Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. The essence of personnel development
- 2. Features of the assessment of competencies in the process of personnel development
- 3. Measures for the formation and assessment of personnel competencies in the process of personnel management
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Some time ago, work with personnel consisted exclusively of activities for the recruitment and selection of labor. It was believed that if you managed to find the right people, then they could do the right job. Modern organizations that have a good management business believe that recruiting the right people is just the beginning, while most of the organization's resources are represented by material objects, the value of which decreases over time through depreciation, the value of human resources can and should increase over the years.
The head of any enterprise is interested in achieving the set goals with minimal costs. This is possible with the rational and economical use of all types of resources. With a personnel development system based on a competency-based approach, all production optimization processes become simpler and easier to execute.
The scientific basis for the study of competencies and the competence-based approach in personnel management is the work of domestic and foreign scientists, among them: E. Brooking, F. E. Weinert, B. M. Genkin, A. I. Dobrynin, A. Ya. Kibanov, Yu. G. Odegov, OI Chulanova and others [3, 11]. However, a number of issues related to this topic, in particular, in the field of forming a competency model at an enterprise, require additional research.
The purpose and objectives of the study. The main goal of the final qualification work is to study the theoretical and methodological foundations of personnel development based on the competence approach of a pharmaceutical enterprise and the development of measures for its improvement.
Tasks of the final qualifying work:
• to reveal the essence of personnel development;
• consider the specifics of assessing competencies in the process of personnel development;
• to reveal the organizational and economic prerequisites for the formation of a personnel development management system;
• analyze the number, composition, structure, quantitative and qualitative indicators of personnel development;
• disclose the issues of labor protection, life safety and civil defense at the enterprise;
• formulate measures for the formation and assessment of personnel competencies in the process of personnel management;
• evaluate the effectiveness of measures for the formation and assessment of personnel competencies.
Relevance of the topic. When people work with less enthusiasm, when there is tension in the interaction of departments and significant disruptions in work, managers begin to realize that the time has come to engage in personnel development. The development of personnel based on a competency-based approach is one of the most important areas of personnel management and a factor in the successful operation of the enterprise.
The object of the research is the processes of personnel development management of LLC DL-V
, Donetsk.
The subject of the research is the theoretical foundations and practical aspects of managing the development of enterprise personnel.
1. The essence of personnel development
The most important condition for the successful functioning of enterprises of any form of ownership is the development of its personnel. Today, there is a rapid process of obsolescence of professional knowledge and skills due to the ongoing scientific and technological progress. The consequence of this is the inconsistency of the competence of the employees of the companies with the positions held and the work performed, which negatively affects the results of both the employee himself and the entire enterprise as a whole.
If the trend towards a decrease in indicators becomes constant, employees do not stay at their workplaces – then this is a signal to carry out activities aimed at personnel development.
Today, the management of any enterprise is interested in training and developing its own personnel. When discussing the problems of personnel development and training, an important concept is “personnel development”. Each author interprets this term differently:
1. A set of organizational and economic measures in the field of training, advanced training and professional skills of personnel, stimulating creativity, etc [1, p. 159].
2. A set of measures, including vocational training for school graduates, retraining and advanced training of personnel, as well as career planning for the organization's personnel [6, p. 234].
3. A set of measures aimed at developing the human potential of the enterprise [10, p. 198]..
4. A system of interrelated actions, including the development of a strategy, forecasting and planning the need for personnel, career management and professional growth, the organization of the adaptation process, education, training, the formation of organizational culture [2, p. 164].
All concepts reflect the essence, but it is necessary to combine the first, third and fourth definitions, and we will get the following generalized concept of personnel development
: a set of activities aimed at developing the human potential of an enterprise, including strategy development, forecasting and planning the need for personnel, career management , organizing the adaptation process, as well as improving the qualifications and professional skills of personnel, stimulating creativity, etc. [8, p. 53].
Personnel development management allows for a more rational use of the labor potential of each employee, contributes to an increase in his social and professional mobility, is engaged in increasing the level of competitiveness of employees, their intellectual and educational level. The result of these actions is the creation of a favorable social and psychological climate at the enterprise, and, consequently, a decrease in staff turnover.
To consolidate the enterprise in the market and confirm its competitiveness, the management should improve the qualifications of its employees everywhere, and the personnel development system will help to do this more effectively. Because, thanks to a systematic approach, the development and training of specialists occurs constantly and gives a noticeable result, which is manifested in an increase in professionalism and improved interaction between team members.
The personnel development system requires skillful management in order to achieve maximum results, therefore it is necessary to involve experienced specialists in the training process, whether they are employees of a given enterprise or third-party consultants.
The optimal personnel development system is a set of measures developed by specialists, taking into account the needs of the enterprise and the potential of its employees.
