Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Analysis studies and publications
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. The main part
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Background. In modernconditions major source of economic development and a means of increase competitiveness of enterprises is a successful innovation. At the same time, Ukraine is engaged in innovative activities only 17.4 % enterprises, the share of sales of innovative products in the amount of industry is 3.3 %, the proportion of completed research and scientific and technical work in the GDP of 0.8 %. To a large extent this state innovation processes associated with a high degree of risk. Therefore, the such circumstances, particular importance will be the management of risks.
1. Analysis studies and publications
It should be noted that the problem Risk management in innovation paid much attention in the works of both foreign and domestic scholars, namely K. Baldin, S. Vasin, V. Vasilenko, E. Volkova, M. Grachova, M. Denisenko, S. Iliashenko, R. Fatkhutdinova, V. Khobta, V. Shmatko and others. At the same time require clarification questions information management, accounting, risk assessment and adaptation to modern business environments.
Based on all above, the relevance is further research on Risk management in innovation. The relevance of these issues and the need to solve them led to theme of master's work, its goals and objectives.
- Analyze innovation activities in Ukraine.
- Explore management system risks of innovation.
- Select and justify stages of risk management.
- Develop a comprehensive system of risk-management of innovation.
- Provide a description of management, analysis and evaluation of risks.
- Develop methodological Recommendations on integrated management of innovation risk.
- Develop a set of measures to improve the forecasting process innovation activities in the risk management system.
- Further development of methods subtracting the amount of risk when evaluating the effectiveness of innovative projects.
- insufficient quality of the business environment, conservation underdeveloped conditions for fair competition in the marketplace, as well as receiving state support;
- preservation of significant barriers to the spread of economics of new technologies due to lack of state Technology Policy and inefficient industry regulation, including certification procedures, customs and tax administration;
- insufficient efforts of regional and local authorities to improving the conditions for innovation;
- interaction between business and the state in shaping and implementing innovation policy does not have a regular basis, not provides a balanced expression of the interests of various innovation active enterprises, especially in new sectors that formed;
- lack of effectiveness of instruments of state support Innovation: limited flexibility, poor distribution mechanisms risks between the state and business, lack of focus on stimulating relationships between the various actors in innovation processes formation and development of scientific production and technological partnerships.
- situational approach;
- process approach;
- integrated approach.
- Set of interrelated formal processes that provide analysis, planning, implementation, operation, monitoring and audit adjustments and improve mechanisms for management of innovation risk.
- Standards and Technology Risk management is presented in the form of regulatory and labor SUIR documentation, which includes risk management policies and risk assessment methodology.
- The organizational structure innovative risk management and properly prepared staff.
- Федулова Л. Концептуальна модель інноваційної стратегії України / Л. Федулова // Економіка і прогнозування. – 2012. – № 1. – c. 87–100.
- Ключник А. В. Організаційно-економічне забезпечення залучення іноземних інвестицій в аграрний сектор економіки Миколаївської області / А. В. Ключник, М. Д. Бабенко // Вісник аграрної науки Причорноморя. – 2008. – вип. 1. – c. 31–37.
- Державний комітет статистики України [Електронний ресурс] Режим доступу: http://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/.
- Стратегія інноваційного розвитку України на 2010–2020 роки в умовах глобалізаційних викликів [Електронний ресурс] Режим доступу: http://kno.rada.gov.ua/komosviti/control/uk/doccatalog/list?currDir=48718.
- Инновационный менеджмент. Учебник / Под ред. С. Д. Ильенковой, – М.: Юнити, 1997 г.
- . Економіка АПК, 2009, № 5 Система управління ризиками інноваційної діяльності – В. І. Покотилова, кандидат економічних наук, доцент Херсонський економічно—правовий інститут.
- Кобиляцький Л. С. Управління проектами: навч. посібник. – К.: МАУП, 2002. – 200 с.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim is to further development of theoretical frameworks, methodological approaches and the development of practical recommendations on risk management in innovation.
For the purpose of the study, need to solve the following problem:
Object of study – risk management in innovation.
The study examined are theoretical approaches, methodological and practical management tools risk in innovation.
Research Methods. The theoretical basis of the work is fundamental assumptions of economic theory ryzykolohiyi and scientific works of domestic and foreign scientists.
The study used methods of analysis and synthesis in order to clarify the nature risks in innovation, methods of system approach (with justification of the risk management process content, methods economic and mathematical modeling, the dialectical method and the methods abstraction and comparisons.
As sources informatsiyidani State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. Used legislative acts of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, Decrees President of Ukraine, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, official predictability.
The practical significance of results. Results in the solution of the tasks are a methodological basis for improving the process of risk management innovation. This study allows subjects entities involved in the development and implementation of innovations more effectively manage risk in this area, thereby increasing effectiveness of innovation.
The main part
Innovation activities in Ukraine by most researchers defined as a crisis and not corresponds to the current level of innovation processes in industrialized countries and the needs of innovation. Stable reduction in real funding of scientific and technical complex and the absence of effective state scientific and technical policy does not allow grounds for a finding of a real foundation for the transition to innovative model of development. Reform of Scientific and Technical Complex built on the principles of frequent changes in goals and objectives, without known factors functioning and development of scientific and technical capacity: active and predictable state support, the formation of demand for scientific achievements from the real economy, and more.
