- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the research the expected results
- 3. A review of existing methods of fuzzy control based on the membership function of several arguments
- 4. The study of information technology implementation of fuzzy control
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In
the area of technical systems fuzzy modeling provides more adequate
results compared to the results, which are based on traditional
analytical models and control algorithms. The range of application of
fuzzy methods is increasing every year, covering areas such as the
design of industrial robots and home appliances, control of blast
furnaces and the movement of subway trains, automatic speech
recognition and image.
The fuzzy logic, which is the basis for the implementation of fuzzy control methods, more naturally describes the nature of the human mind and the course of his argument than the traditional formal logic systems. That is why the study and use of mathematical tools to represent fuzzy initial information allows you to build models that most accurately reflect the various aspects of uncertainty is always present in our surrounding reality.
Handling fuzzy information and fuzzy inference long been used in a variety of intelligent systems, however, the most widely used system of fuzzy systems have gained in the field of management.
In classical fuzzy controllers do not provide mechanisms to adapt in real time to the changing characteristics of the control object interaction with the environment, which does not use fuzzy systems to control objects with time-varying properties. However, there are a number of methods that extend the fuzzy controllers in the field.
1. Relevance of the topic
Handling fuzzy information and fuzzy inference long been used in a variety of intelligent systems, however, the most widely used fuzzy systems have gained in the field of management. To control the bad formalizable objects with complex interactions of control variables suggested to use a method based on the terms of membership functions of several arguments. For practical use of the actual creation of specialized software.
2. The purpose and objectives of the reseearch the expected results
The aim of the study is the development and analysis of algorithms of fuzzy control based on the membership functions of several variables.
The main objectives of the study:
- A review of existing methods of fuzzy control based on the membership function of a single argument.
- A review of existing methods of fuzzy control based on the membership functions of several arguments.
- The study of information technology implementation of fuzzy control.Expected results: the implementation of the software solution with the method of fuzzy control based on the membership functions of several arguments.
3. A review of existing methods of fuzzy control based on the membership function of several arguments
Адаптация метода Мамдани к использованию функций принадлежности нескольких переменных
The method of constructing a
fuzzy controller based on the terms of membership functions with
multiple arguments is presented in Figure 3.1. The construction of
fuzzy controller includes the following steps:
- Formulation of the problem of fuzzy control;
- The formation of terms and their membership functions;
- Forming the base of fuzzy inference rules of the system;
- Fuzzification of input variables;
- Aggregation of sub-conditions in fuzzy production rules;
- Activation prisoners under in fuzzy production rules;
- Accumulation of findings of fuzzy production rules;
- Defuzzification output variables.
Within the formulation of
the problem defined by the input and output variables of the control
object on the basis of input variables selected control variables.
Highlighted values are represented in the form of linguistic
variables.
For each of the linguistic
variables are generated term-set as fuzzy variables [1].
If the linguistic variable has a simple structure, then it
can be selected in terms of the form of fuzzy variables with
one-dimensional membership function. Otherwise, it is recommended to
use the fuzzy variables with multi-dimensional membership functions. By
the formation of the names and terms of membership functions can be
held by experts. In addition to determining the number of terms of the
form and functions of the accessories may be used in methods of fuzzy
cluster analysis. In the future, to build a multi-dimensional
membership functions used in the method of fuzzy c-means.

Picture 3.1
– The method of constructing a fuzzy controller based on
multi-dimensional membership functions
The rule base of fuzzy
inference system is based on empirical knowledge and expert knowledge
in the subject area and is represented in the form of fuzzy
productions [2]:
Rule Rr: IF ПУlkir then ПУzbjr
ПЗjr : B1 IS Btlk,
Sir – truth degree of sub-conditions ПУlkir.
ПЗjr : Wz ЕСТЬ Wtzb,
где Wtzb – b-th term of the output linguistic variable Wz,
Zir – truth degree of sub-conclusion ПУlkir
Fazifikatsii procedure is to
establish a correspondence between the particular value of a single
input variable fuzzy inference system and the value of the membership
function corresponding Sir her term input linguistic variable, which in
the case of multi-dimensional functions, calculated as a
multi-dimensional tabular interpolation (Hermite polynomials) [3]:
where ẍl –
input value of fuzzy inference system;
µlk
(ẍl) –
membership function for the second term included in the sub-condition ПУlkir.
