Content
- Introduction
- 1 Theoretical foundations of the financial condition of the enterprise
- 1.1 The essence of the concept of financial condition
- 1.2 Methods for assessing financial condition
- 1.3 System of indicators and information support for financial condition analysis
- List of sources
Introduction
The problem of studying the financial condition of an enterprise and its assessment is significant, because on the one hand, the financial condition is the result of the company's activities in the past, that is, a characteristic of its achievements, and on the other hand determines the prerequisites for its development in the future.
The change in financial condition over a number of years makes it possible to assess the professional and business qualities of its managers and specialists. The assessment of the financial condition allows investors, lenders and business partners to determine the financial capabilities of the enterprise for the future, the possibilities of its further development.
The relevance of the topic of the thesis can be justified from several positions:
- the financial condition acts as one of the most important characteristics of the economic and financial activity of the enterprise in real time and the predicted future;
- the financial condition is the result of the interaction of all production and economic factors: labor, land, capital, entrepreneurship;
- legal and social responsibility for the results of financial and economic activities is constantly growing;
- increasing the investment attractiveness of the enterprise, in order to increase the quality of production, expand the scope of activity and create additional jobs;
- the financial condition of enterprises has a direct impact on social and budgetary processes, both in an individual region and in the country as a whole.
At this difficult stage, it is important not only to give a correct assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise, but also to offer enterprises new methods of solving old and new tasks, taking into account the peculiarities dictated by the forms of ownership. In particular, it is necessary to develop specific directions for improving the financial condition of the enterprise, increasing its solvency, independence from borrowed capital, there is an objective need to take all measures aimed at improving the economic performance of the enterprise, in relation to industrial enterprises. All of the above, taken together, characterizes the relevance of the topic of the thesis and the need for this research.
The purpose of the thesis is to consider the various approaches of the authors to the essence of the concept and the assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise, to conduct a financial analysis of the enterprise and to determine directions for improving the financial condition of an industrial enterprise.
The object of the study is the financial condition of the economic entity Open Joint Stock Company "Slavic brick".
The subject of the study is the process of assessing the financial condition of the Open Joint Stock Company "Slavic Brick", identifying factors and causes of changes in the financial condition of the enterprise and developing recommendations for its improvement.
Research methods: analysis, synthesis, grouping, computational and analytical, specification.
The theoretical and methodological basis of the work was the works of domestic and foreign scientists, international accounting and financial reporting standards, foreign experience in analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise, materials of international and domestic scientific seminars and conferences.
1. Theoretical foundations of the financial condition of the enterprise
1.1 The essence of the concept of financial condition
The financial condition of an enterprise is an economic category that reflects the state of capital in the process of its circulation and the ability of a business entity to repay debt obligations and self—development at a fixed point in time. The financial condition of economic entities is determined by the efficiency of the use of all elements of the labor process: labor tools, labor items and labor itself. A stable financial condition is a prerequisite for the effective operation of any enterprise, organization, firms and is the pinnacle in the business evaluation system.
The financial condition of the enterprise is characterized by the placement and use of funds (assets) and the nature of the sources of their formation (equity and liabilities, i.e. liabilities). This information is contained in the balance sheet and other forms of accounting statements.
The financial condition is also understood as a characteristic of the investment attractiveness of the enterprise, its competitiveness in the financial market. The assessment of the financial condition provides an opportunity for investors, business partners and creditors to identify financial opportunities and promising areas of the enterprise in the future.
The main goal of improving the financial condition of the enterprise is reduced to one strategic task – to increase equity and ensure a stable position in the market. To do this, the company must constantly maintain solvency and profitability, as well as the optimal structure of the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet.
There is an accounting approach to determining the financial condition as a set of indicators of the company's financial statements. Do not forget that the financial situation is determined by the financial results achieved during the reporting period in parallel with liquidity, solvency and financial stability.
Again, the change in the financial condition over a certain period allows us to assess the professional and business qualities of the company's management and engineering staff. The stable financial position of the enterprise depends on the skillful, calculated management of the entire set of production and economic factors that determine the results of its activities.
The financial condition is studied not only by the managers and relevant services of the enterprise, but also by its founders, investors in order to study the efficiency of resource use, banks – to assess the circumstances of lending and establish the degree of risk, suppliers – for prompt receipt of payments, tax inspections – to fulfill the plan for the receipt of funds to the budget, etc.
An important point for conducting a study of the financial condition of an enterprise and determining its financial stability is the choice of an analysis methodology by which the main indicators will be calculated and the pace of their development is estimated.
