|
Abstract
1.
Introduction.
2.
Relevance.
3.
Goals and Objectives.
4.
The problem at the level of
subject area.
5.
Mathematical
statement of a problem.
6.
Viewing and analysis
of signal electrogastroenterography.
7.
Synthesis of
scientific search and analysis.
8.
Conclusion.
9.
Literature.
1.
Introduction
Researches of last
years reveal the accurate
tendency to increase in disease of digestive organs. In this connection
there was an absolute must of constant improvement of available methods
of diagnostics and also creation and working out of the new, earlier
not used methods, to detect the disease in its early stages, to assess
the extent of lesions, to supervise results of spent therapy.
Electrogastrogram: An electrogastrogram (EGG) is a graphic produced by
an electrogastrograph, which records the electrical signals that travel
through the stomach muscles and control the muscles' contractions. An
electrogastroenterogram (or gastroenterogram) is a same procedure, at
which write down electric signals not only from a stomach, but also
from intestines.
These names are
made of different parts: electro,
because it is related to electrical activity, gastro, Greek for
stomach, entero, Greek for intestines, gram, a Greek root meaning "to
write".[12]
2.
Relevance
Electrogastrogram
non-invasive, has no
contraindications and is well tolerated by all patients. This allows
examining even extremely heavy patients, both before the operation, and
in the first hours of the postoperative period. Considering simplicity
and availability of the methodology can be repeated numerous studies to
assess the dynamics of the treatment process. Data obtained with
electrogastrogram not contradict, and often are ahead of the results of
X-ray and endoscopic studies, which showed a high sensitivity method
for the diagnosis of motor disorders.
3.
Goals and Objectives
The aim of this
work is to improve the timeliness
and accuracy of diagnosis of diseases of gastrointestinal tract through
the establishment of a moderns algorithms of processing
electrogastroenterography signal.
To achieve the
goal, it is necessary to solve such
problems:
1. Develop the technical means of registration
electrogastroenterography signal;
2. Develop a model electrogastroenterography signal
for each of the gastrointestinal tract;
3. Develop algorithms for determining the diseases
of the gastrointestinal tract;
4. Develop software implementing established models
and algorithms.
4.
The problem at the level of subject area
4.1.
Object of the
study.
To better
understand how and why developing
various diseases of the digestive system, must first understand its
structure. Simplified description of the gastrointestinal tract:[11]
1. Esophagus:
it is a long tube of muscle
tissue in which the food moves from mouth to stomach.
2. Abdominal cavity
below the diaphragm.
Here are all the abdominal organs.
3. Stomach
is in the upper abdomen. Here
the food exposed to gastric juice and enzymes produced by gastric
mucosa. Elements of food that are crushed to smaller components.
4. Esophageal
sphincter:the valve which
prevents the release of food mixed with acid back into the esophagus.
5. Porter
: a small circular muscle at the
outlet of the stomach. Controls the flow of food in the masses of the
stomach small intestine (duodenum).
6. Small intestine
the most important
digestive organ man. The total length of small bowel adult 4.5-6
meters. In the small intestine are absorbed proteins, fats,
carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals. Adopted by the department to
allocate the three small bowel: duodenum (duodenum), jejunum (jejunum),
iliac intestine (ileum).
7. В In the duodenal
food delivered from
the stomach, mixed with bile and pancreatic enzymes. Here is absorbed
iron and calcium.
8. В In jejunum
absorbed a large part of
the food items. Jejunum from the inside is covered with a huge number
of villi - thin tubes that increase the suction surface of the bowel.
Chyme (food mass) is moving here in liquid form. Proteins, fats and
carbohydrates from the villi and are absorbed through the bowel wall
into the bloodstream.
9. The last segment of small bowel: iliac
intestine.
Here comes the absorption lip soluble vitamins A, D, E, K, and other
nutrients.
10. Ileotsekalny valve
divides thin and
thick intestines. Valve chyme passes from the small bowel to fat and
prevents a return throw from the seed masses of bacteria in the large
intestine almost sterile thin.
11. В In the large
intestine of chyme
arriving from the small bowel, gradually draw off the water and, thus,
formed stools. Large intestine is home to huge quantities of bacteria
(Escherichia coli, bifid bacteria, lacto bacteria), which are involved
in the process of digestion.