Aggregation is the procedure
for determining the degree of truth conditions for each of the fuzzy
inference rules of the system. If the condition of the rules given in
the form of fuzzy linguistic expressions of the form
«β is α», leaves the stage of
aggregation degree of truth unchanged. If the condition consists of
several sub-conditions, the sub-condition linguistic variables are
pairwise equal to each other, define the degree of truth complex
utterance based on the known truth values sub-conditions. In order to
determine the result of the formula is used:
At the stage of aggregation
are all the values of Sr for each of the rules under consideration
within the framework of the rules of fuzzy inference system.
At the stage of activation
for each of the output linguistic variables in separate productions
prisoners under fuzzy rules are determined by the membership function
of fuzzy sets of values [4].
The calculation of the value of the membership function for each of the considered prisoners undereny output linguistic variables is calculated as follows:
where µlk (ÿz) – membership function of the b-term;
Zir
–
degree of truth
of each of prisoners undereny using the formula:
where Kr –
weighting
rules.
Accumulation phase is to integrate or accumulate operations using max-disjunction of all the degrees of truth of the membership functions for each of the output variables:
Defuzzification is to use the results of the accumulation of all the output linguistic variables, get the usual numerical value of each of the output variables that can be used with special devices that are external to the system of fuzzy inference. For one-dimensional membership functions used standard method of center of gravity. For the multivariate case using the generalized method of center of gravity:
where yzn*
–
defuzzification result;
Vz – the volume of
the figure formed by the membership function µlk
*(ÿz).
Fuzzy inference based on neural network
Very often it is assumed
that the input variables are independent from each other. [5].
This causes separation of the classes illustrated in figure 3.2.

Picture
3.2 – The classic
division of the input space into regions
White field means belonging
to a given class, a gray box – a partial belonging to each of the
neighboring classes (or lack of membership in the class).
In this approach, each input variable has its own entrance set. They are contained in the rules in the form:
R1 :
IF (X1
this negative AND X2
this is more),
R2 :
IF (X1
this negative AND X2
this is a small),
R1 : IF (X1
< X2),
R2 : IF (X1 ≈
X2),
for which the classical
approach is not the most appropriate.

Picture 3.3
– The proposed division of the input space into classes
A solution would be to propose the replacement of all the input variables and one vector to introduce the membership function of several variables. In this case, a description of the rules will have the form [6]:
where X=[X1,…,Xn]T, а Ak – is a fuzzy set
with a multi-dimensional membership function.
The second element of the architecture – the component responsible conclusion of the rule [7]. Use the solution proposed by Takagi and Sugeno, which is described in detail in Section 1.3. The output of the system output is a function of the input variables, ie,
where f(k)(X) – it is a function contained in the k-th rule, and Y – the numerical value of the manipulated variable. When you combine the two elements formed the base of the rules in the form below (marked R(k) refers to the Regulation):
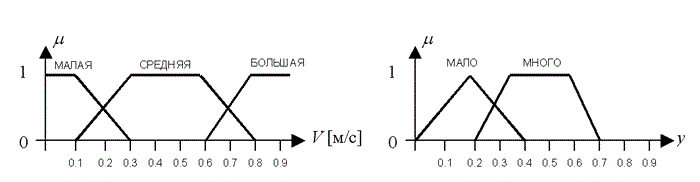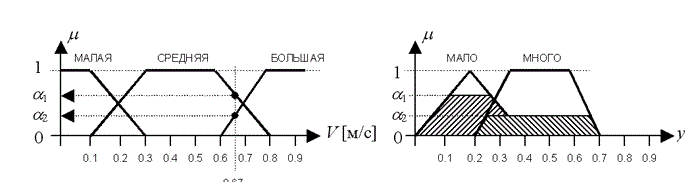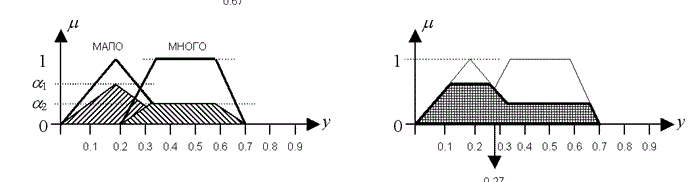
Picture 3.5 – The process of all stages
4 The study of information technology implementation of fuzzy control
Fuzzy Modeling with MATLAB
For further development and
application of fuzzy inference systems in interactive mode can be used
in the following graphical tools that are part of the package Fuzzy
Logic Toolbox.