Many scientists and economists were engaged in the issues of the financial condition of the enterprise. Among them we can distinguish such authors as: A.I. Kovalev, A.D. Sheremet, M.I. Bakanov, R.S. Sayfullin, E.A. Markarian, G.V. Savitskaya, etc. A study of the literature on this issue shows that the financial condition is interpreted by economists from different positions, and at the same time there is no single methodological approach to its definition. The study of the economic essence of the financial condition of the enterprise and the analysis of the scientific literature on this issue allowed us to note some approaches to this definition (Table 1.1).
Table 1.1 - Methodological approaches to the definition of "financial condition"
| n/a no. | Author, source | The basic concept | Advantages and disadvantages of the definition |
| 1. | E.A. Markarian [10] | The financial condition is understood as a system of indicators that reflect the ability to repay the company's debt obligations. Consequently, financial activity should cover the formation, movement and preservation of the company's property, control over its use. The financial condition of an enterprise is the result of the interaction of elements of the system of its financial relations. | It is not enough to represent the economic essence of the financial condition by a system of indicators. In addition to it, it is necessary to add a characteristic of the ability of the enterprise to finance its activities, to sustainable financial development, to fulfill financial obligations. |
| 2. | A.D. Sheremet [17] | The financial condition of an enterprise refers to the characteristics of the composition and placement of funds, the structure of their sources, the speed of capital turnover, the ability of the enterprise to repay its obligations in a timely manner, as well as other factors. They identified four types of financial condition in which an enterprise can be located: absolute stability of financial condition, normal stability of financial condition, unstable financial condition, crisis financial condition. | It should be noted that in order to assess the financial stability of the enterprise, they recommended a certain, only inherent system of indicators, which does not include indicators of solvency, liquidity, rationality of placement and use of property. |
| 3. | G.V. Savitskaya [13] | The financial condition of an enterprise is an economic category that reflects the state of capital in the process of its circulation and the ability of a business entity to self—development at a fixed point in time. The financial condition can be stable, unstable (pre-crisis) and crisis. The financial stability of an enterprise is the ability of a business entity to function and develop, maintain the balance of its assets and liabilities in a changing internal and external environment, guaranteeing its constant solvency and investment attractiveness within the limits of acceptable risk. | The described approach essentially coincides with the characteristics of the financial condition, its stability and the relationship between them, which are given by other authors. On the other hand, the author admits vagueness in the differentiation of such concepts as "financial condition" and "financial stability". The definition also does not take into account the fact that the financial condition is characterized by indicators of business activity, profitability, which reflect the efficiency of use and capital gains of the enterprise. |
| 4. | M.I. Bakanov [1] | The financial condition of the enterprise is characterized by the placement and use of funds, replenishment of own funds due to the amount of profit, as well as other sources, taking into account the plan, the turnover rate of fixed and working capital. The financial condition is manifested "in the solvency of enterprises, in the ability to meet the payment requirements of suppliers of equipment and materials in time in accordance with economic contracts, to repay loans, pay wages to workers and employees, make payments to the budget." | The financial condition of the enterprise is expressed in: - the rationality of the structure of assets and liabilities, i.e. the assets of the enterprise and their sources; - the efficiency of the use of property and profitability of products; - the degree of its financial stability; - the level of liquidity and solvency of the enterprise. |
| 5. | V.V. Kovalev [0] | The basis of the analysis of the financial condition is the economic potential of the enterprise and its constant changes over time. At the same time, the economic potential, according to the author, is the ability of an enterprise to achieve its goals, using, at the same time, the totality of material, labor and financial resources at its disposal. | The author identifies two sides of the economic potential: the property and financial situation of the enterprise. According to the author, the purpose of an in–depth analysis of the financial condition is to characterize the property and financial condition of the enterprise, the results of its activities for the analyzed period, as well as the definition of its financial development strategy. |
| 6. | L.T. Gilyarovskaya [4] | The characteristics of the financial condition of the enterprise in a generalized form are presented by changes in terms of the placement of funds and sources of their coverage (own or borrowed funds) for the analyzed period. | Uses an accounting and analytical approach to the analysis of the financial condition, in which a set of indicators of the financial statements of the enterprise is used. |
| 7. | I.T. Balabanov, N.P. Lyubushin [3] | The financial condition of an enterprise means its solvency and creditworthiness, that is, financial competitiveness, the use of capital and financial resources, the fulfillment of obligations towards the state and other economic entities. | The financial condition is often understood as the solvency of the enterprise, i.e. the ability to finance its activities. However, this judgment does not fully reveal the breadth of the concept of financial condition. The financial condition of the enterprise is understood as the investment attractiveness of the enterprise, the characteristics of its competitiveness in the financial market. |