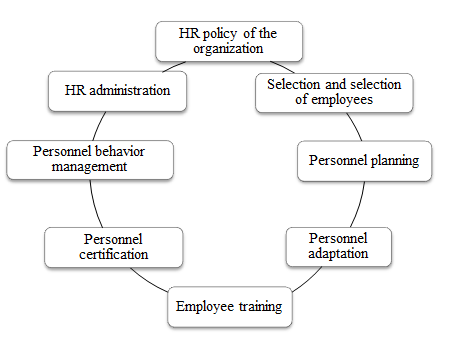
Figure 1 – Elements of the personnel development system
Only in the aggregate are the elements capable of solving the tasks assigned to the system. Moreover, they are solved gradually, as employees acquire the necessary knowledge and skills regarding their professional activities, acquire the skills of communication, mobility, business activity necessary for work, strive for career growth, seeing prospects in this area of work.
The main goals of staff training can be considered [12, p. 143]:
• increasing the efficiency of performing complex tasks simultaneously with their innovative potential;
• readiness for staff rotation;
• mastering related specialties to improve the competitiveness of personnel;
• obtaining knowledge for effective motivation and stimulation of labor;
• expanding horizons;
• development of flexibility of thinking and behavior in non-standard situations;
• development of self-confidence for subsequent decision-making;
• self-education as a tool for further self-improvement.
Advanced training at the enterprise is carried out as needed, and also, it is effective only for those employees who still have much to strive for.
2. Features of the assessment of competencies in the process of personnel development
Today, a manager who wants his enterprise to prosper is interested in the rational use of his own resources, which include human resources. To get the maximum effect from the activities of the staff, you need to work to strengthen its potential, which is possible with an increase in the level of professional competencies.
The competence of the organization's personnel is a combination of knowledge, skills, experience, mastery of methods and techniques of work, which are sufficient for the effective performance of job duties. Moreover, in different sources there are different interpretations of the concept of competence. According to the definition of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), competence is “the ability to successfully respond to needs or successfully complete tasks” [4, p. 256]. According to VP Solovyov's definition, the competence of a university graduate is his ability, which is supported by practice, which allows him to realize his potential (knowledge, skills, experience, personal qualities, etc.) for successful creative activity in the professional and social sphere [4, p. 256]. F. Weinert, one of the most recognized international experts in this matter, argues that there is no uniform application of the concept of competence, as well as a widely accepted definition of this term [13]. In Western Europe and the USA, competence is often viewed as a property of a competent worker, a synonym for qualifications, which is revealed through competence in problem situations.
Competence should be distinguished from competence, which is a characteristic of a position and is a set of powers (rights and obligations) that a certain body and officials have or should have in accordance with laws, regulations, statutes, regulations.
However, there are different interpretations of the term competence
, which often contradict each other or are mutually exclusive. In a legal and organizational sense, the term “competence” means “area of responsibility”. In the field of education, however, its synonym is often “ability” that can be learned, in contrast to the general cognitive abilities of an individual. In addition, competencies are defined as motivational orientations required to perform complex tasks. With all the diversity of views on the essence of this category, most definitions emphasize the ability to apply acquired knowledge, abilities and skills in real situations (fig. 2) [11].

Figure 2 – Operationalization of the concept of competence
in the context of work with personnel (animation: 9 frames, 7 cycles of repeating, 145 kilobytes)
In world practice, there are three main approaches to building a competency model: behavioral, functional and multidimensional approaches.
In particular, the behavioral (personal) approach is based on the definition that competence is a certain characteristic of a person that contributes to high achievements at work.
This approach is characteristic of the United States, since there competencies are considered a characteristic of people that can influence the performance of work in various situations and for a long time. American scientists use the abbreviation KSAO to characterize the qualities included in the concept of competence:
• knowledge;
• skills;
• abilities;
• other.
The functional approach, in turn, deals with the description of the tasks and results of work, i.e. the essence of competence takes the form of a certain sequence of actions that correspond to the standards adopted at a particular enterprise.
The level of qualification laid down by the competencies must meet certain standards adopted on the basis of the analysis of the planned work results.
The multidimensional, or holistic, approach more clearly describes the interaction of competencies in the process of professional activity, which include conceptual (cognitive abilities, knowledge and understanding) and operational (functional, psychomotor and applied skills) competencies [9].
The construction of a competency model is based on two important concepts: a cluster of competencies and indicators of behavior.
A cluster of competencies represents 3–5 competencies closely related to each other. Typical competencies of enterprise personnel include:
• collection and processing of information;
• teamwork;
• personal development;
• coordination of work;
• generating ideas;
• planning of work and results of activities;
• setting goals;
• setting time frames for work performance, etc.
