Abstract
Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. Actuality of theme
- 2. Purpose and objectives of the study, expected results
- 3. Review of Research and Development
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Overview of national sources
- 3.3 Overview of local sources
- 4 The concept of file sharing in Ukraine
- 5.Information and analytical systems for design and analysis of the exchange files
- 6. Analysis of land-cadastral information
- Conclusion
- Literature
Introduction
At the present time the issues are particularly acute operative provision of relevant spatial and legal information on the status of land users. The volume of the collected, processed and disseminated by the cartographic and textual information is gradually increasing. As a result, stands in front of potential users is difficult solvable problem of finding the necessary information.
1. Actuality of theme
Currently, authorities in the management of land use to exchange information filesIN4, progressing to the format of XML. However, the transition from one format to another does not solve the problem effectively. In exchange files still contained some errors, which concern both semantic information and spatial. The organization and content of the base of land and inventory data is a priority across the industry, which certainly must be addressed.
2. Purpose and objectives of the study, expected results
The purpose of research - to identify gaps in information, formalizing the exchange of files to install a set of data for the most efficient use.
Research tasks::
- identify the advantages and disadvantages of existing methods of entry to the exchange of inventory information file;
- perform a statistical study and handling of inventory information;
- identify errors in the XML-files;
- create a program file parsing XML;
- optimize the collection of data that are recorded in the file exchange.
The object is the exchange files of the land cadastre information the Russia
Zlatoust village council in Volnovakha district Donetsk region.
Scope of the work - the land-cadastral information stored in the exchange files.
3. Review of Research and Development
3.1 Overview of international sources
On the world stage are a lot of legally complete automated accounting systems andland management and real estate. Among the countries in which the process of standardization and the introduction of a common information technology architecture has been implemented more comprehensively, thus enabling the full optimization activities in the provision of electronic services at the state and municipal level, are:
- UK: Government Gateway, a government intranet and standard e-GIF;
- Denmark: infrastructure Infostructurebase;
- Sweden: Government Elink (GeL);
- Australia: FedLink - government gateway and a secure government intranet;
- Hong Kong: Government System Architecture (GSA) and the Electronic Service Delivery (ESD) Scheme;
- U.S.: Federal Enterprise Architecture information technology government organizations [1].
3.2 Overview of national sources
Significant contribution to the field of cadastre in Ukraine and its automation are our scientists have made a M.G.Lihogrud (Automated System of the State Land Cadastre of Ukraine (the creation concept)
, The database structure of automated system of land registry)
) U.V. Palekh, L.N.Perovich, R.M.Rudoy, E.S.Seredinin, M.G.Stupen, A.N.Tretyak, M.D.Cheremshinsky (The evolution of cadastral systems in the world and cadastral reform in Ukraine
), L. Shafranska (Cadastral systems: their future under globalization
) and others.
In Ukraine, the transition from paper technology
was delayed for a long time. Thus, to improve the procedure and resolve issues to create an automated system of the state land cadastre (hereinafter - AS SLC) in 2003 as the format of the information about the land was passed a file IN4. However, after seven years (2010) proposed a different format for a more complete XML. These innovations have significantly increased the routine work in enterprises, which could not affect the existing state of the AS SLC.
To date, both in Ukraine and abroad, the main difficulty of the implementation of projects in the field of electronic services at the state level, as well as similar local projects at a time when significant efforts are required to integrate data and applications, is not applying the or other specific technologies, and in organizing the process of adopting appropriate standards and harmonization of information technology architectures of various organizations and agencies.