| 8. | N.P. Lyubushin [9] | The concept of financial condition is presented as the ability of an enterprise to finance its activities. The financial condition is characterized by the availability of financial resources that are necessary for the normal functioning of the enterprise, the expediency of their placement and efficiency of use, the availability of financial relationships with other counterparties, as well as the availability of payment and creditworthiness, financial stability. | |
| 9. | M.M. Glazov [5] | Financial condition is the most important characteristic of an organization's activity, reflecting the availability of financial resources, the expediency and effectiveness of their placement and use, solvency and financial stability. | From the point of view of the short—term perspective, when assessing the financial condition of the enterprise, the author means the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise, from the point of view of the long-term plan - its financial stability. |
| 10. | V.I. Ivashchenko [19] | The result of financial activity, which is characterized by the size of the organization's funds, their placement and sources of income. | The property status of an enterprise changes over time under the influence of various factors, of which one of the main ones is the achievement of financial results over the past period. |
| 11. | O.V. Efimova [6] | The financial condition is characterized by the ability to create added value, the provision of the organization with sources of profit. | The author understands by financial condition only the ability to make a profit. The methodology for analyzing the financial condition of Efimova O.V. is the most perfect. |
| 12. | M.N. Fursova [14] | The financial condition is characterized by financial resources, namely, the indicator of the availability of financial resources, as well as the expediency of their placement and efficiency of use. | It should be noted that the approaches of scientists to the essence of the financial condition of an enterprise differ in the defining category, as which the complex concept, the state of capital and the ability to finance activities are considered. However, scientists agree on the indicators characterizing the financial condition, which reflect the availability, placement and use of financial resources. |
| 13. | S.I. Krylov, N.N. Ilysheva [0] | Financial condition is the ability to finance the activities of an organization, which is characterized by the availability of financial resources necessary for the normal functioning of the organization, the expediency of their placement, the intensity of use. | |
| 14. | S.V. Nedosekin [21] | The financial condition of an enterprise is its ability to finance its activities. | |
| 15. | E.V. Rogatenyuk[0] | The financial condition of an enterprise is a complex concept that is the result of the interaction of all elements of the financial relations system of an enterprise. It is determined by a set of production and economic factors and is characterized by indicators that reflect the availability, placement and use of financial resources." However, this definition does not specify the elements of the financial relations system of the enterprise, which makes it difficult to identify it. | In this definition, the author does not specify the elements of the financial relations system of the enterprise, which makes it difficult to identify it. |
Differences in views on the content of the concept of "financial condition", presented in Table 1.1, are generally manifested in the lack of unity of views on such particular concepts as: solvency, liquidity, financial stability, etc. Ambiguity also occurs in determining other characteristics of financial condition, such as capital structure, property status, financial independence, financial stability, financial stability, etc.
Comparing and analyzing the content of the authors' definitions given above, we can conclude that the financial condition can be defined as a complex economic category that characterizes the real and potential financial viability of the enterprise, as well as the possibility of providing a certain level of financing for its activities. Quantitatively, it can be measured by a system of indicators, on the basis of which the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise is carried out. Comparing the concepts considered with each other, I would like to note that each author has a similar structure for determining the financial condition of an enterprise. The main factors determining the financial condition are:
a) implementation of the financial plan and replenishment of own working capital as the need arises at the expense of profit;
b) the turnover rate of working capital (assets).
In order to achieve a certain unambiguity in assessing the financial condition of the enterprise, we propose to use the content of the concept of "financial condition" as a basis. In accordance with this, three areas of analysis of the financial condition can be distinguished:
1. Placement and ownership of financial resources ("availability of economic potential"), which is analyzed on the basis of Form No. 1;
2. Sufficiency of financial resources, at each moment of time, data from forms No. 1, 2, 4, turnover on cash accounting accounts are involved for analysis;
3. The use of financial resources ("use of economic potential") is analyzed on the basis of Forms No. 1 and 2. The placement and ownership of financial resources, in turn, can be analyzed in three directions with the joint use of both asset and liability data. The first is proposed to be called an analysis of the structure of funds, the second and third – an assessment of liquidity and financial stability.