Behavior indicators are standards of behavior inherent in a person with certain competencies.
A typical competency model is shown in fig. 3.
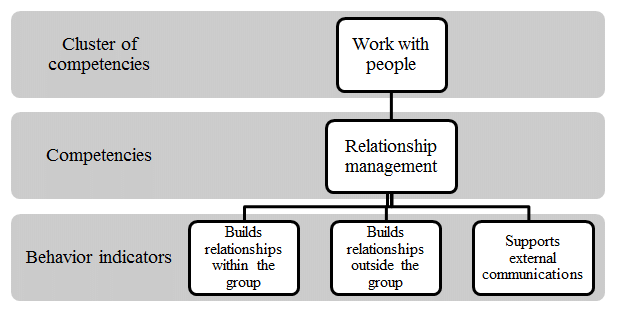
Figure 3 – Typical competency model
The main requirements for the competency model should be [7]:
• simplicity of presentation;
• versatility;
• taking into account the planned changes;
• the use of dissimilar elements in the construction of the model;
• fairness in the distribution of results;
• use in the construction of the main aspects of corporate culture;
• the maximum possible coverage of the working skills of the model participants;
• assessment of the quality of work performance, etc.
Taking into account the above approaches, the proposed requirements for the formation of a competency model, we can make a conclusion. In a broad sense, this model is a set of competencies with a detailed description of the rules of conduct for personnel in their workplaces to achieve the goals of the enterprise. Building a logically correct competency model that takes into account the needs of a particular enterprise can lead to an increase in the efficiency of the entire enterprise in the future.
3. Measures for the formation and assessment of personnel competencies in the process of personnel management
The development of the company's personnel on the basis of a competency-based approach is of particular importance today. To achieve success, an enterprise must constantly improve itself, and this is easier and more efficient to do precisely through personnel training. The personnel development system is everywhere individual in nature, associated with the characteristics of the production activities of the enterprise and is relevant in a specific period of time. The creation of such a system is a necessity, therefore, one should approach the solution of this issue rationally, having carried out a preliminary analysis of the state of the company's personnel, the legal framework and the financial capabilities of the enterprise.
To organize the effective work of the personnel development system based on the competence-based approach and its further improvement, it is necessary to implement the following recommendations:
1. To introduce a competency model, it is necessary to purchase special software – 1C: Personnel Assessment. Software product 1C: Enterprise 8. Personnel assessment is a joint solution of 1C and Personnel Soft firms to automate the testing of candidates and assess employees, including the 360-degree method and for compliance with the job profile according to the developed model.
Based on this software, the following competency model can be developed, consisting of several groups of universal competencies (fig. 4).
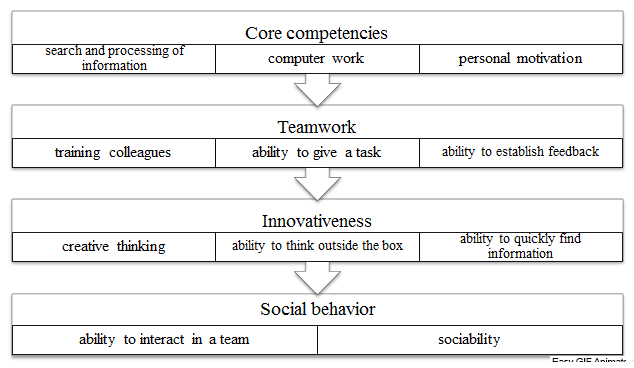
Figure 4 – Competency model
Also, this software will be able to facilitate the work of the HR department when processing data on:
• professional and qualification level of employees of the enterprise of various categories;
• planning subsequent training of employees, if necessary;
• concluding agreements with educational institutions in order to attract young specialists;
• formation of a personnel reserve, etc.
It should be noted that the organization of internships for students is a good advertisement for DL-V LLC among promising young professionals. Evaluation of trainees for compliance with the profile of the position will lead to a conclusion about the need to develop the missing competence or about full compliance. Young specialists need to be familiarized with the current incentive system and orientate them towards the professional development of their competence.
The result of using the software will be the creation of a complete database on the training and retraining of the personnel of DL-V LLC.
2. Introduce the position of a specialist psychologist into the staffing table or offer the personnel department employees (if they have a certificate of education) the opportunity to combine with the main type of employment in order to involve it in the educational process, since the personnel training system deals with an adult audience. First of all, it is the possibility of changing the quality of groups of students – from the “diffuse” level to the “associative” one. Listeners are people of different ages, intelligence, temperament and emotional state, so it is difficult for them, even temporarily, to change their usual status to the role of a student. The task of the psychologist is to transfer the group to the associative level in the allotted hours, in which there is an awareness of unity, interests are integrated, public opinion appears [5, p. 63].
