Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. The effect of the rolling of a slab on the press on their form
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In world practice, a pressing problem in the production of broadband steel is the reduction of metal waste, not only by building new mills, but also by modernizing existing units and improving rolling technology. The use of continuously cast slabs on broadband mills results in a low metal consumption ratio. The work of the continuous casting machine depends on the number of slab sizes, so the need for reducing slabs has arisen.
The unification of the width of the slabs requires the use of high reductions in width when reducing them in vertical rolls. This leads to the fact that a large part of the displaced metal, on the main part of the length of the slab goes into the influx of the side edge of the roll. Also formed are the concavity of the ends and the weighting of the width at the ends of the rolls, or "fish tails", which go into cutting, reaching 2-5%, depending on the length of the slab.
Today, the technology of reducing slabs in a special reducing universal stand of wide-strip mills has been widely used. This technology allows to obtain strips with a width of 200-250 mm less than the width of the original slab.
A wide range of slab widths are obtained by rolling them on slabs or by casting steel on a large number of continuous casting machines.
In order to reduce metal waste together with the end trimming and the approximation of the shape of the slabs to the rectangular plan, various technological solutions are used, such as: reducing the slabs in the vertical rolls of the reducing universal roughing stand, forming the ends, side edges and slab cross-section, reducing the slab using horizontal press.
In this regard, the study of the process of reducing slabs in a stream of a wide cavity mill is relevant.
1. The effect of the rolling of a slab on the press on their form
A pressing problem in world practice in the production of broadband steel is the reduction of metal waste. The use of continuously cast slabs on broadband mills results in low metal consumption. The work of the continuous casting machine itself depends directly on the number of slab sizes, which in turn makes it necessary to reduce the slabs.
There are several ways to implement the reduction process: the first method is to use an aggregate that stands alone and consists of horizontal and vertical rolls, and the second is in the roughing line of a wide-strip hot rolling mill (SHSGP). The technology of slab reduction in the roughing line of SHSGP using powerful universal reversing stands became more widespread [1].
The process of reduction can be implemented as a classical method or as part of the combined process of reduction - rolling. The classical method is characterized by two types of operations: transverse compression in vertical rolls (BB) and ironing in horizontal rolls (GW) of slabs. The latter is designed to eliminate local inrushs near the edges, which in turn are formed after rolling in vertical rolls. The process of stroking is characterized by a large uneven compression width.
The sagging during ironing goes into broadening and partially into the hood. The reduction is carried out only in the first universal stands of the draft group, since at large ratios of the width of the roll to its thickness, which occurs when rolling in the rough group of continuous sheet mills, the reduction in the vertical rolls to 2 - 3% has little effect on reducing the width.
After reducing the slab in the system, the vertical rolls (BB) - horizontal rolls (T), the shape of the front (PK) and rear (Z.K) ends is characterized by a narrowing width, length of the stretched section and concavity of the ends (fig. 1).
There are various measures to reduce the loss of metal with end-cutting, the most common of which is the formation of the ends, side edges and the slab cross-section.
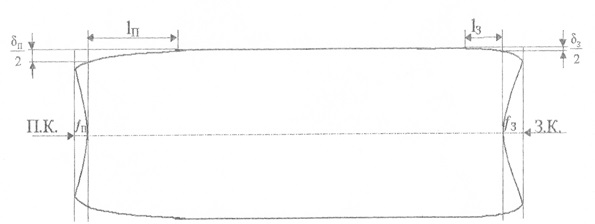
Figure 1 - The form of roll in the plan after the reduction of the slab in BB-GV
In [1], a method is presented that reduces the distortion of the shape of the ends of a slab during reduction in vertical rolls (width reduction), which consists in preliminary lateral reduction of the slab in the strikers of a horizontal press. In this paper, there is no information on the modes of compression of the ends of slabs and their influence on the shape and size of the ends.
In this regard, we carried out a study of the parameters for forming rolls in terms of the physical modeling of the conditions of compression of the end sections of the slab in flat strikes. The studies were carried out on a laboratory hydraulic press of DonNTU and on a proglazhivaya stand with rollers with a diameter of 50 mm. Lead was chosen as a modeling material. Modeling scale 1:30. Simulated the process of reducing slabs with dimensions: thickness 240 mm, width - 1200 mm, 1650 mm and 2100 mm. The length was taken equal to 1.5-2 width. According to the scale of modeling, three batches of lead samples are produced. The thickness of the samples is 8 mm, width 40, 55, 70 mm.
For crimping the ends on a laboratory hydraulic press, flat strikers with an edge bevel (chamfer) at an angle of 30 degrees were used. The length of the crimped ends was taken equal to half the width of the samples. Samples of each width were compressed on the press at 1.5, 3, 4.5 mm. As factors that influence the parameters of the form, adopted: the cross-section factor; relative compression across the front end; relative reduction across the width of the rear end; absolute compression.
After crimping on a hydraulic press, proglazhivaniya performed in the GW and measured the arrows of concavity of the front and rear ends of the rolls (fig. 2).
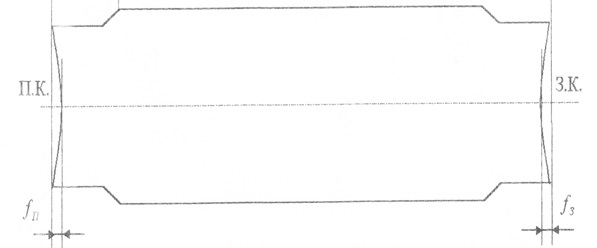
Figure 2 - Parameters of the shape of the ends of the samples in the plan after compression on a horizontal press and ironing in the cage with horizontal rollers
According to the results of measurements of the parameters of the ends of rolls, graphs were built (fig. 3).
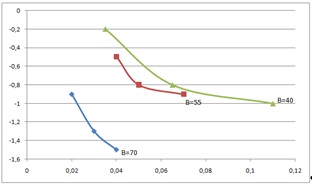
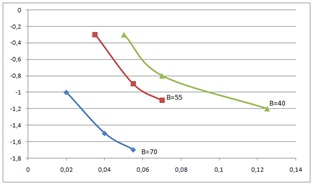
Figure 3 - The influence of factors on the parameters of the shape of the ends
Conclusion
It follows from Figures 1 and 2 and the graphs that the proposed method for improving the shape of the ends of a slab when reducing in the BB-GV system using pre-crimping of the ends on the press has a significant effect on the shape parameters of the plan. Utyazhka width is eliminated, arrows of concavity are reduced.