It should be noted that at the present time in Ukraine, there are many developments that provide software maintenance of the SLC. Among them are the ASLC Donbass 2000
(Donetsk), GIS 6 (Kirovograd), GIS TEREN-REGISTER (Poltava, Zhytomyr, Lviv) and others [2].
At the enterprises to create and exchange files with AutoCad is used to convert the suspended features, Delta Digitals, GIS 6, manager exchange files
and others.
An important difference in the formation of the cadastral system of Ukraine from other countries is parallel development of cadastre system and its maintenance in an automated way, which leads to a significant number of errors and shortcomings of the legal and institutional arrangements. Thus, as is currently necessary to direct all efforts to solve the problem of quality and organization of the inventory in the AS SLC. This requires that the following conditions:
- presence in the database (the DB) true and complete and full information;
- instant access to the data (possibly for a fee);
- the presence of a common data format.
Thus, we can conclude that in Ukraine at this stage there is no centralized legislative and continuity
, which leads to wasted time and money, but does not address the issues of quality management of inventory.
Ukraine does not stand apart from the processes that take place in the world. So, now the legislative and regulatory framework to create and maintain inventory in Ukraine include:
- Land Code of Ukraine of 25.10.2001 № 2768,
- Laws of Ukraine
About the survey and mapping activities
from 23.12.1998 № 353About the state assessment of land documents
from 17.06.2004 № 1808 and others; - Decree of the President.
About measures to create a unified system of state registration of land, property and rights to them within the state land cadastre
of 17.02.2003 № 134/2003; - Decisions of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
About the order of the state land cadastre
of 12.01.1993 № 15About the program of creation of an automated system of the state land cadastre
of 02.12.1997 № 1355,Conduct of Land records
of 09.09.2009 p. N 1021,About the unified system of state registration of land, property and rights to them within the state land cadastre
of 17.07.2003 № 1088,The execution of land-cadastral works and services for a fee by the state land
on 01.11.2000 № 1619; - • Order of the State Committee
About approval of Requirements to the structure, content and format design work results from land use in electronic form (exchange file)
from 02.11.2009 № 573 (files of type XML) and others.
In order to establish the legal, institutional framework and Pripet activities in the State Land Cadastre Act of Ukraine On State Land Cadastre
from 07.07.2011 № 3613-VI. The law came into force on January 1, 2012.
3.3 Overview of local sources
Among the literature on the local level (based on faculty, graduate students and undergraduates DonNTU) should be made of D.U. Gavrilenko (The rationale and study information and topological models for spatial objects cadastre systems
), E.A.Germonova Improving thetechnology of creating and editing index and cadastral maps
) E.V.Kiyashko (Investigation and analysis of land information in the database
) and others.
4 The concept of file sharing in Ukraine
The exchange file XML, in accordance with the Decree of the State Committee of 02.11.2009 № 573 are formed with a view to the data to the Land of the book and the book records the registration of acts of state ownership of land and the right of permanent use of land, land leases, which are maintained in electronic form , and define a set of basic lexical and syntactic rules for constructing the exchange of files.
File Exchange - an electronic document standard format for information exchange, which is used in the management of the Land of the book and the book records the registration of acts of state ownership of land and the right of permanent land use, land lease agreements in electronic form, the state land cadastre and topographic implementation - surveying, land development works from [3].
The content of the exchange file is based on the information contained in paper documents, drawn up by the performers work. The information entered in the exchange file is shown in Fig. 1.

