Abstract on the topic of graduation work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Essence and content of financial instruments as an object of accounting
- 2. Classification of financial instruments
- 3. State of the problem and regulation of financial instruments
- 4. Primary accounting for financial instruments
- 5. Analytical accounting of financial instruments
- 6. Audit of financial instruments
- Conclusion
- List of sources
INTRODUCTION
The development of an efficient financial market is one of the priorities of the state at the present stage. The factor that determines the attractiveness of the market for investors and the effectiveness of its functioning is the availability of instruments on it that meet the interests of participants and allow them to effectively perform their functions [1]. Providing the financial market with the most reliable information on the financial statements of organizations, on the use of new and more effective tools for managing interest rate, currency and price risks, derivative financial instruments can reduce the likelihood of financial crises.
Object of study
- accounting processes in the conditions of Sunflower Group LLC.
Subject of research– theoretical and organizational-practical aspects of accounting and audit of financial instruments.
The purpose of the workis to identify shortcomings and problematic aspects of accounting for financial instruments in the conditions of Sunflower Group LLC, their impact on the company's activities and develop specific recommendations for their elimination.
To achieve the goal, the following tasks
have been set and solved:
- to consider the essence and content of financial instruments as an object of accounting; classification of financial instruments; the state of the problem and the legal regulation of financial instruments, as well as the tasks of improving their accounting and the formation of an accounting policy;
- disclose the structure of the accounting object in relation to financial instruments; primary, analytical and synthetic accounting of financial instruments;
- to reflect the practice of preparing financial statements for Sunflower Group LLC;
- disclose the audit of financial instruments;
- disclose the issues of labor protection, life safety and civil defense issues.
1. Essence and content of financial instruments as an object of accounting
Financial assets include:
- unrestricted cash and cash equivalents;
- receivables not held for resale;
- financial investments held to maturity;
- financial assets held for resale;
- other financial assets [8].
Financial liabilities include financial liabilities held for resale and other financial liabilities.
Equity instruments include common shares, shares and other types of equity.
Derivative financial instruments include futures contracts, forward contracts and other derivative financial instruments.
Recognition of financial instruments. A financial asset or financial liability is carried on the balance sheet if the entity is the party to the agreement for the financial instrument.
Unconditional claims and obligations are recognized as financial assets and financial liabilities if, under the terms of the contract, the entity is entitled to receive cash or assumes an obligation to pay cash.
