Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theoretical studies of the financial and economic security management process
- 1.1 The essence of financial and economic security of the enterprise
- 1.2 Factors and elements affecting the financial and economic security of the enterprise
- 1.3 Research of the process of ensuring financial and economic security of the enterprise
- List of sources
Introduction
The relevance of this work is associated with a high risk of the company's activity in conditions of uncertainty, which leads to a late reaction to these threats to reduce the competitiveness and efficiency of the enterprise.
Confirmation of the great urgency of the issue of ensuring financial and economic security of enterprises is also the fact that many large enterprises do not have an effective system for assessing financial and economic security, which significantly reduces the productivity of their activities and determines the current high demand for scientific developments in the field of financial and economic security.
Approaches to the study and implementation of a set of measures to improve the level of enterprise security are different for each enterprise, so it can be concluded that this issue has a significant level of relevance not only as a theoretical study in economics, but also as practical developments for existing business entities.
The object of the study is the process of analyzing the financial and economic security of the enterprise.
The subject of the research is the principles, tools and methods of determining the level of financial and economic security of the enterprise.
Research methods both general scientific and special methods were used. The use of methods of analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction made it possible to form the conceptual apparatus of the study. The analysis of the level of financial and economic security was carried out using the method of a systematic approach and a graphical method.
The purpose of the study is theoretical studies of the essence of the process of managing the financial and economic security of the enterprise, analysis of the mechanism of managing the financial and economic security of the enterprise.
To achieve the goal of the work, it is necessary to perform the following tasks:
1. To determine the essence of financial and economic security;
2. Identify factors and elements affecting financial and economic security;
3. To investigate the methods of assessment, mechanism and main directions of increasing the level of financial and economic security;
4. To get acquainted with the general characteristics and analyze the financial condition of Technoservice LLC;
5. To make an assessment of risks for the company LLC "Technoservice";
6. To assess the financial and economic security of Technoservice LLC;
7. To analyze the main directions of increasing the level of financial and economic security of the enterprise.
1. Theoretical studies of the financial and economic security management process
1.1 The essence of financial and economic security of the enterprise
To work with the category of economic security of an enterprise, first of all it is necessary to understand what security is in general.
Security is primarily the state of protection of an object, its personal interests from internal or external threats, as well as the ability to survive destructive influences.
Security, in turn, is a state of reliable protection of someone from something.
Internal risks are presented in Figure 1.1
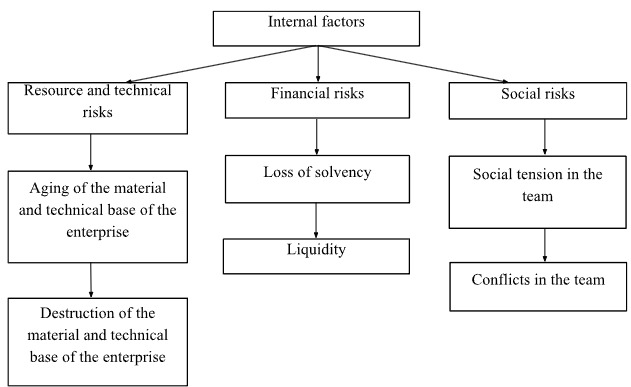
Figure 1.1 - Internal risks of financial and economic security
Threats to the financial and economic security of an enterprise are potential or actual actions of individuals or legal entities that damage the protection of the enterprise, thereby leading to disruptions in its activities or even to the closure of the business as a whole, as well as to economic and other losses. It should be borne in mind that a threat to the economic security of an enterprise is a certain act that entails negative consequences [8, p. 155].
Today, an organization must be able to adapt to changing environmental conditions, and this requires a well-functioning organization that can optimally adapt to future predicted changes in the external environment [7, p. 9]. We can talk about the economic security of an enterprise as the security of interaction between the enterprise and external entities.
