Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Determination of method for mine hoist productivity control
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Mine hoist is the most important process in technological chain of coal production. Being a horse-drawn transport, a hoist belongs to discrete mode of transport when the delivery of coal when the delivery of coal to a certain point is put into practice by limited portions of mass [2]. Overloading of this transport leads to reducing of a term of rope service and the whole unit. Shortfan also reduces the efficiency of the transport. Therefore, it is impossible to overestimate the importance of automation of the object for mining industry.
1. Actuality of the topic
Modern means of automation can improve the reliability and durability of the equipment, increase productivity, reduce energy consumption, give a diagram to work out optimum speed without emergency inrush current and torque drive, having destructive forces on the lifting equipment, ensure complete control over
all the necessary parameters that influence the operational status of the unit and appropriate responses to their changes.
From this point of view the most effective are multi-circuit systems with subordinate adjustment of parameters. These systems foresee varouus return links giving opportunities to observe anomalous changes of controlling parameters and control in accordance with getting information. Return links foresee presence of devices transforming a controlling parameter into a signal, which is used in control, a return link, in this case, will be a speed and skip quickening, as well as the time of moving cycle, a rope strain and a quantity of consuming energy.
A control system of
mine hoisting plant weight and average
speed of the cycle, which determine the overall cycle time, is one of
the main parameters. To do this, it must be reached all of the
following requirements:
analysis of the acceptable parameters of regulation of high-speed mine hoisting unit parameters, motion corresponding to the requirements of the Safety Rules [1];
- evaluation of ways to
reduce the average cycle time of the motion of lifts;
- selection of the most appropriate way to regulate the velocity parameters for the different skip velocity conditions;
- modeling and study of the influence of speed changes on the dynamic processes of mine hoist drive.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim is to increase the efficiency of the lifting process by developing a system of adaptive management productivity of mine hoisting plant. The main objectives of the research are:
- development of a mathematical model for a given mine hoist modes;
- determination of performance, the tension on the hoisting ropes, as well as electric power consumption for a given condition;
- The object of this research is the hoist unit.
In the frames of the master's work it's planned:
- analysis of the ways to manage performance in a various speed conditions;
- determination of the most rational ways of operation by adjusting the speed parameters.
For the experimental evaluation of the theoretical results and further research foundation, as the practical results of the management I plan the engineering of device,which will allow speed control of mine hoisting plant as a part of the automated mine lifting process control system (PCS).
Requirements for the automation system recovery for further PCS:
- operative mapping of the current information about instantaneous and average parameters of hoisting unit;
- ensurance of reliable operation of the system under dynamic conditions of extraction and transportation of coal;
- work in a continuous production cycle;
- reliability, control and measurement system of developed devices and the system in general.
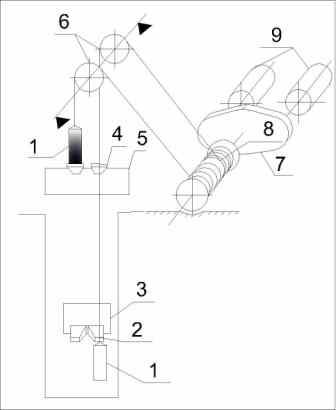
Figure 1 – Mine hoist
1 – Skip, 2 – Schieber tank, 3 – Hopper, 4 – Receiving hopper, 5 – Schieber hopper,
6 – Lifting pulleys, 7 – Gear, 8 – hoist drum , 9 – hoist drive engine
Research object: Mine hoist
Research subject: mine hoisting plant control methods in different speed modes.
3. Identification of method for mine hoist productivity control
Modern automation tools allow machines to increase unitt productivity,
optimize the speed chart, as well as reduce the magnitude of the
average consumption of electrical energy per cycle of motion of lifting
the vessel through the fidelity of defined parameters. However, these
solutions do not provide the productivity management of mine hoist,
taking into account requirements of daily changes of electric power
consumption, the tension of the rope hoist, and also depending on
the size of the average cargo traffic on the loading site. Since,
according
to safety rules [1],
the permissible speed for cage hoists is limited to
12 mps, and to skip – is determined by project indicators of
expediency of efficient control implementing of a hoist limit during 24
hours.