In recent years, there was no measures implemented within the framework of innovation policy to improve business environment, encouraging companies to innovate, develop different tool support technological upgrading, but the presence of some improvements remains fragmented and general instability progress in this area. Key issues in the formation and implementation of state innovation policy in Ukraine include the following [1]:
Ukraine has a large scientific potential, there are many discoveries and inventions accumulated many innovative projects in the resource, in biotechnology, laser technology and more. It is necessary to determine the most breakthrough areas in which, according to the critical point of phase transition can be add a minimum investment in the form of resources and will move in new quality – of innovative profitable business that will generate infrastructure to other industries [2].
The analysis showed that innovation processes in the country have become significant proportions condition innovative activity does not correspond to the current level and needs innovation development in the industrial-countries. Therefore, the urgency is the acceleration of innovation processes, the main constraint which is the risk. This necessitates the further study of the material on risk management innovation activity and formation of risk management.
In theory and practice management entails the following basic approaches to management:
These management approaches used in the construction and management of risks in plants (Figure 1).
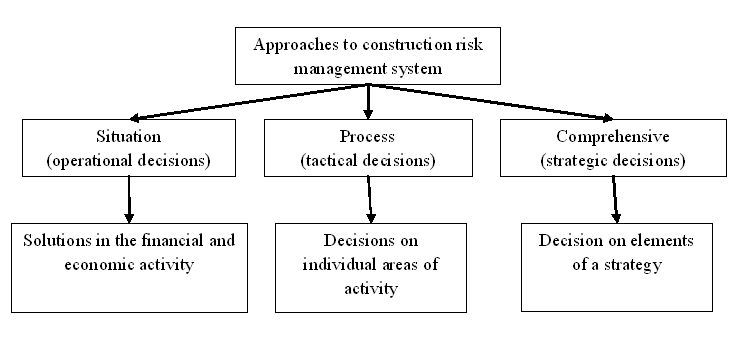
Figure 1 – Approaches to building a risk management system
Management System innovative risk – the foundation on which a risk management organization. This is the most important and the most difficult for the implementation of all subsystems. Processes Risk management is proposed to implement this.
In Fig. 2 shows a series of risk management processes and shows the relationships within this risk. The risk management process includes innovative activity definition of context, risk assessment, risk treatment, making risks, risk communication, as well as monitoring and review risks.
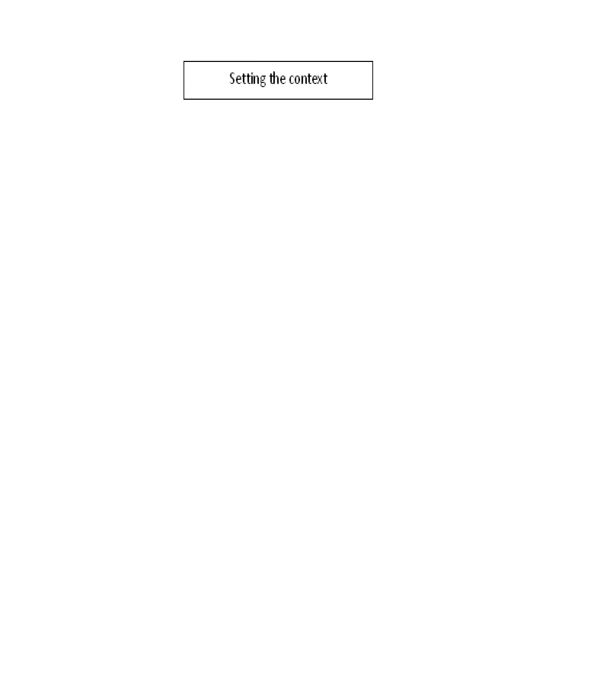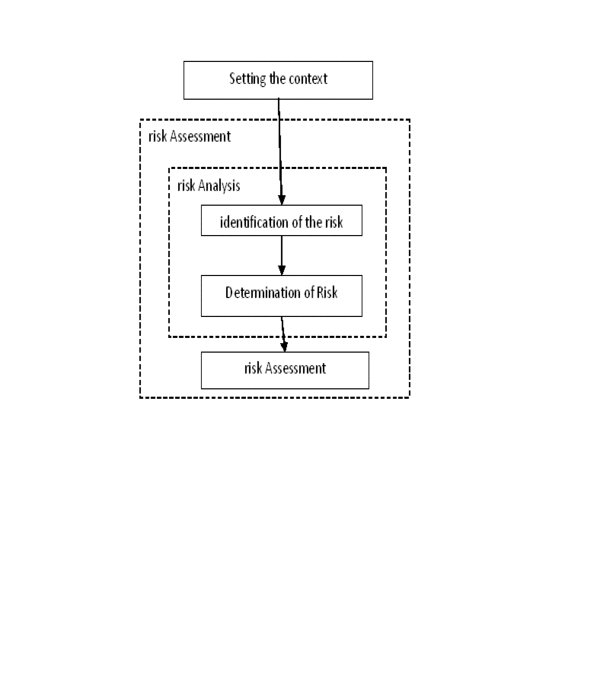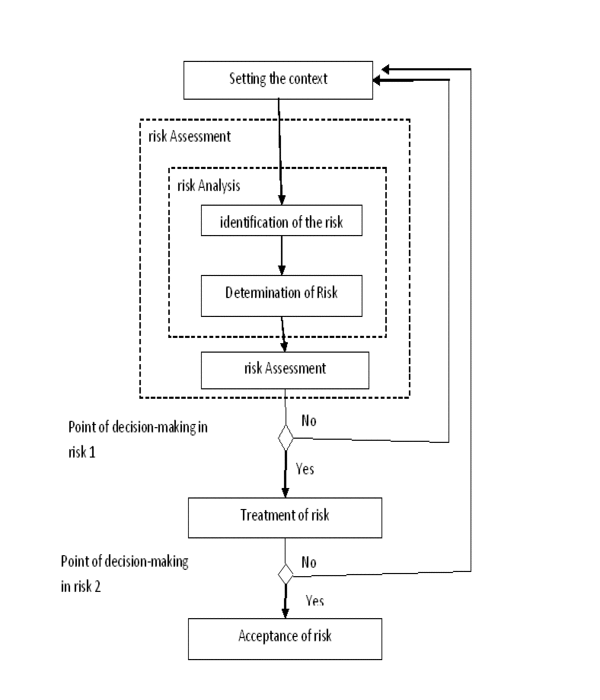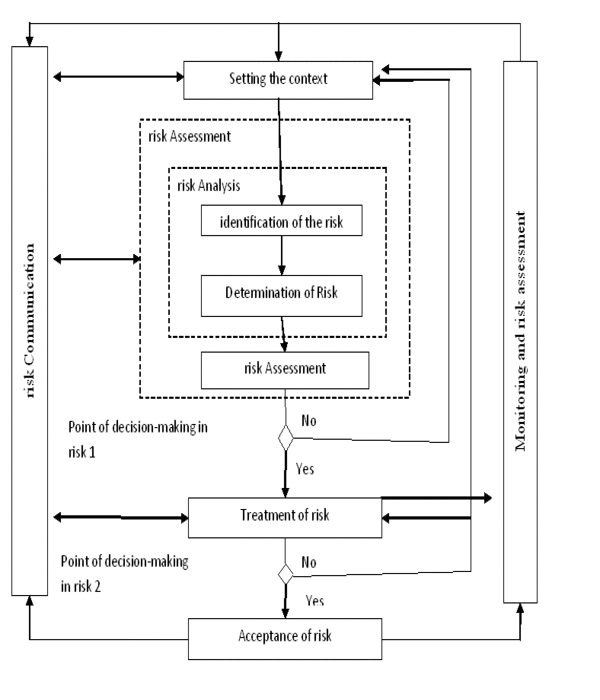
Figure
2 – Relationship processes risk Management
(animation: 8 frames, continuous cycle of repetition, 164 kilobytes)