In turn, the organization, being a structural element of the country's economy, provides livelihood for many people and thereby ensures sustainable economic development, social and political stability in the regions and throughout the country. Thus, the financial and economic security of the organization affects the economic situation of the state and its economic security.
Interacting, the organization and the state distinguish functions, in particular: the organization builds a system to ensure financial and economic security, and the state simultaneously becomes a guarantor of compliance and application of the law. The state regulates economic relations between organizations, conducts antimonopoly policy.
Currently, the following difficulties arise in ensuring the financial and economic security of the organization: insufficient coordination of executive and legislative authorities, criminalization of economic sectors, corruption in government activities, including law enforcement. All this indicates inconsistency in the system of ensuring financial and economic security and ultimately causes economic damage to the enterprise and the state. This state of affairs requires immediate action to eliminate significant deficiencies in financial and economic security. [9, p. 15]
It should also be understood that the company's management activities, which include risky actions: investments in securities (private or public), investments in the latest organizational forms, coordination of the introduction of new services, products, work processes should not be considered as a threat to the financial and economic security of the enterprise. All these management decisions will be risky and may be negative, since negative economic consequences may arise for the enterprise, since the situation on the securities market may change significantly, the needs of the population may change, and it is also possible that new organizational forms will not bring the proper result. It is important to remember that all this is ultimately intended for the main purpose of the enterprise to achieve its future development. [10, p. 45] This type of solution includes an integral part of doing business. Also, at the beginning of the company's activity, the establishment of reduced prices for services and goods is not considered a threat to the security of the enterprise. But in this case there can be no profit, and, conversely, there may be losses, but this is a general marketing technique aimed at attracting buyers to an unknown seller. After some time, the difference in the cost of products will change.
The types and types of threats discussed above make it possible to identify the enterprise security system as a set of effective measures (management decisions) taken to reduce the risks associated with real and potential threats, which must be justified by assessing these threats, analyzing crisis situations and other factors that hinder the achievement of the enterprise's goal and creates a risk for it. [11, p. 43]
It should also be understood that there are various methods for quantitative and qualitative assessment of risks and threats associated with the company's activities. There are also different approaches to the implementation of the measures themselves related to maintaining an appropriate level of financial and economic security of the enterprise.
These methods and approaches are subjective for each individual enterprise and depend on the level of management qualifications, the territorial location of the enterprise, financial independence, the type of activity of the business entity and other factors [4, p. 16].
In most cases, the financial and economic security of an enterprise is understood as management aimed at increasing competitive advantages at the expense of available resources, as well as maintaining a sufficient level of financial stability, which is necessary for the implementation of the goals and objectives. At the same time, the main goal of the financial and economic security of the enterprise is to ensure its sustainable and maximally effective functioning in the current period and to ensure a high potential for development and growth in the future [8, p. 54].
1.2 Risk factors and elements, their impact on the financial and economic security of the enterprise
Since resistance to factors and elements affecting the financial and economic security of an enterprise is one of the fundamental qualities of the category under consideration, it is necessary to consider these factors in more detail and in detail, classify these factors.
A factor is the cause, the driving force of a process. For us, this process is the emergence of risks that violate the financial condition of the enterprise. There is no unified classification of these factors, but a general view can be presented in Figure 1.3.
Next, we will discuss each type of such factors in more detail. To begin with, it should be understood that each factor can have both economic and non-economic content. And in addition, there may be objective factors that arise without the participation of the enterprise or its employees. As well as subjective, arising from intentional or not intentional actions of the business entity or its employees.
These factors can affect the state of financial and economic security of an enterprise either singly or several at the same time. They can be a consequence of each other and their influence takes on a cascading character.