Economists unequivocally propose to evaluate the use of financial resources by means of turnover indicators (the sales revenue indicator is involved in the calculations) and profitability (profit indicators are involved in the calculations). It is also advisable to analyze the structure of the results according to the data of form No. 2.
Profitability coefficients, being indicators of efficiency, in the economic literature are divided into cost-type indicators and resource-type indicators. So, the concept of financial condition directly includes only resource-type indicators.
The formed content of the concept of "financial condition" is shown in Figure 1.1.
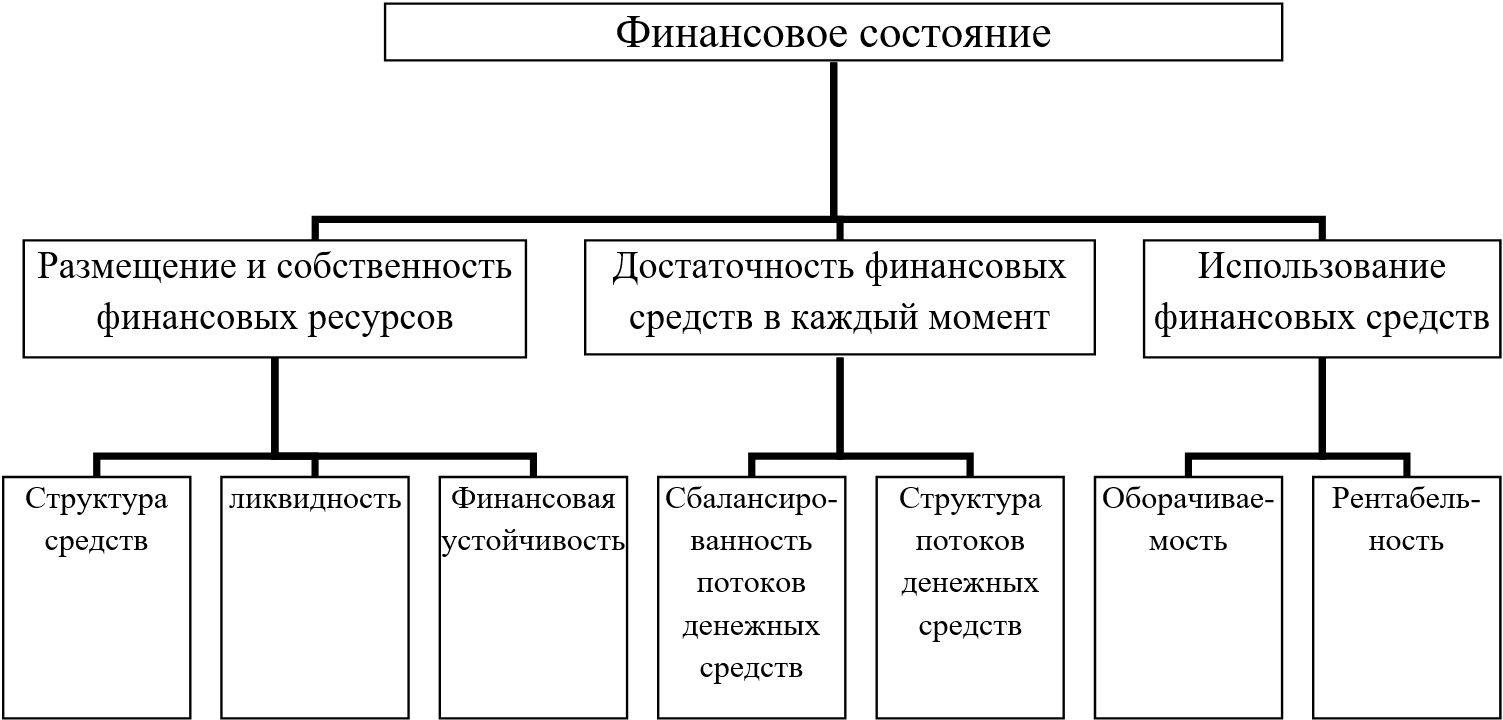
Figure 1.1 – The formed content of the concept of "financial condition"
The main tasks of the financial condition are to determine the quality of the financial condition, to study the reasons for its improvement or deterioration over a given period, to prepare recommendations for improving the financial stability and solvency of the enterprise. These tasks are solved by studying the dynamics of absolute and relative financial indicators and are divided into the following analytical blocks proposed by A.D. Sheremet and shown in Figure 1.2.