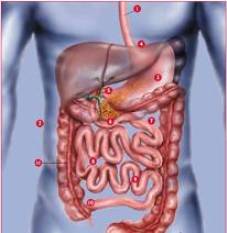
Figure 1. General scheme of the digestive system of man. Promotion of food
to the digestive tract, the
mechanical treatment, mixing with digestive juices is one of the
important functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Doctors called the
motor-function evacuative.
Food ball when
swallowing esophagus comes in
under the pressure and moving it through a rhythmic wave of reductions.
Then, passing the esophageal-gastric passage (it is also called the
lower esophageal sphincter), it enters the stomach.
In the stomach the
food is mixed with a bundle of
digestive juices and is machined through the peristaltic short cuts and
slow long-term changes in tone. Upon completion of processing in the
stomach the food in small portions with a period of about 20 seconds
goes to the duodenum, where its further processing enzymes allocated
pancreas and gall. And its movement is provided by peristaltic
undulating cuts.
Then the food
Became the original pulp, chyme,
enters the jejunum further in iliac intestine where further digestion
and absorption of nutrients. Further it is the way into the colon.
Here, food is delayed a long time - up to 20 hours. There are three
types of motor activity of colon cancer: a direct displacement of the
mass, retrograde (reverse) to promote and rhythmic reductions in
individual segments of intestine. Such complex behavior is fully
intestine absorption of salt and water from the stool and regular bowel
movement.
It is the
coordinated work of the esophagus,
stomach and intestine ensures proper digestion and that its
coordination disorder underlie or are a consequence of many diseases of
the digestive tract. And that is why on the motor-function evacuative
need to know everything.
4.2
Methods of
research.
Currently, there
are two groups of study
motor-evacuative function gastrointestinal tract(GIT).
The first group
includes methods to record
contractile activity GIT by measuring the pressure inside of a division
GIT using cylinders micro detector, radio pill open water perfusion
catheters. Unfortunately, the introduction of a foreign body, which is
any of the above sensors, resulting in irritation and body changes its
motor activity.
The second group
includes electrophysiological
methods based on the relationship of electricity and refractive
activity GIT. They include a registration biopotentsial to fixed on the
walls of the electrodes, the so-called direct electrogastroenterogram
or register biopotentsial with skin electrodes, fixed to the abdomen or
extremities - an indirect or peripheral electrogastroenterogram.
Naturally, the
need for implantation of
electrodes limits the use of direct electrogastroenterogram in clinical
practice. Peripheral electrogastroenterogram being not invasive, does
not require any intrusion into the human body, is well tolerated by all
patients. This allows examining even extremely heavy patients before
the operation, and in the early hours of the postoperative period.
4.3.
Electrogastroenterogram.
Electrogastroenterogram: method of study to
evaluate the bioelectrical activity of the stomach, duodenum and other
divisions GIT. It is based on registration of changes in electrical
potential from the GIT. [8]
In the quiescent
state of smooth muscle cells, and
cells of the heart muscle or skeletal muscle, resting membrane
potential are due to concentration gradient of ions across the cell
membrane. Periodic changes in membrane potential known as slow waves or
transmembrane building peace. A transmembrane potential of resting
understand potential difference between intra-and extracellular
environment in the absence of changes in electrical activity. The value
of transmembrane capacities ranging from 20 to 90 mV. The slow
electrical waves are a periodic depolarization and repolarization
phases of smooth muscle cell membranes. In the stomach, slow waves are
generated miogennym peysmeykerom, located in gastric body. The slow
waves occur with a constant for each department GIT frequency. As we
have seen a number of researchers in the intestine, there is
proximal-distal gradient of frequency of slow waves, the maximum
frequency observed in the duodenum and the primary department jejunum
rectum, in a distal direction frequency decreases. It is important to
note that the frequency of electrical slow wave determines the maximum
possible reductions in the frequency of smooth muscles of the
gastrointestinal tract. The experiment revealed that out of
bioelectrical activity of the digestive gastrointestinal tract is
characterized by phases of relative calm and the phases of enhanced
activity (starvation peristaltic activity).