Figure 1 - Data exchange file
The basic elements of the formation of the exchange file is geodetic data(coordinates of the turning points of the limits of land cadastral units), which provide the spatial basis of other data exchange file and the possibility of their use in the automated system of the state land cadastre (hereinafter - AS SLC).
The exchange file is created in the form of XML - file encoded in Unicode (UTF-8).
The structure of the exchange file consists of two parts: service and information (Fig. 2).

Figure 2 - Structure of the exchange file
The Additional Part is used to generate and share informationon the details of the exchange file and executor. The Service section consists of:the exchange of information on file, information about persons who have formed, to validate (correction) of the data exchange file. The structure of the complex type Information about exchange file
and Information about the artist works
can be found in Tables 1-2, respectively.
Table 1 - Structure of the complex type Information about exchange file
[4].
| UkrainianCadastralExchangeFile/AdditionalPart/ ServiceInfo | |
| ServiceInfo Information about exchange file (information service) | |
| The composition of the element | |
| FileID Identifier of exchange file |
FileDate Date of formation the file |
| FileGUID The unique file identifier | |
| FormatVersion Exchange file format version | |
| ReceiverName Name of division of the Center SLC | |
| ReceiverIdentifier Identifier unit of the Center SLC Min -0, max-1 | |
| Software The name of the software | |
| SoftwareVersion Software Version | |
Table 2 - Structure of the complex type Information about the artist works
| COMPLEX TYPE | ||
| ExecutorInfo Information about the artist of works | ||
| The composition of the complex type | ||
| CompanyName Artist of works | ||
| EDRPOU The identification code in accordance with the Single State Register of Companies and Organizations of Ukraine | ||
| TaxNumber The identification code in accordance with the State Register of Physical Persons of Ukraine (in the presence) | ||
| License Information about licenses for the works Min -1,max-2. |
LicenseSeries A series of license | |
| LicenseNumber License number | ||
| LicenseIssuedDate Date of licensing | ||
| Chief Data about the responsible person Min -1, max-2. | ChiefName Сtype FullNameType Full name of person responsible | |
| ChiefPosition Position of the responsible person | ||
| Executor Data about direct artist Min -1, max-2. |
ExecutorName type FullNameType Full name of artist | |
| ExecutorPosition Artist position | ||
| ContactInfo Contact information | Phone Telephone number Min -1,max-N | |
| Fax The fax number Min -0,max-N | ||
| Email The artist E-mail Min -0,max-N | ||
| Address type Address Location | ||
The information part (InfoPart) is used to exchange information on land-cadastral units, territorial areas and their metric information. The information part consists of the following elements: the metric information exchange file; territorial zone; cadastral zone. Cadastral Zone consists of cadastral districts, which, in turn, consist of land [5].
In this section, special attention should be paid to the complex type coordinates of nodes polygon cadastral unit
and boundary object
(Tables 3-4).
Making information about the coordinates of nodes polygon cadastral unit is shown in scheme 1. This element identifies all the points with measured coordinates.

Scheme 1 – Making information about the coordinates of nodes polygon
Table 3 - Structure of the complex type Coordinates of nodes polygon cadastral unit
| COMPLEX TYPE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PointInfo Coordinates of nodes polygon cadastral unit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The composition of the complex type
| Point |
The node polygon cadastral unit UIDP | The unique number of the node polygon cadastral unit
| PN | The name of the node polygon cadastral unit
| DeterminationMethod | Method of determination Selects 1 of 4 Survey | Geodetic survey GPS | GPS surveying Digitization | Digitization of maps Photogrammetry | Photogrammetric measurements
| X |
| Y |
| H | Min -0, max-1
| MX | Min -0, max-1
| MY | Min -0, max-1
| MH | Min -0, max-1/td>
| Description | Description of point Min -0, max-1
| | ||
Table 4 - Structure of a complex type of Object boundary
| COMPLEX TYPE | ||||||||||
| Boundary Object boundary | ||||||||||
The composition of the complex type
| Lines |
Block description of all the polylines / lines of the object Line | A description of each polyline / line object Min -1, max-N ULID | The unique number of polyline object FP | The unique node number the beginning of the line Min -0, max-1 TP | The unique number of the node end of the line Min -0, max-1 Closed | Sign of closed polygon
| | |||
An entry on the border of the object above scheme 2.