External factors are presented in the form of the external environment of the enterprise:
- Natural factors may be tied to a certain territory and cause risks to financial and economic security on a regular basis. Such factors include: earthquake, flood, tsunami, hurricane and others. And also without territorial and regional reference, outbreaks of viral diseases can be attributed to such factors. These factors can provoke natural and environmental risks. In cases where these risks are regular and predictable, the company has the opportunity to protect itself from them by insuring these risks or by carrying out preparatory work. However, when the risk cannot be predicted, it can become a serious threat to the financial and economic security of the enterprise [32, p.3].
- Competitive factors can be divided into two types. Fair competition, when a competing company was able to reduce the cost of goods or capture sales markets by finding internal reserves or the qualities of its goods. And unfair competition, when competitors resort to dumping, industrial espionage, bribery of employees, contractors and others. This factor is associated with the risks of the development of monopolism in the markets. In cases of fair competition, an enterprise in market conditions must either find new sales markets or reduce its cost
- The factors that affect the occurrence of a risk to the financial and economic security of an enterprise at the state level can be divided into: political, economic, regulatory. The political factor is political stability, which is the basis for the stable functioning of all economic entities in the country. Economic factors are represented by indicators of consumer demand, inflation, economic growth rates, the value of the national currency, and others. Regulatory factors are presented in the form of changes in legislative acts directly or indirectly related to the company's activities. Such changes include permits or bans on the type of activity, changes in tax and duty rates, Central Bank rates, environmental, technical standards and others [30, p.55].
- International factors include changes in international law, changes in the regulatory framework of the countries with which foreign economic activity is carried out. Also, such factors include volatility in international commodity markets, international financial crises and international STP, from which both the fixed assets of the enterprise itself and the goods produced on them can become obsolete.
- One of the factors for creating a threat to the financial and economic security of the enterprise is the condition and number of consumers of goods produced by the business entity. If the only consumer or the main consumer of goods is one counterparty, then the financial and economic condition of the enterprise becomes directly dependent on the financial stability and stability of the counterparty.
- Also, in addition to the risks associated with the consumer, it is necessary to take into account the factors causing risks associated with the supply of the enterprise. If the activity of an enterprise depends on the supply of all or a significant amount of resources by one counterparty, the financial and economic condition of the enterprise also becomes directly dependent on the stability and stability of this counterparty [31, p. 10].
Internal factors are represented by processes directly occurring at the enterprise itself:
- Personnel factors are presented in the form of a shortage or excess of employees with the necessary qualifications to carry out stable and effective activities of a business entity. Also, insufficient control over employees can be added to this factor. Which in turn can lead to damage, theft and other criminal actions with the property of the enterprise.
- Factors related to investment activity can be divided into internal and external investments. If we consider internal ones, then there may be a risk associated with insufficient investment in the enterprise itself to update fixed assets. Or the situation may be reversed, with economically unverified investments, the company may suffer losses or receive less than the planned profit. In the case of investments in other companies, the company faces the same set of risks [33, p.32].
- Factors of a production nature are directly related to the product and the production process itself. This factor can be divided into 3 elements. The first element is resource. First of all, this element is connected with the availability of the necessary stocks at the enterprise to ensure uninterrupted operation in the event of a delay in the supply of raw materials and materials. The second element is production. It is associated with the optimization of the production process of goods and the formation of a competitive cost of goods. The third element is qualitative. It depends on the consumer qualities and properties of the product.
- Factors of a managerial nature are associated with the action or inaction of the company's management. Incorrect decisions can significantly worsen the state of the enterprise not only in the short term, but also in the long term.
The influence of all the factors listed above is reflected in one way or another on the main financial indicators of the enterprise.
1. The first such indicator is the financial stability of the enterprise. In itself, the state of financial stability is the state of an enterprise when it is able to guarantee full solvency.