1.
Editor
fuzzy
inference
systems FIS (FIS Edition) or abbreviated pedaktor FIS shown in Figure
4.1. Editor fuzzy inference systems FIS is the primary tool used to
create and edit fuzzy inference systems in graphical mode. If the fuzzy
function is called with no arguments, the editor of the FIS called for
the newly created system of fuzzy inference with the name Untitled by
default. In this case, the default is also set a number of parameters
such as the type of fuzzy inference system (Mamdani), fuzzy logic,
methods of implication, aggregation and defuzzification, and others.
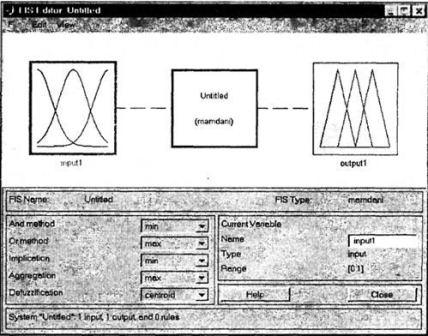
Picture
4.1 – The
GUI editor FIS
2. Editor of membership
functions of fuzzy inference system (Membership Function Editor) or
abbreviated editor of membership functions shown in Figure 4.2. The
editor of the membership function is used to set and edit the
individual terms of membership functions of fuzzy inference in
graphical mode [8].
To display graphs of
membership functions, select the desired variable in the left side of
the GUI editor titled FIS Variables.

Picture
4.2 – The
editor of the membership function, the function mfedit
3. Editor of fuzzy inference
rules (Rule Editor) or abbreviated rule editor shown in Figure 4.3.
Editor fuzzy inference rules
of the system, as its name implies, is designed to set and edit the
individual rules of fuzzy inference in graphical mode.

Picture
4.3 – Rule
Editor, the caller ruleedit
Rule Editor has a main menu
that allows the user to call other graphic tools to work with fuzzy
inference system FIS, download and save the structure of FIS in
external files, etc.
4. Viewer fuzzy inference
system rules (Rule Viewer) or abbreviated viewer inference rules in
Figure 4.4;
The main purpose of the
rules of the viewer is the ability to visualize the results of fuzzy
inference and receive output values depending on the initial values
of the input variables [9].
Viewer allows you to edit
the rules are not the rules and membership functions of terms and
variables used after the development of fuzzy inference system at the
stage of analysis and evaluation. The function is also suitable for use
in the case when it is necessary to visualize the entire fuzzy
inference process from beginning to end. The user also has the power to
evaluate impact values of the output variables of fuzzy model and the
impact of each of the rules on the result of fuzzy inference by
changing the values of the input variables;

Picture
4.4 –
Viewer rules by calling ruleview
5. Viewer surface
fuzzy inference system (Surfase Viewer) or abbreviated viewer output
surface in the picture 4.5.
Viewer surface fuzzy
inference system allows you to view the system with fuzzy inference,
and visualize graphs of the output variables of the individual input
variables.
Viewer output surface does
not allow changes in the fuzzy inference system and the corresponding
structure of the FIS. Using the main menu, the user can select the
input variables and the corresponding horizontal axis of the coordinate
system (X and Y), and an output variable which corresponds to the
vertical axis of the coordinate system (Z).