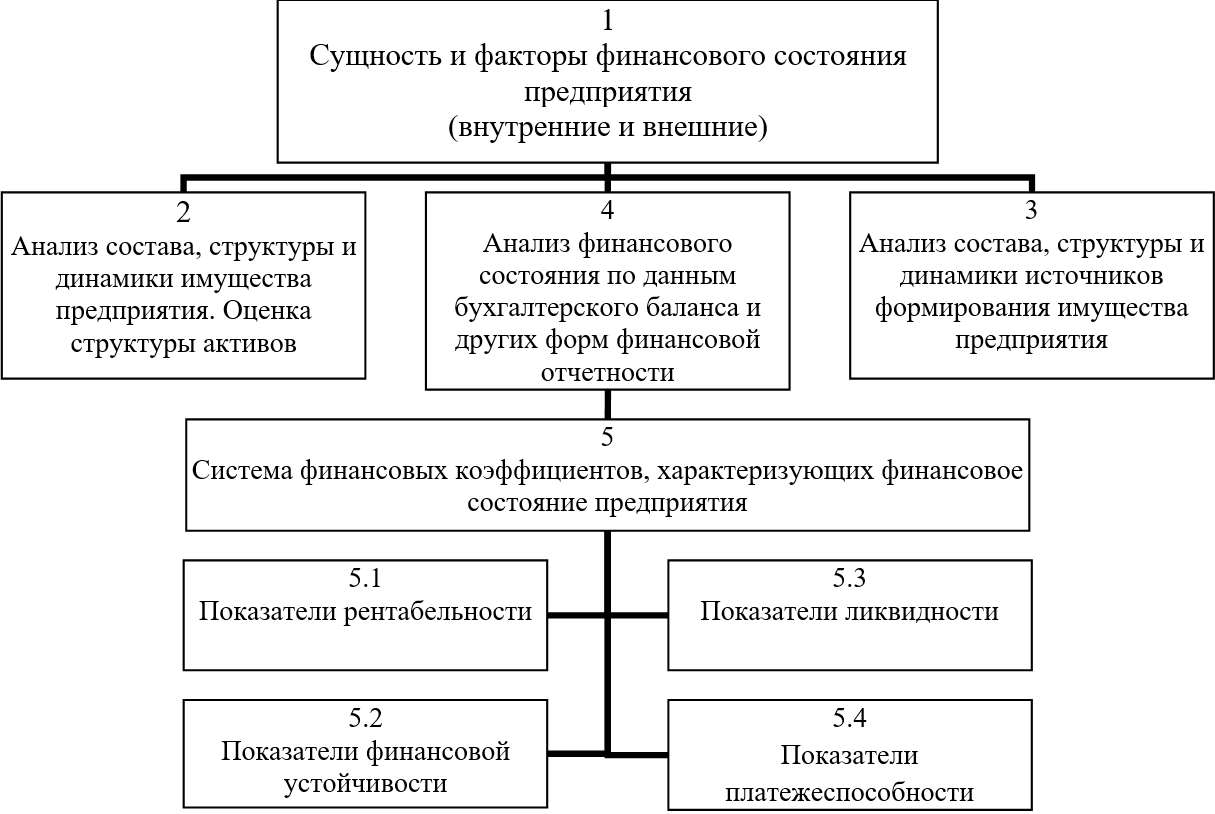
Figure 1.2 - The scheme of the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise
Structural elements of analysis such as assessment of potential bankruptcy, analysis of investment attractiveness, business prospects, etc. are much less common. These elements are not integral parts in the analysis of the financial condition, they should disclose the features of the analysis with the appropriate target setting: the choice of the object of investment, forecasting, etc.
The sufficiency of financial resources at any given time (solvency) can be analyzed in two ways. The first is proposed to be called an analysis of the structure of cash flows (direct method), the second is an analysis of cash flows in relation to financial resources (indirect method).
The main stages of financial analysis are presented in the form of a diagram in Figure 1.3.