The slow waves by themselves do not cause muscle contraction. Reduction
of smooth muscle tissue occurs when you are on a plateau of slow waves
of fast electrical oscillations, action potentials (AP). Action
potentials are a relatively rapid change in membrane potential, which
is closely related to the level of capacity at rest and the amplitude
of electrical slow waves, and reflect a local decrease in muscle
fibers. Single cause tonic decrease in PD, PD group are rhythmic
contractions. The strength of reduction of muscle fiber is proportional
to the number of DD in the group. The slow wave is created in the
muscles of the potential close to the threshold of activation, which
enables the emergence of PD with a consequent reduction of muscle
fibers. With the lack of depolarization of cell membrane PD fade, with
a high depolarization can initiate propagating slow wave. However, some
authors believe that the decrease in muscle fiber possible, and in the
absence of peak potentials. At the same time recorded minimum in
amplitude reduction of ulcer sites, the relevant basic electrical
rhythm.The mechanism of generation of electrical slow waves is stable.
They are little changed under the influence of acetylcholine, atropine,
adrenaline, morphine, histamine, cocaine, nicotine. However, all these
substances are definitely affect the appearance of the peak potentials
and a reduction in smooth muscle.
In the early 20 th century, the researchers measured the electrical
activity of smooth muscle cells. To do this, use as intracellular or
extracellular means of allocating the signal. At the present time to
determine the bioelectrical activity of the gastrointestinal tract
using direct methods with the implanted electrode and indirect methods,
based on registration of changes in electrical potential
gastro-intestinal tract of the body surface. Direct techniques allow
more accurate assessment of the motor-evacuative function of the
intestine studied, as it allows to record action potentials. However,
invasiveness method imposes some restrictions on its use. Indirect
method biopotentsial has several advantages over direct. He no
invasive, has no contraindications, a measure bioelectric activity of
all divisions GIT. Electrogastroenterogram indirect method allows to
register only change the slow waves. However, as mentioned above, slow
waves do not cause muscle contraction intestine, resulting in not fully
reflect the motor-evacuative activities intestine. Nevertheless,
studies have shown that rates of change between the slow waves, and DD
has a high correlation. This relationship so close and reliable than
the intense peak power and motor activity of the body. With reductions
in active and appears to packs DD states and increasing the amplitude
of slow waves. Register биоэлектрического building was carried out from
the surface of the skin in the stomach. Currently, this method of
allocating the signals commonly used in our clinics, as well as abroad.
Negative features of this method is the inability to assess the
bioelectric activity of various departments GIT.
Thanks to the work of rib VG, a method of peripheral
electrogastroenterogram in which the registration signal various
divisions GIT made from limbs. The ability of this method is due to
constant frequency of smooth muscle cuts in various departments GIT. To
register the electrical activity of the various divisions GIT using
highly bandwidth amplifiers with low frequency (0 to 1 Hz), with a
strengthening of the DC, thus eliminating noise being made in
high-frequency signal capacities of other bodies. Scheduled
spectrogram, and the digital data obtained after processing the signal
level of electrical activity of the stomach and duodenum, iliac, and
colon, the rhythm of cuts and coordinating the work of neighboring
departments GIT. Frequency reductions GIT various divisions, as was
shown in a number of works are stable parameter. The boundaries of
these frequency intervals are shown in the table.
Table
1. The frequency
intervals of electrical activity of the various divisions
gastrointestinal tract
| Division
gastrointestinal tract |
Frequency
(Hz) |
| Colon |
0,01 - 0,03 |
| Stomach |
0,03 - 0,07 |
| Small
intestine |
0,07 - 0,13 |
| Jejunum |
0,13 - 0,18 |
| Duodenum |
0,18 - 0,25 |
4.4.
Equipment for the study.
Modern
instrumentation used for diagnostics and
research, provide admission and registration of signals from skin
electrodes for a period of 1 hour to 24 hours, as well as storage,
processing and document submission of the information obtained.
Installed filter device simultaneously to evaluate the electrical
activity of gastric, duodenum, jejunum, small intestine, and colon, in
the frequency range 0,01-0,25 Hz.

Figure 2. Electrogastroenterograph EGEG-01K Gastroscan-HEV:

Figure 3. "Gastroscan HEV" - computer-based instrumentation to monitor
both pH and electrical activity GIT 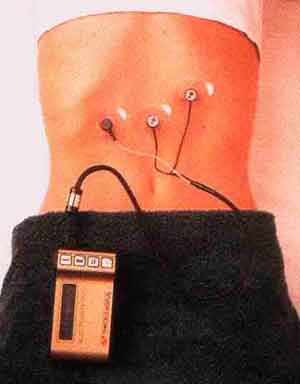
Figure 4. Portable apparatus for electrogastroenterogram "Digitrapper
EGG".
|
|