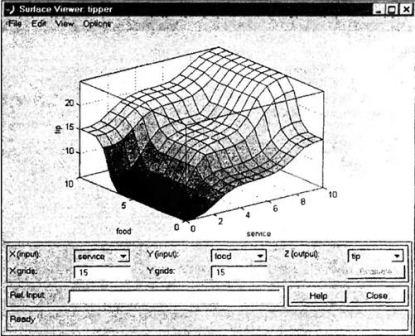
Picture 4.5 – Viewer output surface, the function surfview
In addition to these
graphical tools in the package Fuzzy Logic Toolbox also includes the
following special programs [10]:
1. Editor adaptive
neuro-fuzzy inference (Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Editor) or
abbreviated editor or editor of hybrid networks ANFIS in the picture
4.6.
Further setting options to
build and train a hybrid network can be performed using the previously
considered standard graphics tools in the Fuzzy Logic Toolbox. It is
recommended to save your fuzzy inference system in an external file
with the fis, then you should download this file in the editor of fuzzy
inference FIS.Дальнейшая настройка
параметров построенной и
обученной гибридной сети может быть выполнена с помощью рассмотренных
ранее
стандартных графических средств пакета Fuzzy Logic Toolbox.
Для
этого
рекомендуется сохранить созданную систему нечеткого вывода во внешнем
файле с
расширением fis, после чего следует загрузить этот файл в
редактор
систем
нечеткого вывода FIS.

Picture
4.6 – The
GUI editor for FIS generated fuzzy inference system
2. The program is fuzzy
clustering method of fuzzy average (fuzzy with-means clustering) in
Figure 4.7.
Thus, the system allows
MATLAB to solve the problem of fuzzy clustering in two ways: by using
the command-line functions and using the graphical interface of
clustering. The first of them is more time consuming, but has more
flexibility and the ability to display in the command window of the
matrices centers of fuzzy clustering, the membership functions and the
objective function. The second method is the most convenient to perform
a series of calculations for various values of the input parameters
to a visual analysis of the results obtained.

Fuzzy modeling in the environment fuzzyTECH
The program fuzzyTECH,
developed and continuously updated by INFORM GmbH (Inform Software
Corporation, Germany), is designed to solve different problems of fuzzy
modeling. In contrast to MATLAB, the program fuzzyTECH is a specialized
tool that allows you to develop and explore a variety of fuzzy models
in graphical mode, and convert them into code for a programming
language with the possibility of implementing a programmable
microcontrollers.
FuzzyTECH program has the
ability to use it as a server or a client in a fuzzy control remote
objects. An interesting feature of the program fuzzyTECH, which should
also be sure to point out is the ability to automatically generate
documentation for fuzzy models in the form of text with illustrations
in the format of RTF.
Although the program and the
system fuzzyTECH MATLAB using common principles of fuzzy modeling,
there are some fundamental differences in the implementation of fuzzy
inference systems in the FLS program fuzzyTECH of FIS systems
previously considered in the package Fuzzy Logic Toolbox. The main ones
are set out below [11].
1. The system design of a
fuzzy inference in fuzzyTECH may have multiple blocks rule (Rule
Blocks) fuzzy productions, each of which may have its own input and
output linguistic variables. The individual units of the rules can be
connected in series or in parallel fashion as shown in Figure 4.8.
2. In addition to
the input (Inputs) and output (Outputs) projects fuzzyTECH linguistic
variables can have so-called intermediate (Intermediates) linguistic
variables. These variables appear in cases when the blocks are
connected in series rules, ie the output of one block of rules
connected with the input of another unit of the rules as shown in
Figure 4.8.

Picture
4.8 – The
editor of the draft program fuzzyTECH
3. All operations on the
development, editing, debugging, and analysis of projects in the
program fuzzyTECH performed in graphical interactive mode, and for
prototyping projects and specifications of their individual components
can be used in various wizards (Wizards).
4. Based on the developed
and debugged the project fuzzyTECH program can be generated code of the
fuzzy inference system in one of the programming languages (C, Java,
MS Visual C + +, MS Visual Basic, MS VBA, COBOL, Assembler, tongue
m-file of MATLAB ). Subsequently obtained similarly Listings code can
be compiled to a particular computer platform used, and regardless of
the program to be implemented fuzzyTECH fuzzy microcontroller.
