organization.
Priorities in the selection of certain areas of work with personnel differ depending on the categories of departments of the company.
The first step in involving employees in the company's affairs is to understand their role in the company's activities and the results achieved by it. The main reason for unsatisfactory work lies in the fact that people do not have an understanding of what they do and why they come to the service [16, p.189]. Motivation of employees is no less important than understanding the needs of customers and their satisfaction. If a person has time to really realize what is expected of him and what the results of his work contribute to, then motivation will follow automatically.
However, delegation of authority cannot proceed without delegation of responsibility for a particular action.
First of all, it is the responsibility for the products produced. Fixing the responsibility for the worker, strengthening his sensitive attitude to the product that he produces, allows you to reduce the number of shortcomings, and, consequently, save significant funds by reducing the return of defective products.
In addition, the transfer of responsibility to employees frees administrators from unproductive opec day – to-day supervision and leaves them time to do what they are required to do-develop sales technologies, reduce the labor intensity of production, study the probability of releasing new products, improve processes and think about the increasing role of the enterprise in the markets of the Donetsk People's Republic, increase revenue.
All businesses have a strategic goal – to increase the satisfaction of their employees by taking care of them. This is achieved through an informal atmosphere (collective birthdays of employees, New Year, etc.) and the creation of the most convenient working conditions.
The company takes care of the health of its employees: regular medical examinations are carried out, a wellness center is made at the company, including swimming pools, a stadium, sports grounds.
However, despite the wide range of methods of non-material incentives, financial remuneration remains the basis without which the involvement and participation of employees in the company's affairs is unthinkable. The bonus system is directly related to the performance indicators of performers. The size of the monthly premium is determined by such parameters as the volume of products produced; its quality, the number of defects; the organization of the workplace and compliance with safety requirements. All these indicators have the same weight. In addition, there are bonuses for each staff for ensuring universal customer satisfaction [8, p. 246]. And this is an effective method of ensuring the quality of products and motivating employees.
But for the effective use of the potential of employees, the corporate culture of the company should be focused on continuous improvement of activities.
Drawing 2.3 – The place of corporate culture in the management system of the industry organization At the same time, the improvement should be considered from 2 sides: coming from the authorities and coming from the staff.
The company's management shows a commitment to improvement, introducing new ways of production and management, information technologies, as well as supporting innovative ideas from the staff. However, innovation does not have to be an end in itself. They are obliged to move the company towards the realization of its mission and tactical goals, to help to increase customer satisfaction.
A common way to implement the continuous improvement rule is to create teams that evaluate the progress and plan upgrades.
The company also pays special attention to the system of personnel development and training. The system of training and retraining of workers and experts is of a constant nature, which ensures the necessary level of training and qualification of personnel. The management team is continuously engaged in training the personnel that affect the quality.
Every employee of the company is not left without attention.
Various corporate events help to unite the team and the subsequent prosperity of the company.
Indicators of work to increase the qualification of the enterprise are: the share of workers improved their qualification (in General population), the design of students in the forms of increasing qualifications in terms of training, the growth of labor productivity (percent standards development), decline of marriage, etc.
Personal control in the company is carried out by order of the authorities. The company trains administrators for acceptable substitution-replacement of middle and top-level administrators. The atmosphere of healthy competition and at the same time partner support contribute to a high level of business culture in the company.
– the company's business culture includes joint events to celebrate the company's birthday, generally recognized holidays and personal birthdays of employees;
– great attention is paid to relationships with enterprises partners and customers;
– representatives of enterprises and large customers are invited to corporate events [22, p. 113]
Each employee of the organization involved in the implementation of quality is the main source for the implementation of the quality policy. The company maintains a team spirit of cooperation and respect for each team member, recognizes the individual contribution of each employee and does not allow discord. Consequently, the management of the enterprise needs to introduce measures to:
– selection of personnel based on their abilities and probabilities to fulfill the requirements set out in the job descriptions;
– providing typical, excellent working conditions;
– awareness of each employee of his personal power on quality;
– creation of plans for the development of a career personnel;
– development of planned actions to improve the level of personnel qualification [19, p. 36].
Corporate culture is understood as an integral part of successful production of decent wages, but also implementing a wide range of different programs and activities that make up the corporate package. Among them:
1) health protection and medical care of employees;
2) creating conditions for work and training of employees;
3) help from young experts, care for pensioners.
Thus, the improvements coming from the staff largely depend on the attitude of the bosses and the established corporate culture. An important factor that encourages employees to innovate is the creation of open and accessible communication channels that allow ideas to pass unhindered from employees to senior managers.
Currently, educational organizations are striving to develop a future-oriented culture. Today, such personal qualities as success, competitiveness, respect for customs, ideas, tolerance, and willingness to accept the corporate culture of the organization in which you will work are in demand. The relationship between value-motivational oppositions and ideas about the ethics of business interaction of teachers is necessary. It is extremely important to consider the corporate culture as a means of improving the efficiency of the organization, in connection with the implementation of the concept of Effective corporate culture is the most effective way for an organization and its staff to interact today. It becomes better with the participation of the team, sets the long-term goal of the organization's existence, creates corporate standards that must be adhered to in order to effectively achieve this goal, convinces the employees of the organization of the correctness of these goals and standards, and finally introduces a mechanism for transferring corporate values to employees to optimize their work.