Financial assets or financial liabilities arising from firm contracts for the purchase or sale of resources (works, services) are reflected in the balance sheet after the right to receive the asset or the obligation to transfer it arises.
2. Classification of financial instruments
Financial instruments are a variety of circulating financial documents that have a monetary value, with the help of which operations are carried out in the financial market. Instruments circulating on the financial market, servicing transactions in its various types and segments, are characterized at the present stage by a great variety. In this regard, classification is important, thanks to which it is possible to single out certain features characteristic of a particular class of financial instruments [2].
Main financial andThe stock market instruments can be presented in the form of a diagram, Fig. 1.1.
It is possible to single out two specific features that allow one or another procedure, operation to be qualified as related to a financial instrument: the basis of the operation should be financial assets and liabilities; the transaction must be in the form of a contract.
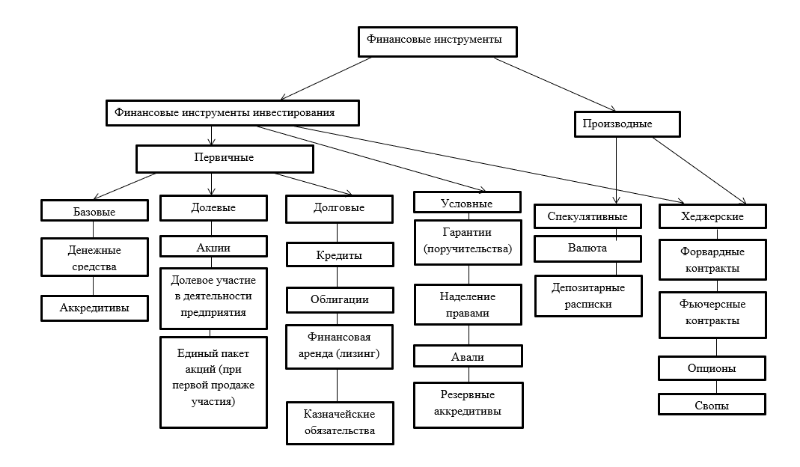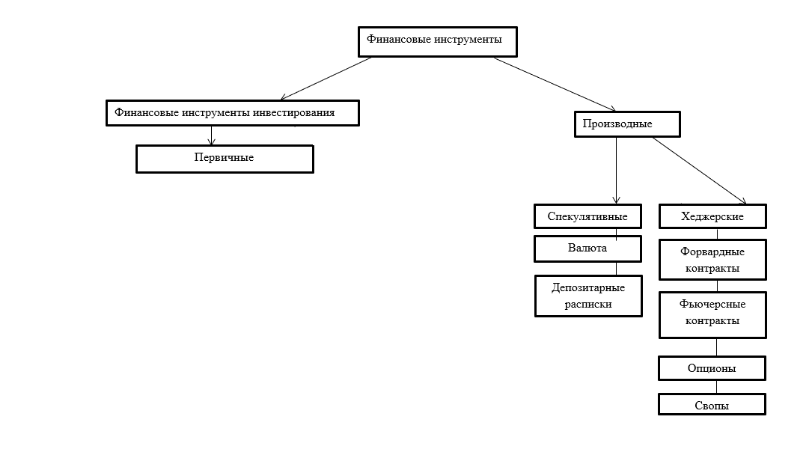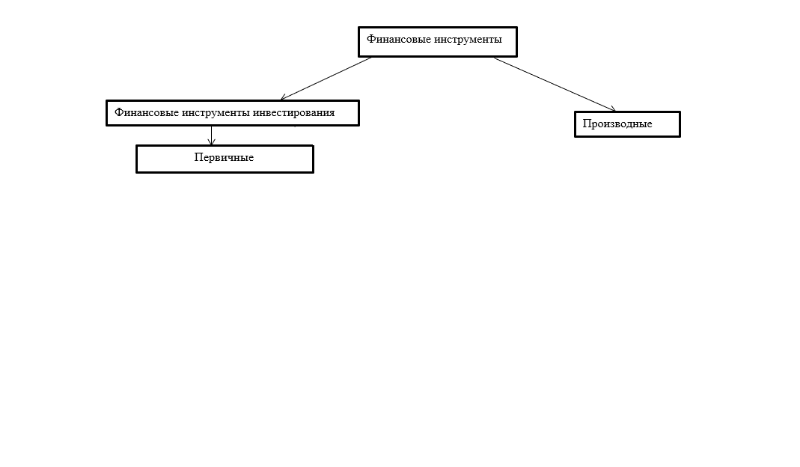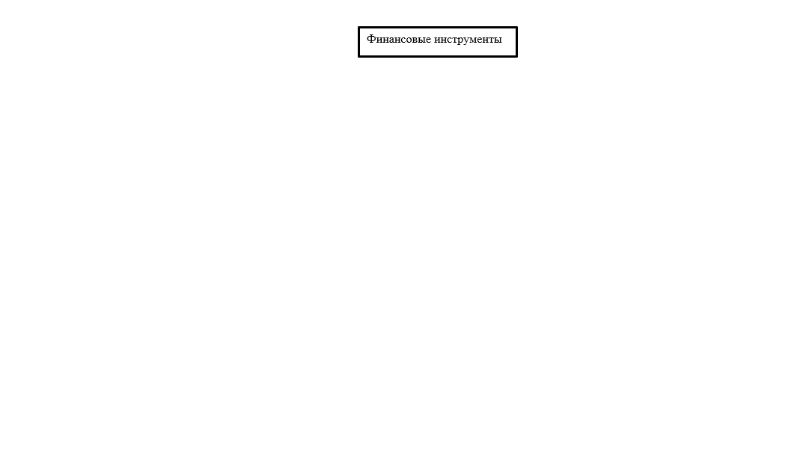
Figure 1 - The main financial instruments of the stock market
The most important characteristics of most financial instruments are return and risk. In this regard, it is advisable to talk about the classification of financial instruments according to the guaranteed level of return and the level of risk.
3. State of the problem and legal regulation of financial instruments
One of the most controversial issues in accounting is the valuation of financial instruments. The works of Yu.A. Astakhova, T.Yu. Druzhilovskaya, E.S. Druzhilovskaya, N.A. Dobrolyubova, S.A. Isakova, N.G. Sapozhnikova, Yu.A. Tarasova and others
P(S)BU 13 “Financial Instruments” states that a financial instrument is a contract that simultaneously predetermines the emergence (increase) of a financial asset for one enterprise and a financial liability or equity instrument for another [8]. A similar definition is provided by IAS 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation: a financial instrument is any contract that gives rise simultaneously to a financial liability or equity instrument on one side and a financial asset on the other [2].
In International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), several standards are devoted to these assets:
- IAS 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation of Information;
- IAS 39 Financial Instruments – Recognition and Measurement;
- IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures;
- IFRS 9 Financial Instruments.
A financial instrument in IAS 32 is any contract that simultaneously gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another. Thus, the definition of a financial instrument is based on two other concepts: financial assets and financial liabilities. They are also defined in IAS 32. These standards enable the development of accounting policies and procedures for accounting for financial instruments.