In the context of financial stability, it is considered with the help of which sources the enterprise forms noncurrent assets and reserves. If an enterprise is able to form both noncurrent assets and reserves at its own expense, then such a state is absolutely stable in the context of the formation of its own production resources. In this state, the level of risk of the company's activities is minimal and, consequently, the level of financial and economic security is sufficient. However, if longterm or short-term borrowed funds are used in the formation of reserves, this significantly undermines the level of financial stability and leads to the appearance of an objective risk of activity. And in the event that not only stocks, but also noncurrent assets are formed at the expense of borrowed sources, then this situation is critical and the level of risk in the company's activities is very high, and a sufficient level of financial and economic security is not even worth talking about.
The next no less important objects when considering financial stability should be to study the level of dependence on borrowed capital.
In the case of the predominance of borrowed sources of funds in the enterprise, the enterprise itself and its decisions begin to be dependent on creditors. In this case, the risk of activity increases because the needs of creditors may not coincide with the needs of the enterprise itself. And, consequently, the decisions taken may be dangerous for the enterprise in the future. This condition significantly reduces the level of financial and economic security for an industrial enterprise.
Thus, we can say that the current and prospective level of financial stability is the basis for the effective operation of the enterprise, and maintaining such a level is one of the key goals in the management of financial and economic security.
2. The second important financial indicator influenced by risk factors is the liquidity of the balance sheet. By itself, the liquidity of the balance sheet is the degree to which the company's liabilities are covered by its assets, the term of conversion of which into monetary form corresponds to the maturity of the obligations.
Most often, 3 stages of liquidity are considered according to the rate of conversion of assets into cash.
At the first stage, short-term liquidity is considered, which involves the payment of short-term liabilities at the expense of absolutely liquid assets.
At the second stage, the liquidity of the turnover period of accounts receivable is considered, due to which the most urgent obligations should be repaid.
At the third stage, in addition to absolutely liquid assets and receivables, the option of repayment of the most urgent obligations through the sale of assets is considered.
1.3 Investigation of the process of ensuring financial and economic security of the enterprise
The object of ensuring financial and economic security is the formed complex of priority financial interests of the enterprise that require protection in the process of carrying out activities.
The managers of the enterprise, headed by the leading managers, act as subjects of financial and economic security.
The subject of the study of financial and economic security is a set of tools that allow for effective management activities to maintain and develop its competitiveness. These include laws, patterns, principles, categories, mechanisms, models, etc. [34, p.4].