3. Theoretical aspects of the influence of corporate culture on the production efficiency of the enterprise
3.1 The essence of corporate culture in the enterprise
Dell
ranked by the magazine Fortune
among the best American companies, draws attention to the fact that employees see the company as a place where they build a career, which for many is a key factor in life, and not just a place where they come to socialize, drink coffee or smoke [1, p. 45]. Therefore, the company Dell
is focused on making employees feel involved and belong to a common meaningful cause. The employees are supported by the enthusiasm and the idea that there is every opportunity to achieve heights in this company, which is developing and growing rapidly thanks to the efforts of its employees. Thanks to this approach to employees and their abilities, American companies working in the IT industry were able to quickly achieve success.
IBM
, which, being a giant and a leader in its industry, was almost on the verge of financial collapse. The Board of Directors decided to hire an independent external consultant from the company McKinsey
. One of the first recommendations of the consultant was to change the management style, and for this it was necessary that the management staff worked as a single team, adhering to the new management principles, thereby changing the corporate culture of IBM. The huge bureaucratic apparatus, which worked on the principles of the corporation – machine
, was not able to respond to the dynamic changes in the surrounding world, which jeopardized the financial well-being of the company.
Reebok
suggest eliminating the main problems of internal competition by training staff to work in a team and interact with colleagues [3, p. 224].

3M
– six interviews. The requirements for candidates are standard: higher education, a foreign language, as a rule, work experience. Also, foreign companies have very specific requirements for the psychological type of employee. Most American companies are characterized by an aggressive policy in conquering the market, so they select very efficient and determined candidates [15, p. 86]. In addition, the desire of a person to work in their company is very important for them. The Germans are cool to such enthusiasm, for them a serious, pedantic professional is preferable. The French and Italians are very sociable and gentle. For example, in Loreal
, the main thing is that the person is dynamic and able to work in a team. Japanese and other Eastern companies, in addition to professionalism, value loyalty to the company, manageability, conflict-free, and collectivism.
3.2 Factors affecting the corporate culture of the enterprise
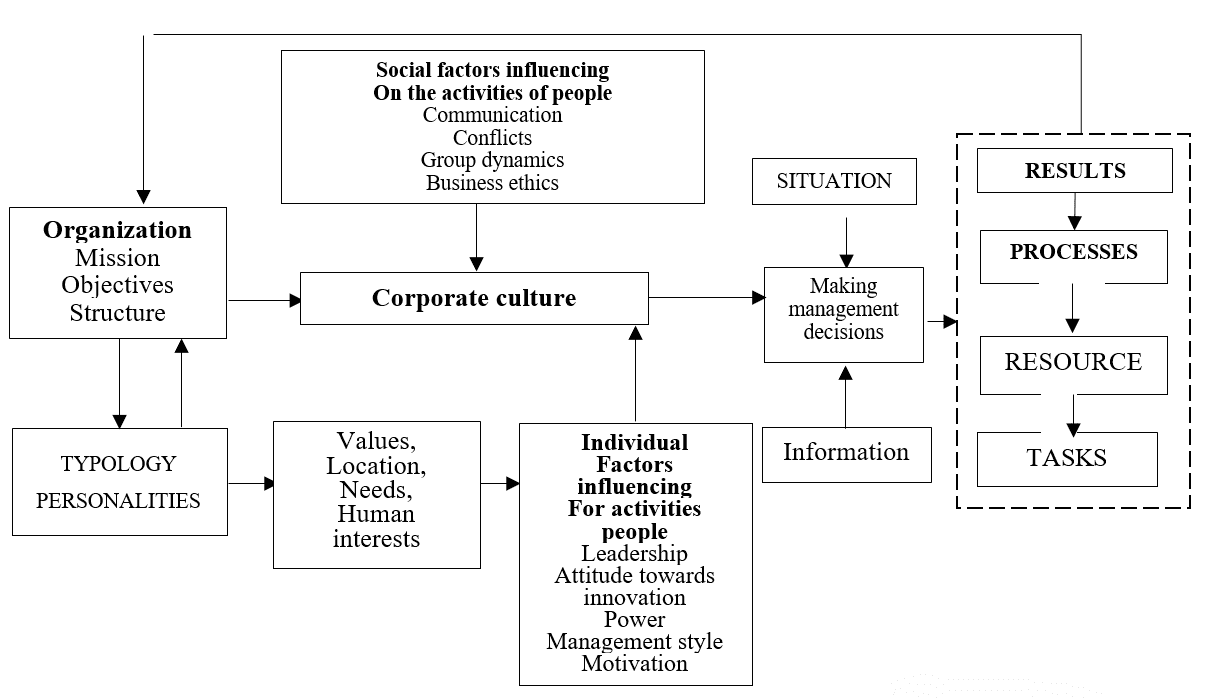
Conclusion
human capital
. The new paradigm of personnel management implies a change in the functions of personnel, the accumulation and development of human capital
, on which the quality of educational services depends.
References
Управление персоналом
Менеджмент организации
/ Т. Ю. Базаров. – Москва: ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, 2009.
Технопарк
ДонГТУ Унитех
, 2016. – 366 с.