The study of the essence of financial instruments gave grounds to define them as financial documents, the movement of which leads to an increase in the volume of financial resources and a cumulative effect from their investment by producers and recipients of financial assets [4]. The classification of financial instruments has been supplemented in the context of financial liabilities with peer-to-peer lending.
4. Primary accounting of financial instruments
For accounting purposes, business transactions must be constantly documented (registered) either at the time of their completion or immediately after their completion. The primary accounting document must have:
- name;
- name, and in some cases addresses and current bank accounts of the parties (legal entities and individuals) participating in this business transaction;
- date of compilation;
- the content of the business transaction (documentation object) arising from the name of the document;
- meters of the ongoing business transaction. the absence of meters in the document deprives it of an accounting and calculation base;
- signatures of responsible persons.
Let's consider the list of primary documents used by the enterprise in Table. 1 in the context of business transactions.
Table 1 - Primary documents in the context of business transactions
| Type of operations | Primary documents |
|---|---|
| Cash transactions | Incoming cash order, outgoing cash order. |
| Current account operations | Payment order, payment request, bank statement. |
| Operations with receivables and payables | Invoice, act of work performed (services rendered), act of acceptance and transfer, accounting statement, accounting calculation, material report. |
| Operations with securities | Securities forms, act of acceptance and transfer, accounting statement, accounting calculation. |
| Rental operations | Acceptance certificate, valuation certificate, invoice, accounting statement, accounting calculation, material report, certificate of completion, payslip. |
Documents are filled out by accounting staff clearly, legibly using manual writing with ink or ballpoint pen paste, on a typewriter or using computer technology. As a rule, standard forms are used for documents.
Cash transactions in the territory of the Donetsk People's Republic are carried out in accordance with the Decree of the Board of the Central Republic of the DPR dated September 28, 2015 No. 18-3 "On the procedure for using currencies in the territory of the Donetsk People's Republic" [7].
Cash documents - documents (cash orders and statements for the payment of money, settlement documents, receipts for self-service software and hardware systems, information on balconies, other cash receipts and expenditure documents), with the help of which, in accordance with the legislation of the DPR, cash transactions and reports are processed on the use of funds, as well as the relevant journals of the established form for the registration of these documents and accounting books.
5. Analytical accounting of financial instruments
Analytical accounting allows you to detail and specify information on specific accounting objects with subsequent consolidation on synthetic accounts [5]. The procedure for the formation of analytical information is determined by the accounting policy of the enterprise and is fixed by the Order on accounting policy in the form of a working chart of accounts.
The development of analytical accounting in financial instruments is accompanied by problems - the lack of standardized analytical accounting registers, unreasonable recommendations contained in regulatory documents on the formation of analytical accounts of financial assets, financial liabilities, equity and derivative financial instruments.
In accordance with P(S)BU 13 “Financial Instruments”, cash and cash equivalents are classified as financial assets, with the exception of the mandatory balance on the current account, seized funds, letters of credit and other restrictions on the availability of funds; receivables arising in the course of normal operating activities; current financial investments held by the enterprise to maturity or presentation, financial assets held for resale, other financial assets [4].
To account for the availability and movement of cash on hand, the Chart of Accounts provides for an active account 30 "Cash" and which has the following sub-accounts: 301 "Cash in national currency"; 302 "Cash in foreign currency" [8].
6. Audit of financial instruments
Audit - verification of accounting data and indicators of financial statements of a business entity in order to express an independent opinion of the auditor on its reliability in all material aspects and compliance with the requirements of the laws of the DPR, accounting regulations (standards) or other rules (internal regulations of business entities) in accordance user requirements.
The audit process in the DPR is regulated by the Law of Ukraine “On the Audit of Financial Statements and Auditing Activities” [6].
The purpose of the audit is to confirm by an independent expert, who is the auditor, the reliability of the financial information of the enterprise, both in general and in relation to its individual aspects.
A statutory audit is an audit of the financial statements (consolidated financial statements) of entities that, in accordance with the law, are required to disclose or provide financial statements (consolidated financial statements) to users of financial statements along with an audit report conducted by the subjects of audit activities on the grounds and in the manner provided for by the Law of Ukraine "On the audit of financial statements and audit activities".
An initiative audit is carried out at the request of the owners (participants) and shareholders by an independent audit company checking both the state of accounting in general and its individual sections, the compliance of reporting with the actual state of affairs at the enterprise, the presence of declared assets and liabilities. Including review checks.
Audit of a special purpose - to confirm the accuracy of accounting and display in the reporting certain aspects of the enterprise's activities, for example, accounting for inventory items or settlements with debtors and creditors, the correctness of the calculation and payment of taxes - a tax audit.
Tax audit is a type of initiative audit, during which the correctness of the formation of the tax base for all taxes and fees, the timeliness of their transfer, the correctness of the preparation of tax returns, and other significant aspects of taxation are checked.