Analyzing the above-mentioned features of the financial and economic security of the enterprise, it should be noted that resistance to external and internal factors is one of the fundamental qualities. This approach allows us to formulate the following tasks of ensuring the financial and economic security of the enterprise:
- system monitoring of the company's activities;
- elimination of insolvency;
- maintaining a sufficient level of financial stability;
- minimizing possible and occurring consequences of adverse situations.
Ensuring the financial and economic security of an enterprise can be represented as a continuous process in time, which is shown in Figure 1.2.
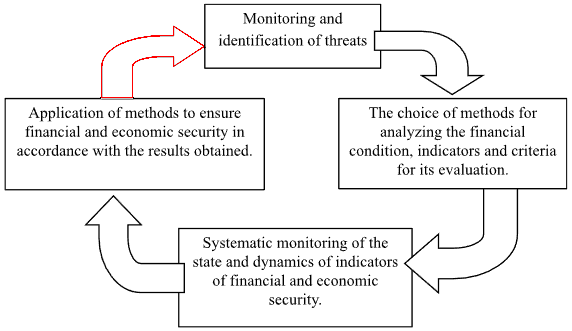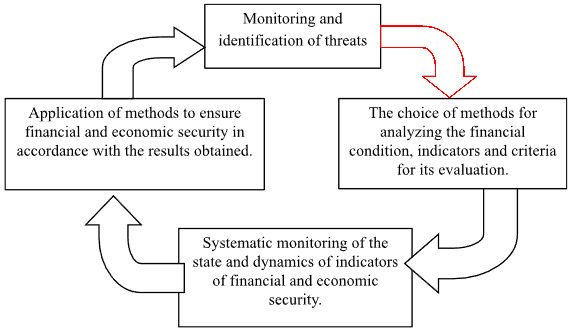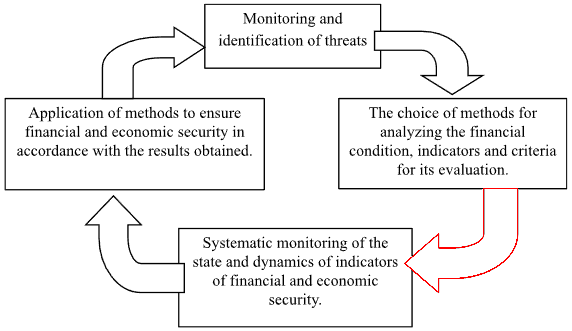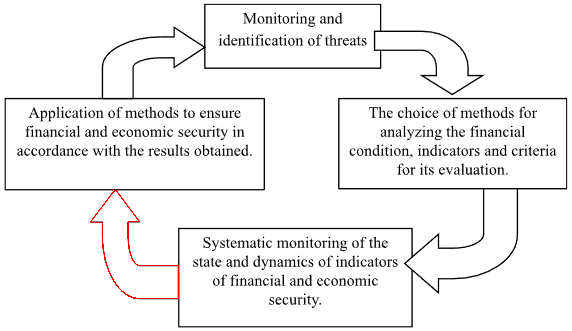
Figure 1.2 The process of ensuring financial and economic security of the enterprise
Monitoring is carried out in order to identify early signs of threats to the financial and economic security of the enterprise. The significance of this stage allows us to identify factors that have a negative impact on the financial condition and other aspects of the economic activity of the enterprise.
The choice of methodology for determining the level of financial condition of the enterprise depends on many factors. The most important factor in choosing a methodology is the purpose of the analysis. The final result is influenced by a number of objective factors such as the industry and type of activity, the size of the enterprise, the dynamics and structure of property, etc. Subjective factors should include the one who conducts the analysis, i.e., for example, whose head is interested in the enterprise as a whole or the department manager who is interested in a segment of his activity. It is worth noting that there is no single approach to assessing the financial and economic condition and the choice of indicators [36, p.6].
After determining the essence of financial and economic security and the factors affecting it, it is necessary to disclose the issue of assessing the level of financial and economic security and the direction of the enterprise, the result of which will be a sufficient level of security.
First of all, it is necessary to understand that many methods are used to assess the level of financial and economic security, which can be divided into enlarged groups presented in Figure 1.3.
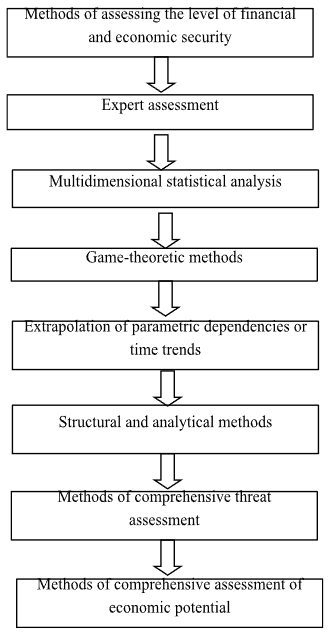
Figure 1.3 Methods of assessing the level of financial and economic security of the enterprise
Expert assessment of financial and economic security is an assessment by highly qualified specialists in this field. The disadvantage of this method is the subjectivity of the assessment and the possible discrepancy between the final results of the assessment of various specialists.
Multidimensional statistical analysis is a method of mathematical statistics that involves combining a number of methods (factor analysis, principal component analysis, discriminant analysis, cluster analysis) to express objectively existing relationships between phenomena and processes, but this method is prone to variation and its use requires the highest quality and reliable data.
Game-theoretic methods imply a formalization in the game formulation of multilateral situations and control parameters with the expectation of the influence of these parties on each other. The disadvantage of this method is the rare possibility of application.