As shown in Fig. 2 this process can be worn to the cyclical nature of assessment activities and/or handling risks. Cyclical approach to risk assessment lets make it more deep and detailed in each subsequent iteration. In this case, should be provided a balance between minimizing time and effort expended in determining the mechanisms of control and ensuring proper assessment of high risk.
Originally defined context. Then, the risk evaluation. If the result obtained sufficient information to determine effective measures to be take to reduce the risks to an acceptable level, the task done and can move on to handling risks. If the information enough, by another cycle of risk assessment in the revised context, perhaps for some parts of the field evaluation (see Fig.2 – "Point of Decision Risk 1").
The effectiveness of treatment risks depends on the results of their evaluation. If the treatment of risks not lead to an acceptable level of residual risk may need duty cycle risk assessment can then be made optional handling risks (see Fig.2 – "Point of Decision Risk 2 ") [7].
The following describes governance cycle moves to a new level, again passing the planning stage implementation, monitoring and improvement. Process operation, development and improvement SUIR implemented in a spiral. Eventually all Four groups of processes run in parallel and continuously. Original some processes incoming data to the input of other [5].
Conclusions
Innovative developments in the economy not yet significant scale, the number of companies implementing innovation, decreases with each passing year and now stands at 17.4 %, which is less 3 – 4 times than the innovative developed economies. Knowledge-based industrial production is at 0.3 %, which is much less the world level. Almost a third of the funds spent on innovation, accounts for the purchase of equipment while on the acquisition of rights to new intellectual property. About half of innovative enterprises generally do not fund holding interests of its production research [3].
This situation is caused by the lack of funds and lack in recent years of an effective public of fostering innovation, the beginnings of which were gradually eliminated during the last 5 years the amendments appropriate fiscal and other laws. Moving stairs Ukraine innovative development will require enormous effort, resources, political will and mobilization of high public [4].
Management System innovative risk is the foundation on which to build organization and represents:
In writing this essay Master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: January 2015 year. Full text of the materials can be obtained from author or his manager after that date.
