| Materials on the theme of master's work: | Main page | Abstract | Links | Autobiography | Library | Hobby |
Traditional stages of reception of electric energy are far from optimum when their number joins process of burning of fuel, reception water steam of the set parameters, reception of mechanical energy in the turbine, and then its transformation into the generator. The modern society constantly pays attention to prevention of environmental pollution both with harmful chemical wastes, and thermal emissions. Thermal power stations, the industry and automobile facilities are the basic sources of pollution.
Direct generation of the electric power occurs in a fuel cell (FC). These are chemical sources of a power current. They carry out direct transformation of chemical energy of fuel into electricity, bypassing ineffective, going with greater losses, process of burning. This electrochemical arrangement in which as a result of highly effective "cold" fuel burning the electric power is directly developed.
In FC energy of oxidation-reduction reaction is transformed in electric, energy thus processes of oxidation and restoration are spatially divided by electrolyte. The substance of an electrode and electrolyte do not participate in reaction, but in due course become soiled impurity of fuel. Processes in FE go at low temperatures and practically lost-free.
Special interest represents FE in which fuel is coal, and an oxidizer - oxygen of air. In the metal cell filled by the fused electrolyte (NaOH), the prepared coal is located. It is kept in electrolyte by a wire lattice on which the negative charge collects. The electrolyte, together with the case of the generator, is charged positively.
Thus the oxidizer does not contact directly with surface of coal in order to prevent ignition, and necessary contact is carried out through ion-conducting electrolyte to which air is supplied continuously. There is an ionization of atoms of fuel and potential arises on electrodes. In this case the reserved energy of coal turns both to heat, and to an electricity.
The electrolyte, vessel and coal should be at uniform temperature. It is reached by the air barbotage through electrolyte. Such hashing helps to remove products of reaction from a surface of coal that opening a surface for influence of oxygen from electrolyte.
In this process coal gradually turns to carbonic gas, part of it incorporates with sodium and forms its carbonate which, together with ashes, gradually pollutes electrolyte, reducing its efficiency. Modeling of chemical processes was conducted by the analysis of quasi-balanced composition structure at course of chemical reactions of low temperature ionization in thermodynamic approach. In a general view process is described by such equation:
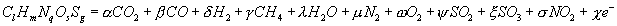 where
where
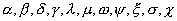 - quantity of a component in system in the certain moment of time.
- quantity of a component in system in the certain moment of time.
Oxygen passes in the ionic form on the cathode by the formula
O 2 + 4e - =2O 2-
Thus oxygen interacts with coal, forming СО 2 according to reactionC + O 2 = CO 2
Collateral reaction that was spoken above looks thus2 NaOH + CO 2 = Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O
In the reduced ionic form such2OH - + CO 2 = CO 3 2- +H 2 O
In total in FC proceeds m reactions. The law of operating mass gives n equations of material balance. The others m-n equations that is necessary for definition of unknown quantities, we can receive from the law of operating mass in the form of the equation of balance. The received system of the nonlinear equations is solved by an iterative method of Newton-Rafson. For this purpose we shall present each equation of system in the form ofF(x)=0
Thus for the decision we shall search on a parityx n+1 = x n - F(x n ) / F'(x n )
It is necessary to note, that for the decision according to the given method, performance of convergence conditions is necessary. They have such appearance:1.Initial value x 0 should be chosen close enough to a root of equation F(x) = 0 ;
2. Derivative F'(x) is not strongly close to zero.
Carried out researches enable to plan further carrying out experiments in more details for the choice of necessary FC components, to pick up the most effective pair of electrodes, to study conditions of processes, to receive the competitive device for direct power generation, to predict its technical-and- economic parameters.
Перечень используемой литературы:
| 1. | Форсайт Дж. Машинные методы математических вычислений 1980. |
| 2. | Термодинамические свойства индивидуальных веществ в 2 т./под ред. Глушко В.П. - М.:Наука, 1965 г. - 978с |
| 3. | Термодинамические и теплофизические свойства продуктов сгорания в 10 т./ под ред.Глушко В.П. - М.:1971 г. - т 1, 278с |
| 4. | Справочник по расчетам равновесий металлургических печей - М.: 1963г - 365с |
| 5. | На Цунг-Йен Вычислительные методы решения прикладных граничных задач 1982 |