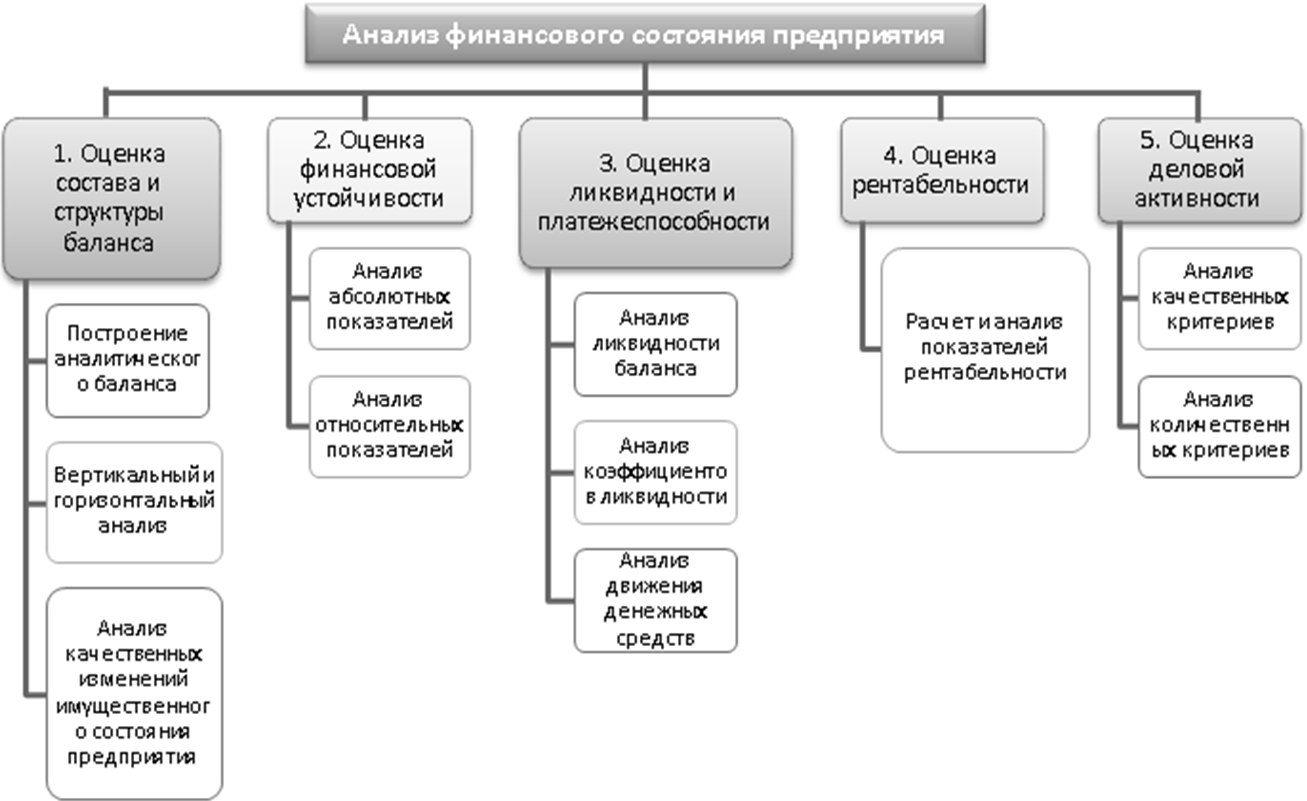
Figure 1.3 - The scheme of the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise
The groupings of directions of financial condition analysis considered in Figure 1.3 are based on the content of the concept of financial condition interpreted by various authors. Therefore, along with the analysis of the financial condition in each direction of its structure, it is advisable to conduct a systematic analysis of the indicators of the financial condition of the enterprise. It will ensure the interconnection of various analytical coefficients.
Summing up the above, based on the comparison of the concepts of "financial condition of the enterprise" from the point of view of different authors and their assessment, it should be concluded that the financial condition acts as one of the most important characteristics of the economic and financial activities of the enterprise from the standpoint of the internal and external environment, its reliability. The financial condition of an enterprise largely determines the potential of an economic entity in business cooperation, its competitiveness, and acts as a guarantor of the effective realization of the economic interests of all participants in economic activity, both the enterprise itself and its partners.
1.2 Methods of financial condition assessment
In modern conditions, when the independence of enterprises and organizations in making and implementing management decisions increases, as well as the degree of their economic and legal responsibility for the results of financial and economic activities, the role of financial analysis in the life of organizations also increases. An assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise is necessary for owners, investors, creditors, financial managers, department heads and the entire public, who should receive good results from the expectation.
It is known that an assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise is a set of methods that allow determining the state of affairs of an enterprise as a result of analyzing its activities over a finite time interval.
The studied methods of analyzing the financial condition make it possible to judge the features of analytical work. Based on the concept of methodology — "this is a set of special techniques and methods of research" — we found that in general, the set of basic techniques that are used in the study of the financial condition of the enterprise are the same for different authors.