Extrapolation methods are the most common forecasting methods in economics and involve a combination of two components: deterministic and stochastic. The forecast is created separately for each parameter based on statistical observation and determination of the trend of parameter change over time. The disadvantage of this method is the need for statistical data for a long period of time.
Structural and analytical methods are the easiest to use and represent the division of the parameters of financial and economic security into components, their analysis and determination of the share of the influence of one parameter on the overall condition. Such methods include: decomposition, modeling, matrix method, network analysis.
Methods of comprehensive threat assessment imply the definition of each threat, the development of thresholds for these threats. Financial and economic security is assessed on the basis of a cumulative criterion by adding up individual criteria weighted by the level of influence.
Methods of comprehensive assessment of economic potential imply an analysis of the entire activity of the enterprise, both internal and external, using SWOT analysis, assessment of competitive status and other tools [37, p. 3].
From all the variety of the listed methods, it can be concluded that there is a lot of variability in assessing the level of financial and economic security of an enterprise, and, consequently, the reliability of the final result depends on the chosen method or group of methods, the quality of the assessment.
After assessing the level of financial and economic security, the company's management needs to understand how a sufficient level of financial and economic security will be maintained or formed in the future.
The main difficulty in this process are 2 factors:
- the company is ultimately aimed at maximizing net profit;
- and as a consequence of the first factor, the managers of the enterprise strive to produce only expenses that allow them to increase income in this period. At the same time, often ignoring the necessary expenses to reduce costs in the future.
Such a relationship of factors is a common case in enterprises where the financial situation is difficult. And such a management style only unwinds the spiral of declining financial and economic security in the future.
When forming a promising, sufficient level of financial and economic security, one of several approaches can be applied, which are presented in Figure 1.6
The approaches can be divided into internal and external.
1. The first internal approach is to develop measures that in the future will be able to reduce the likelihood of an emergency, and in the aftermath of its occurrence to reduce financial losses and costs associated with this situation. This approach is based on maximizing preventive costs until the total costs of the enterprise in the event of an unusual situation that undermines financial and economic security are minimal.
Sometimes it is difficult for business entities to find sufficient funds to carry out these activities, however, statistical studies show that the ratio of costs spent before the onset of a negative event is a multiple of the costs of normalizing the operation of the enterprise [37, p. 9].
However, the main problem of this method is the calculation of the required amount of costs for preventive measures, such complexity arises because these costs should be correlated with possible losses. And possible losses are costs that should be made in the future, they are stochastic in nature and their volume is influenced by many factors.
Also, when using this method, there is a difficulty in classifying costs. It is not always unambiguously possible to attribute certain costs to liquidation and preventive ones. For example, the costs of collecting data and analyzing a negative phenomenon that has already occurred can be attributed both to the costs of eliminating the consequences and to preventive costs, which should ensure that this phenomenon does not repeat.
2. The second approach is based on determining the cost of a negative event. The principle of this method is based on a prospective assessment of the consequences of negative phenomena. This method has an ambiguous assessment about the effectiveness of using its data to prevent negative events.
According to this approach, the costs of the occurrence of a negative event are divided into direct and indirect. Direct costs include direct damage incurred. And indirect costs include costs associated with equipment downtime, under-release of products, failure of the contract and other ensuing consequences.
The complexity and disadvantage of this method is that indirect costs are even more problematic to calculate than direct ones.
3. The third approach is called accounting and is based on the financial statements of the enterprise. His assessment is retrospective and evaluates the result that has already been recorded in the reporting.
Within the framework of this approach, data before and after the negative event are evaluated and compared. This method is the most accurate, but it works late. Because after analyzing the accounting statements, you can only prepare for a repeat event, but you can not analyze an event that has not yet happened.
All these approaches allow us to collect information and evaluate the effectiveness of measures taken to improve the level of financial and economic security of the enterprise, predict future events and take a number of preventive measures to reduce the risk of the business entity. These methods are internal and all activities carried out at the enterprise are carried out by the company's own forces and means.