Scheme 2 – An entry on the border of the object
Description of polylines and lines indicated in MetricInfo / Polyline with a ULID Boundary should point to the appropriate ULID in MetricInfo / Polyline. If the polyline/ line in the Boundary should be in the reverse direction that FP and TP should point to the latter and, accordingly, the first node of a polyline / line. Symptom Closed polygon must point to a true
to all area objects or false
for linear objects.
5. Information and analytical systems for design and analysis of the exchange files
To process the inventory data are used as proprietar (Mapinfo, ArcGIS, etc.), and open GIS (Geographic Resources Analysis Support System, Quantum GIS, etc.). When comparing them you can see a significant difference between the price of licenses for commercial and open source software. However, be aware that the total cost of production and possession of open source software, however, is not zero. Whatever type of software, the price should include costs for installation, technical support, training and other related expenses. The benefits of open GIS other than price, are also included greater independence from the developer, the very model of development, ease of introduction of innovations. Among the current problems of public release of their lack of GIS functionality and performance, the complexity of licensing, support and reliability as a whole, as well as the embeddable in technological processes [6].
For the analysis of XML-files used by a number of software products, the possibilities which can be found in Table 5.
Table 5 - Applications for XML Parsing
| XML-Validator | XML Viewer, XML Marker | Manager of exchange files | Digitals |
| - checks the XML-files for validity (reliability, a measure of compliance) | - display of hierarchical and tabular nature of XML data;
-checks XML-files for validity. | - convert data from format IN4 in XML and conversely; - validation of IN4 and XML files for correctness and completeness of the attributes, and save lists of errors found in the files; - display of spatial data. | - validation of IN4 and XML files for correctness and completeness of the attributes; - display of spatial data; - acceptance of files. |
At the enterprises to create exchange files and conversion is used, fitted with AutoCad functions, Delta Digitals, GIS 6, Manager of exchange files
and others.
6. Analysis of land-cadastral information
At the beginning of all the files have been checked for validity.
Initial analysis of the initial information is made in the File Manager exchange.
Performing the analysis is carried out simply enough (Tools - Check). With this software you can convert files to XML format, IN4, and conversely [7]. Catalogue of the analysis is shown in Figure 3, the identified errors are described in Table 6.

Figure 3 - Catalog of analysis Manager of exchange files
Table 6 - Errors in exchange files checking in the Manager of exchange files
| № | Location of the error | Error |
| 1 | Date of adoption of a document forming the basis for property rights | not valid(blank) |
| 2 | First term of this law | not valid(blank) |
| 3 | Date of right to use | not valid(blank) |
| 4 | Date of issue passport person providing the land for use | not valid(blank) |
| 5 | The number of State Act | fails constraints (empty) |
| 6 | The number of section in the book of registration | fails constraints (empty) |
| 7 | Registration number in the Register book | fails constraints (empty) |
| 8 | Date of registration in the Register book | not valid(blank) |
| 9 | Date of issue the State Act | not valid(blank) |
| 10 | Date of issue passport to the recipient the State Act | not valid(blank) |
| 11 | Foundation issuing the State Act | not valid(blank) |
Identification of errors relate only to format values (an invalid value, the failure limit) and are defined in the case where the field is empty. Therefore, the decision was made later create your own software product that performs the parsing of XML files (parsing, which automatically made the parser) [8]. In our case, we propose the implementation of parsing through established programs in the environment of Delphi Parsing
(Fig. 4).

Figure 4 - The main form of the Parsing
With this program you can:
- create a database (including adding and deleting records);
- editing data in the database (available functions: cut, copy, paste, select all, rewind, delete);
- the performance of sorting the data in the database (sorting is possible on the cadastral number, identification code, the full name, passport data, area, perimeter);
- implementation of the filter (search for a given parameter);
- calculation of the total area and total perimeter of the base stations;
- queries in the language of SQL;
- the verification of the data for errors;
- graphical rendering the file.
With graphics rendering is performed check area of the site through its conversion analytically by the formula:
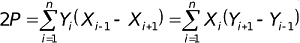
In the form of graphs can open the file exchange in AutoCad, export data to a format GBD, a catalog of coordinates (Fig. 5)

Figure 5 - Form of graphics
Form validation is shown in Fig. 6, detected errors are described in Table 7.