The daily productivity of the lift installation is determined from the
expression.
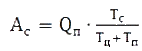 ,
,where Ac – mine hoist daily productivity, tons;
Qп – hoisting capacity, tons;
Tc – mine hoist daily work duration, sec
Tц – lifting cycle duration, sec;
Tп – technological pause duration, sec.
Analysis of this expression shows that mine hoist productivity depends on cycle duration is shown as:
 ,
,
where Н – depth of mining, m;
vc – average skip velocity per cycle, m/sec
The average value of expendable electric power is given by:
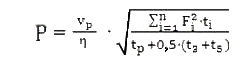 ,
,where vр – hoisting plant contant motion velocity , m/sec;
η – mining hoist general efficiency
Fi – dynamic forces acting on the vessel to lift specified range chart speeds, KN
t3, t5 – duration of periods of acceleration and deceleration respectively.

Figure 2 – Mine hoist work
(animation: 17 frames, 6 cycles of repeating, 45 kilobytes)
To ensure safe lifting operation is necessary to monitor the maximum tensile hoisting rope force is given by::
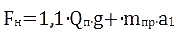 ,
,where
Fн – maximum tensile hoisting rope force, KN;
mпр – reduced to the axis of the lifting machines mine hoist weight;
a1 – the main lifting vessel acceleration
Using these formulas, we obtained a comparative table showing change parameters effect of the average daily productivity rate and recovery, and and consumption values drive motor power depending on the parameters of the speed limit (Table 1).
Table 1 – speed modes variables dependence
| Mode 1 – Changing the uniform velocity (a1, a2=0,8) | ||||||||
| vр |
8,5 | 9 | 9,5 | 10 | 10,5 | 11 | 11,5 | 12 |
| vcр |
7,16 | 7,49 | 7,8 | 8,1 | 8,39 | 8,67 | 8,93 | 9,19 |
| Ac |
4830 | 5040 | 5250 | 5460 | 5640 | 5850 | 6030 | 6180 |
| P |
637,44 | 641,23 | 645,24 | 649,46 | 653,89 | 658,51 | 663,33 | 668,34 |
| Fн |
487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 |
| Mode
2
– acceleration and slowdown change a1
a2
(vp=
10) |
||||||||
| a1, a2 | 0,6 | 0,7 | 0,8 | 0,9 | 1 | 1,1 | 1,2 | 1,3 |
| vcp |
7,89 | 8,01 | 8,1 | 8,17 | 8,23 | 8,28 | 8,32 | 8,35 |
| Ac |
5310 | 5400 | 5460 | 5520 | 5550 | 5580 | 5610 | 5640 |
| P |
636,3 | 640,5 | 645,2 | 650,5 | 656,3 | 662,6 | 669,5 | 676,8 |
| Fн |
449,6 | 468,7 | 487,8 | 506,9 | 526 | 545,1 | 564,2 | 583,3 |
| Mode 3 – slowdown change a2 (vp=10, a1=0,8) | ||||||||
| a2 | 0,6 | 0,7 | 0,8 | 0,9 | 1 | 1,1 | 1,2 | 1,3 |
| vcp |
7,16 | 7,49 | 7,8 | 8,1 | 8,39 | 8,67 | 8,93 | 9,19 |
| Ac |
5400 | 5430 | 5460 | 5490 | 5490 | 5520 | 5520 | 5460 |
| P |
632,9 | 641,4 | 649,5 | 657,2 | 664,7 | 672,2 | 679,6 | 690,2 |
| Fн |
487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 | 487,8 |
Analysis of Table 1 shows that in mode 2 when the quickening of movement increases linearly, the dynamic force of the tension increases greatly. The quantity of electric power consumption, and in modes 1 and 3, the tensile force of the rope remains constant
Conclusion
Thus, the most efficient operating mode of the mine hoist performance is themode of change of velocity of constant motion of lifting unit, which does not contradict with the requirements of the Safety Rules [1]. However, the development of automatic control systems and modes of the brake system will improve the efficiency of lifting.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2011. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