5. The use of technology in
the program fuzzyTECH Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE) allows sharing of
developed fuzzy models with other programs and tools, such as MS
Access, MS Excel, MATLAB. The program fuzzyTECH can act both as a
server and as a client, which greatly expands the range of possible
applications of the developed fuzzy models. In the latter case, fuzzy
control remote objects need to use a particular communication protocol
(TCP / IP, IPX / SPX) and additional interfaces (serial interface
RS232, SDI 5, SFS, FTOCC).
6. All projects in the
environment fuzzyTECH stored in separate project files format FTL
(Fuzzy Technology Language), which have the extension ftl. They are
plain text files that can be viewed and edited by any ASSII-editor (eg,
MS Notebook). FTL format was specifically designed by Intel Corp. and
Inform Software Corp. at 1991 r. for presentation systems nechetkoro
output in the form of structured text. This format is supported by all
leading developers of software and hardware solutions based on the use
of fuzzy logic systems, allowing them to carry out the transfer on
different platforms..
7. In format FTL files may
be presented projects format FTR (fuzzyTECH Runtime), respectively,
with the expansion ftr. File format FTR, unlike format FTL, projects
are in binary form. In this form of representation depends on the
version of fuzzyTECH. FTR file format contains all the information
about the project and can be used to convert to the appropriate project
file format FTL.
8. In the fuzzy
fuzzyTECH projects can use different types and forms of membership
functions of terms of linguistic variables. Regarding the types of
membership functions, the user can select one of the options listed
below:
– A standard
version of the membership function (Standard MBFs), which is sometimes
called the "4-point" option, as it is based on the use of four
characteristic points or parameters to set the appropriate membership
functions;
– Random variation
of the membership function (Arbitrary MBFs), in which you can use up to
16 characteristic points or parameters to set or approximating the
appropriate membership functions;
– Inverted version
of the membership function (Inverse MBFs), which may be useful in
determining the rules of fuzzy productions with the negation of the
existing project in terms of the (inverse terms) for individual
linguistic variables;
9. Each type of membership
function can have one of the forms when administered as follows::
– Linear
(L-shape), which involves the representation of the membership function
in the form of triangular, trapezoidal function, or some combination of
them;
– S-shaped
(S-shape), which involves the representation of the membership function
in the form of a S-shaped, Z-shaped or U-shaped curve.й.
10. The program may be
fuzzyTECH various methods fuzzification of input variables. The user
can select one of the following options fuzzification
– A standard
method of fuzzification (Compute MBF) involves the use of a standard
type of membership functions of triangular, trapezoidal, and
piecewise-linear curves;;
– Fuzzy input
(Fuzzy Input) indicates that all the terms of the respective linguistic
variables are presented in the form of a vector of values of the
membership function. This is more efficient in the implementation of
fuzzy inference on a particular hardware platform;
– Fuzzy input in
the form of a table (Look-up-MBF) indicates that the corresponding
fuzzy linguistic variable values are calculated using an algorithm
and are presented in tabular form. This embodiment can be used to
increase speed in some types of computing microcontrollers and
microprocessors fuzzy;
– Quick
fuzzification method (Fast Computation of MBF) is a variation of the
standard method applied to certain specific types of microcontrollers.
This embodiment has the highest efficiency when using specific hardware
platform.
– Regular input
(Categorical) indicates that all the terms of the respective linguistic
variable represented in the form of a conventional vector of values.
11. In the fuzzy fuzzyTECH
projects can also be used a variety of methods of aggregation,
composition, accumulation and defuzzification of the results of fuzzy
inference;
12. The conclusions of the
rules for the composition of fuzzy productions, you can use one of the
following tasks weighting rules::
– Standard
(Standard), where the value of the weighting factor for each rule is
assumed constant and equal to 1;
– User-defined
(Fuzzy Associative Maps or abbreviated FAM), in which the weight value
for DoS kazhdoro rules can vary within the interval [O, 1].
13. For the accumulation of
findings of fuzzy rules of productions, you can use one of the
following methods:
– Common (max) at
which the fuzzy inference result in a block of fuzzy rules of
productions is defined as the union of fuzzy sets;
– Limiting the
amount (bsum), in which the fuzzy inference result in a block of fuzzy
rules of productions is defined as the union of fuzzy sets.