It seems to me that the most effective is the symbiosis of all three of these methods, it will allow us to achieve the best results in reducing the level of risk and, consequently, to increase the level of financial and economic security.
List of sources
- Litvinenko Alexander Nikolaevich Economic and national security: the problem of correlating concepts // Scientific and Technical Bulletin of St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University. Economic sciences. 2013. ¹3 (173).
- Lyashenko, A.N. Specific properties of financial security of the enterprise (Text)/ A.N. Lyashenko // Project management and production development. - 2012. - No. 4. pp. 1-7
- Manokhina N.V. Economic security: A textbook / N.V. Manokhina, M.V. Popov, N.P. Kolyadin, I.E. Zhadan. M.: SIC INFRAM, 2016. 320 p.
- Musataeva M.O. Sources, types and factors of threats to economic security, the creation of an economic security service // Scientific and methodological electronic journal Concept. 2015. Vol. 23. pp. 26-30.
- On state supervision in the sphere of economic activity: Law of the DPR No. 76-IHC of August 21, 2015 Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- On Industrial safety of hazardous production facilities: DNR Law No. 54-IHC of June 05, 2015 Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- On information and information technologies: DNR Law No. 71-IHC of August 07, 2015 Donetsk : [B.I.], 2015. Systems. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- On remuneration: DPR Law No. 19-IHC of March 06, 2015 Donetsk : [B.I.], 2015. System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- About vacations: Law of the DPR No. 16-IHC of June 06, 2015 Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- On labor protection: Law of the DPR No. 31-IHC of April 03, 2015 Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. Title. With a title. The screen.
- Oleynikov E.L. Economic and national security / E.L. Oleynikov. M.: Exam, 2014. 182 p.
- Papekhin Roman Sergeevich / Factors of financial stability and security of the enterprise: abstract of the dis. ... Candidate of Economic Sciences/; [Place of protection: Volgogr. State. Un-t]. Volgograd, 2017. 21 s
- Podvolodina I. M., Voronin V. P., Approaches to the assessment of economic security of enterprises // Vestnik VGUIT. 2017. No. 4. pp. 47-49.
- Pyatov M.L. Development of elements of the accounting policy of the organization // Accounting, - 2017. No. 5. pp. 15-18.
- Reverchuk N.I. / The influence of marketing security on the business reputation of an enterprise /// Reverchuk N.I. Dzyamulich E.C / Universum: Economics and jurisprudence. 2014. ¹5 (6).
- Savitskaya G.V. Analysis of economic activity of enterprises Mn.: Novoe znanie, 2015 85 p.
- Modern methods of managing the economic security of organizations / V. P. Mac-Mac ; M-vo of education of the Moscow region, Academy of Social Sciences. Upr., Kaf. Obshch. Management. Moscow : ASOU, 2015. - 175
- Sorokina O. N. Essential characteristics of financial security of the enterprise // Almanac of modern science and education. - 2015. No. 6. pp. 224-225.
- Sorokov A.V. Economic security: actual problems of modernity // "Legal initiative" 2016. No.9. p. 45.
- Trofimova L.A. Economic indicators used to assess the effectiveness of the enterprise // Auditor. 2016. No. 9. p. 12.
- Firsova O.A. Economic security of the enterprise / Publisher Litagent "MABIV", 2017. 220 p.
- Sheremet, A.D. Finance of enterprises: textbook/ A.D. Sheremet, R.S. Saifulin. M.: INFRAM, 2015. 589s.
- Shlykov V.V. Complex provision of economic security of the enterprise / V.V. Shlykov. St. Petersburg: Aleteya, 2019. 237 p.
- Economic security: textbook for universities / under the general editorship of L.P. Goncharenko, F.V. Akulinina. M. : Yurayt Publishing House, 2015. 478 p. Series : Specialist