Assessment of financial condition (English estimation of financial position) is a method that allows you to reveal the financial well–being and dynamics of development of an economic entity. The assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise is carried out in the following cases:
- Reorganization, restructuring, liquidation of the company.
- The transaction of purchase and sale or lease of a business (moreover, both individual parts and the entire property).
- Revaluation of financial assets.
- Obtaining various loans and investments.
- Insurance of the company's property.
- Bankruptcy procedure with forced sale of the enterprise or its part [2, с. 47–55].
The main purpose of the financial condition of the company are:
- Assessment of the dynamics of movement and the state of the composition and structure of assets.
- Assessment of the dynamics of movement, composition, condition and structure of sources of equity and debt capital.
- Analysis of calculated and absolute indicators of the company's financial stability, assessment of changes in the level and identification of trends in change.
- Analysis of the solvency of the company, the liquidity of its balance sheet assets.
The result of the assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise is:
- Established indicators of the financial situation.
- Revealed changes in the financial condition of the company in the spatial and temporal context.
- Identified the main factors that cause changes in the financial condition.
- Conclusions and forecast on the main trends of changes in the financial condition of the company [7, с. 247–251].
In order to ensure the survival of the enterprise in modern conditions and, especially in the conditions of the global financial crisis, management personnel must, first of all, be able to realistically assess the financial condition of both their enterprise and existing potential competitors.
Currently, there are many methods, criteria for assessing the financial situation, characteristics of the flow of economic processes, which include:
- methods developed on a system of coefficients;
- methods containing integral indicators;
- techniques containing systems of inequalities;
- multidimensional statistical methods and elementary economic and mathematical methods and models [22].
It is also possible to assess the financial condition of an enterprise by analyzing accounting statements. It includes the use of various techniques and methods, which include:
1) grouping method;
2) graphical method;
3) index method;
4) the dynamics series.
The indicators calculated on the basis of the company's balance sheet are static indicators, since financial statements data at a certain point in time were used to calculate them. The values of the reporting indicators at a certain moment may be unusually large or unusually small, and in this case the calculated coefficients will not reflect the real ability of the enterprise to pay off its debts. Calculation of indicators using cash flows will smooth out the static nature of the previously considered indicators, analyze the real solvency of the enterprise.
Financial condition analysis specialists are united by a common approach based on the use of the method of analytical coefficients. It boils down to the calculation of coefficients and indicators according to the reporting data, the number of which is on average from 50 to 200 pcs. Recently, there has been a tendency to create a system of indices and coefficients that determine all aspects of the company's activities, which led to an increase in the calculated indicators several times. Other authors consider the main ability to correctly evaluate the results of the calculation. At the same time, they try to minimize the number of indicators (9-14 criteria).
The practice of financial analysis has developed the following main methods of its implementation:
1) horizontal analysis — analysis of dynamics. It is a comparison of each item of the current reporting with the reporting parameters of the previous period;
2) vertical (structural) analysis — allows you to determine the structure of the final indicators with the identification of the impact of each reporting position on the result as a whole;
3) comparative analysis — comparisons with competitors' positions, with planned indicators, with average industry data;
4) factor analysis — analysis of the influence of individual factors, causes on the effective indicator;
5) coefficient analysis — determination of correlations of indicators.
Economists divide all assessment methods into traditional analysis and factor analysis of financial condition, shown in Figure 1.4.