Figure 6 - The form validation error in the Parsing
Table 7 - Errors in exchange files detected by the program Parsing
| № | Check on errors | Criterion |
| 1 | The code of the exchange file | Completed |
| 2 | Сadastral number | 19 characters |
| 3 | Number of zones | 2 characters |
| 4 | Purpose | Completed |
| 5 | Name of owner | Completed |
| 6 | Identification number | 10 characters |
| 7 | Passport | 8 characters |
| 8 | Date of issue the passport | 10 characters |
| 9 | Place of residence | Completed |
| 10 | Area | Completed |
| 11 | Units of measurement area | Completed |
| 12 | Perimeter | Completed |
On Fig. 7 shows the distribution of errors in the passport number and series, shown on Fig. 8 - distribution of errors in a residence of the owner.
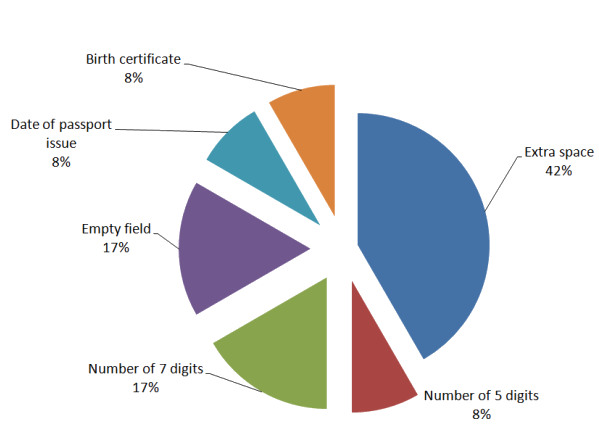
Figure 7 - Distribution of errors errors in the passport number and series

Figure 8 - Distribution of errors in a residence of the owner
The analysis revealed that frequently exchange files do not fill line on the passport data of land owners (including passport number and series, issue date, the address of residence).
Conclusion
According to the author to optimize the data set, data entered in the XML-file and reduce its size should be:
- back to the way the coordinates of the file IN4, but using the tag XML, because the coordinates in the XML registration is very complex and intricate structure. In the XML of priority given by the coordinates of the polygon, then the nodes are combined into lines and polylines that have a unique number. Polylines form the boundary of the site. In a separate set IN4 each boundary area that is convenient enough;
- to simplify the description of the neighbors. At the moment, allied to indicate sufficiently detailed passport data, which are difficult to collect. This greatly slows down the process of formation of the AS SLC.
In the future we plan to evaluate graphical errors in the formation of exchange files using software MapObject.
Master's thesis is still under development, so the article reflects the state of research at the moment. Completing the plan in December 2012 for more information about the final results can apply to the scientific adviser
Andrey Sholomitskij
Literature
- Общая информация о зарубежном опыте стандартизации при применении информационных технологий при организации оказания услуг в электронном виде [Electronic resource].– Access mode: http://www.pandia.ru...
- Гавриленко Д.Ю.
Обоснование и исследование информационных и пространственно-топологических моделей объектов земельно-кадастровых систем»/Диссертация на соискание ученой степени кандидата технических наук, Донецк -2011 г.
- Приказ Государственного комитета Украины по земельным ресурсам
Об утверждении Требований к структуре, содержанию и формату оформления результатов работ по землеустройству в электронном виде
№ 573 от 02.11.2009 г.- Методичні рекомендації при формуванні обмінного файлу XML [Electronic resource].– Access mode: www.geosystema.net...
- Изготовление обменного файла XML [Electronic resource].– Access mode: http://geotop.com.ua...
- Открытые настольные ГИС: обзор текущей ситуации [Electronic resource].– Access mode: http://www.gisa.ru...
- Менеджер обмінних файлів [Electronic resource].– Access mode: http://zemres.com...
- Парсинг [Electronic resource].– Access mode: http://markup-javascript.com...
- Приказ Государственного комитета Украины по земельным ресурсам