14. In projects fuzzyTECH
may use different methods of defuzzification output variables. In this
case, user can select one of the following methods of defuzzification:
– A standard
method (Center-of-Maximum or abbreviated CoM), which, according to
developers, is by the best compromise to get the final output values.
The program fuzzyTECH CoM defuzzification method works similarly to the
method of center of gravity of CoO;
– The method of
the center area (Senter-° F-Area or abbreviated CoA);
– The method of
the average maximum (Mean-of-Maximum or abbreviated IOM), which,
according to developers, is the most flexible method and is defined as
the arithmetic average between the left and right modal values at the
same time as the fashion of a fuzzy set is considered the maximum value
of its membership function;
– Method
hypercentre maximum (Nurer Center-of-Maximum or abbreviated HyperCoM),
which can only be used in other program modules fuzzyTECH. This method
takes into account the positive and negative fuzzy conclusions and in
accordance with this forms a optimum value for the output variables.

Picture 4.9 –
Graphical Viewer three-dimensional surface of fuzzy inference
Conclusion
The main result of the
present work is that considered fuzzy control algorithms, as well as
options for programming environments for implementing the algorithm in
the system.
One of the main reasons for
the use of fuzzy logic for the evaluation mechanism is the ability to
set the desired depending on the language close to natural. The most
suitable framework for this knowledge are used in the methods of
Mamdani, Larsen, and the new algorithm, which is described in Section
2.1. The algorithm of fuzzy inference system provides the flexibility
to decide by adjusting the evaluation criteria and rules of inference.
In this study were
investigated different development environments. MatLAB has more
features than MathCAD, Maple and Mathematica, as this package is so
versatile that it can solve almost the entire range of tasks. MathCAD,
Maple and Mathematica is more aimed at solving the various equations
with clear input data, and more easier to write code.
On the basis of the
described environments fuzzy control algorithm implementation, it was
concluded that MathLab – an environment with the best possible
implementation of the algorithm with results displayed in the form of
multi-dimensional graphs, as well as a more intuitive graphical
interface.
Thus, the implementation of PP, which provides solutions to the problems of fuzzy input data is an important task. The analysis and the very formulation of the problem show that the new algorithm and the PP will provide adequate and effective output tasks users.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: January 2014. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
1.
Заде
Л. Понятие
лингвистической
переменной и его применение к принятию приближенных решений.
– М.: Мир,
1976. –[djvu]
2. Заде
Л.А. Тени
нечетких множеств –
[pdf]
3. Губко
М.В. Лекции
по
принятию решений
в
условиях нечеткой информации –
[pdf]
4. Круглов
В.В., Дли М.И. Интеллектуальные
информационные
системы: компьютерная поддержка систем нечеткой логики и нечеткого
вывода. –
М.: Физматлит, 2002.
5. Леоненков
А.В. Нечеткое
моделирование в среде MATLAB и
fuzzyTECH. – СПб., 2003.
6. Рутковская
Д., Пилиньский М., Рутковский Л. Нейронные
сети, генетические алгоритмы и нечеткие системы.
– М., 2004.
7. Масалович
А. Нечеткая логика в бизнесе и финансах. www.tora-centre.ru/library/fuzzy/fuzzy–.htm
8. Kosko
B. Fuzzy systems as universal approximators //
IEEE Transactions on
Computers, vol. 43, No.
11,
November 1994. – P. 1329–1333.
9. Cordon
O., Herrera F., A General study on genetic
fuzzy systems // Genetic
Algorithms in
engineering and
computer science, 1995. – P. 33–57.
10. Тарасевич, Ю.Ю. Математическое и компьютерное моделирование / Тарасевич, Ю.Ю. – М.: Едиториал УРСС, 2004. – 152 с.
11. Рутковская Д., Пилиньский М., Рутковский Л. Нейронные сети, генетические алгоритмы и нечеткие системы: Пер. с польск. И. Д. Рудинского. –М.: Горячая линия –Телеком, 2006. –452 c.