Fictitious bankruptcy audit during reorganization, liquidation, babankruptcy of enterprises - to confirm the true net worth of assets and liabilities of the enterprise.
Audit of the solvency and financial condition of partners and customers - for banks when issuing loans, for all enterprises that want to make sure of the "reliability" of their potential partner.
International audit - for foreign investors, to enter foreign financial markets.
An entity classifies financial instruments into four groups: cash and cash equivalents; loans; accounts receivable; securities. Consider an audit of these groups.
The purpose of the audit of funds is to establish the reliability of data regarding their availability and movement, the completeness and timeliness of the reflection of information in primary and summary documents and accounting registers, the correctness of accounting for funds and settlements in accordance with the accepted accounting policy, the reliability of displaying balances in the statements business entity.
The subject of a cash audit is business processes and operations related to the movement of cash and other funds, as well as the relationships that arise in this case at the enterprise and beyond.
The objects of the audit of funds can be elements of the accounting policy:
- P(S)BU, which guides the company when keeping records of cash
- nomenclature of working accounting accounts, as well as the structure of analytical accounts for accounting for funds;
- distribution of job responsibilities among employees and a workflow schedule, a schedule for submitting cashier reports;
- the procedure for the delivery of proceeds by the cashiers of the enterprise;
- forms of forms of documents, registers of accounting and reporting;
- the procedure for concluding an agreement on full liability;
- determination of the limit of the central (main) cash desk and operating cash desks in the context of individual divisions of the enterprise;
- the procedure for conducting an inventory of funds.
Conclusion
Theoretical foundations of accounting for financial instruments were studied in accordance with the regulatory framework P (S) BU 13 "Financial Instruments", IAS 32 "Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Provision of Information"; IAS 39 Financial Instruments – Recognition and Measurement; IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures; IFRS 9 Financial Instruments.
A financial asset or financial liability is carried on the balance sheet if the entity is the party to the agreement on the financial instrument. Financial assets or financial liabilities arising from firm contracts for the purchase or sale of resources (works, services) are reflected in the balance sheet after the right to receive the asset or the obligation to transfer it arises. Financial assets acquired as a result of systematic transactions are recognized on the date the contract is entered into or the date the contract is settled. The recognition method must be applied consistently to each class of financial asset. If an entity recognizes a financial asset and an associated financial liability on the contract date, interest is accrued from the date the contract is settled, when ownership passes.
REFERENCES
- Civil Code of the Donetsk People's Republic [Electronic resource]: Law of the Donetsk People's Republic No. 81-IIHC of December 13, 2019, in force. ed. // Official website of the People's Council of the DPR - Electron.dan. – Donetsk, 2021. – Access mode: https://dnrsovet.su/ zakonodatelnaya-deyatelnost/prinyatye/zakony/grazhdanskij-kodeks-donetskoj-narodnoj-respubliki/
- International Financial Reporting Standard (IAS) 32 "Financial Instruments: Presentation of Information" [Electronic resource]. – Electron. Dan. – Donetsk, 2021. – Access mode: http://www.ifrs.org.ua/wpcontent/uploads/2013/04/ Mezhdunarodny-j-standart-finansovoj-otchetnosti-IAS-32-Finansovye-instrumenty-predstavlenie-informatsii
- National accounting regulation (standard) 1 "General requirements for financial reporting" No. 73 as amended. March 14, 2013 [Electronic resource]. – Electron. Dan. Donetsk, 2021 .html
- On security [Electronic resource]: Law of the Donetsk People's Republic No. 04-IHC dated 12.12.2014, in force. ed. // Official website of the People's Council of the Donetsk People's Republic. – Electron. Dan. – Donetsk, 2019. – Access mode:
- About accounting [Electronic resource]: Law of the Donetsk People's Republic No. 223-IINS of December 18, 2020, in force. ed. // Official website of the People's Council of the DPR - Electron.dan. - Donetsk, 2021. - Access mode: dnrsovet.su/zakonodatelnaya-deyatelnost/prinyatye/zakony/zakon-donetskoj-narodnoj-respubliki-o-buhgalterskom-uchete/
- On the audit of financial statements and audit activities [Electronic resource]: Law of Ukraine No. 2258-VIII as amended. as of 07/01/2020 // Official website of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine - Electron. Dan. – Access mode: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/2258-19
- On civil defense [Electronic resource]: Law of the Donetsk People's Republic No. 07-INS dated February 13, 2015, in force. ed. // Official website of the People's Council of the Donetsk People's Republic. – Electron. Dan. – Donetsk, 2019. – Access mode: https://dnrsovet.su/zakon-dnr-o-grazhdanskoj- oborone/
- On the approval of the Model Regulations on the labor protection service: adopted by Resolution No. 354 of August 27, 2015 / DPR. – Electron. Dan. (1 file: 151 Kb). – Donetsk: [b. i.], 2015.