3. Considering that pharmacology is a specific branch of activity, it will be effective to introduce the experience of testing, developed by the heads of pharmacies, in order to assess the knowledge gained by trainees and internship pharmacists after they have completed their internship or internship period.
4. It is proposed to introduce the experience of manufacturing products on the basis of the prescription-production department of DL-V LLC, by creating video clips dedicated to drugs, care cosmetics and hygiene products and their subsequent posting on the Internet.
5. Staff training is impossible without methodological support of the educational process, without replenishing the funds of educational and methodological literature. This is due to the fact that the library fund is rapidly becoming obsolete and the replenishment and renewal of the fund requires significant funds. It is necessary to create an electronic library, which will make it possible to constantly update the fund with new literature.
Thus, the main task of personnel development is to enable workers to master new professions, equip them with knowledge, teach them to apply the obtained theoretical knowledge and practical skills in work and, on this basis, create conditions for further growth of the main indicators of labor efficiency.
The developed recommendations for improving the personnel development system will allow DL-V LLC to change the qualitative composition of personnel, improve the selection of applicants for vacant positions, and conduct personnel training at a high level.
Conclusion
Management of personnel development contributes to the effective use of the labor potential of an individual, increasing his social and professional mobility, implementing technological and structural restructuring, as well as increasing the level of competitiveness of the employees themselves, their intellectual level. The consequence of this work is to improve the socio-psychological climate in organizations, increase the motivation of workers in a team, reduce the level of staff turnover.
Implementation of measures aimed at improving the personnel development system based on a competency-based approach requires significant financial costs. But, investments in human capital are the most effective, because compared to investments in other forms of capital, they are longer-term, wear out less, the return depends on the interests and will of the person himself.
References
- Веснин, В. Р. Управление персоналом: теория и практика / В.Р. Веснин. – Москва : Проспект, 2009. – 688 с.
- Иванова-Швец, Л. Н. Управление персоналом: Учебно-методический комплекс / Л. Н. Иванова-Швец, А. А. Корсакова, С. Л. Тарасова. – Москва : Изд. Центр ЕАОИ. 2008. – 200 с.
- Кибанов, А. Я. Управление персоналом организации: отбор и оценка при найме, аттестация: учеб. пособие для вузов / А. Я. Кибанов, И. Б. Дуракова; Гос. ун-т управления. – 2–е изд., перераб. и доп. – Москва : Экзамен, 2004. – 416 с.
- Кондаурова, И. А. Компетентностный подход в процессе формирования человеческого капитала Формирование механизма управления конкурентоспособностью банка: комплексный подход / И. А. Кондаурова // Друкеровский вестник. – № – 3. – 2018. – С. 255–263.
- Лебедева, Н. В. Обучение взрослых на курсах переподготовки и повышения квалификации: принципы и условия / Н.В. Лебедева // Научный диалог. – 2013. – № 4 (16). – С. 63.
- Лукичева, Л. И. Управление персоналом :учеб. пособие / Л. И. Лукичева. – 4–е изд., испр. – Москва : Омега-Л, 2008. – 262 с.
- Модели профессиональных компетенций в управлении персоналом [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: http://e-biblio.ru/book/bib/09_ekonom....
- Русина, В. А. Система развития персонала: основные элементы и принципы построения / В. А. Русина, И. В Барыло // Инновационные технологии в машиностроении, образовании и экономике. – 2016. – № 2. – С. 52–57
- Рябов, В. В. Компетентность как индикатор человеческого капитала: Материалы к четвертому заседанию методологического семинара 16 ноября 2004 г. / В. В. Рябов, Ю. В. Фролов. – Москва : Исследовательский центр проблем качества подготовки специалистов, 2004. – 45 с.
- Скопылатов, И. А. Управление персоналом :Учеб.пособие для вузов / И. А. Скопылатов, О. Ю. Ефремов. – Санкт-Петербург : Изд-во Смольн. ун-та, 2000. – 399с.
- Чуланова, О. Л. Формирование и развитие компетентностного подхода в работе с персоналом: теория, методология, практика : автореф. дис. док. эконом. наук : 18.03.15 / Чуланова Ольга Леонидовна. – Москва, 2014. – 51 с.
- Шаталова, Н. И. Консультирование в управлении человеческими ресурсами: учеб, пособие / Н. И., Н. А. Александрова, О. Ю. Брюхова, О. Б. Гилева; под ред. Н. И. Шаталовой. – Москва : ИНФРА-М, 2016. – 221 с.
- Weinert, F. E. Konzepte der Kompetenz / F.E. Weinert. – Paris: OECD, 1999 – 269 р.