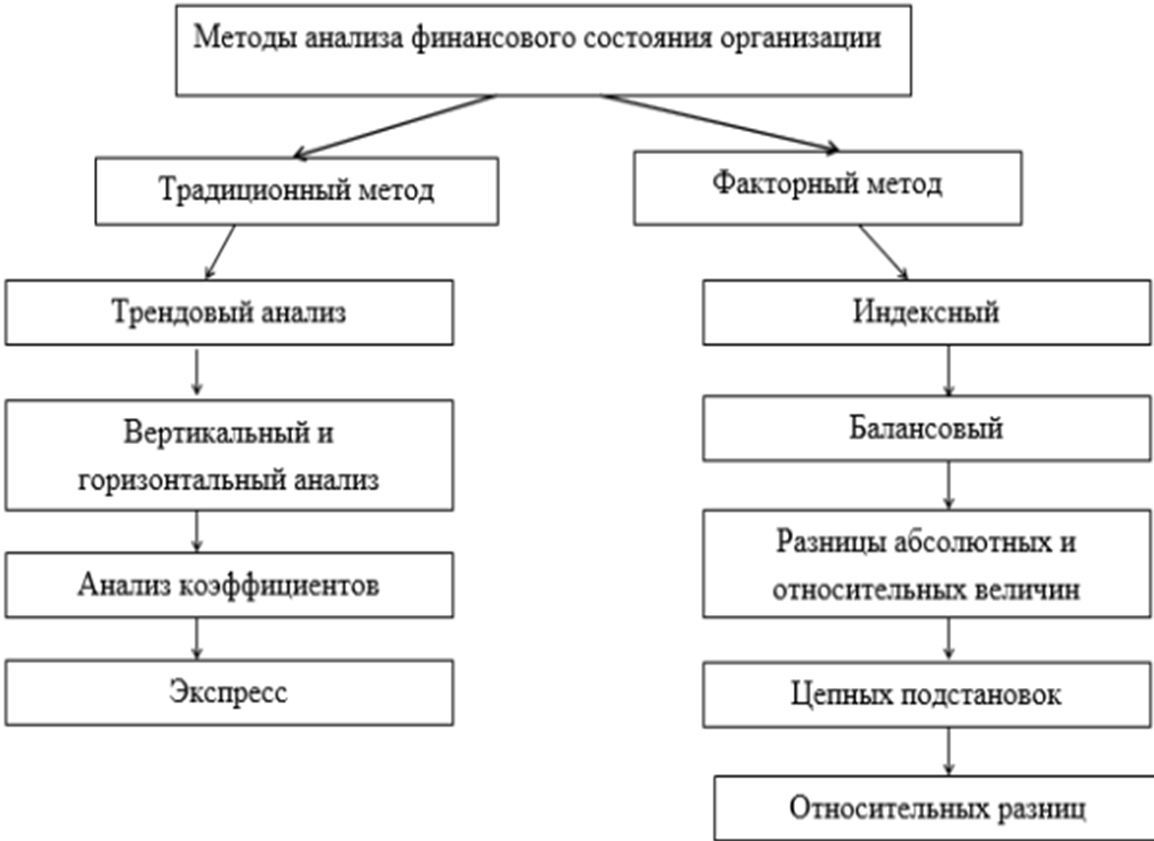
Figure 1.4 - Methods of financial condition assessment
Figure 4 shows the basic methods for determining the evaluation of the effectiveness of the organization. The traditional method is used to study the dynamics and composition of technical, economic and financial indicators. The factorial method is used to investigate the causes of changes in technical, economic and financial indicators. This method is used to analyze internal financial analysis, while using the method of chain substitutions. Factor analysis reveals the influence of factors on individual financial results that negatively affect the organization in order to understand the cause of the factor [21].
The analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise is completed with its comprehensive assessment. After a comprehensive assessment, measures are developed to improve the financial condition, paying special attention to the development of the company's financial strategy for the future and in the coming periods. The result of the financial analysis is mainly recommendations aimed at improving the financial condition of the enterprise.
The methods of analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise, set out in the works of A. D. Sheremet, E. V. Negashev, V. V. Kovalev, O. V. Efimova, G. V. Savitskaya, L. T. Gilyarovskaya, N. N. Selezneva, etc., are intended primarily for internal users of financial statements. Employees of accounting services of enterprises, managers, financial directors, auditors can conduct a full analysis of the financial condition of enterprises using any of the selected methods. However, when choosing a technique, it should be taken into account that, as practice shows, the results can be contradictory.
It should be noted that for the most complete and satisfactory analysis, the use of any one of these techniques will not be enough. In order to obtain better and more specific results of the analysis, we recommend combining various methods depending on the goals set by the enterprise. We also believe that the main thing in the analysis is not the number of indicators, but their qualitative content and the ability to reveal the level, dynamics of the financial condition and identify the reasons that influenced its change.
1.3 The system of indicators and information support for the analysis of the financial condition
Currently, a huge number of indicators used to quantify the state of enterprises are known in the world accounting and analytical practice. Indicators of the financial condition of the enterprise are divided into two main categories: volume and relative. The latter are called financial ratios or financial indicators. Financial indicators characterize the proportions between different reporting items. The advantages of financial coefficients are the simplicity of calculations and elimination of the impact of inflation.
The various indicators are related to each other and reflect a view from only one of several possible points of view of the enterprise. Therefore, they talk about a system of financial indicators. Among the volume indicators of the company's activity are used:
- The currency of the balance.
- The company's own or paid-up authorized capital.
- Net assets of the enterprise.
- Sales volume (sales revenue) for the period.
- The amount of profit for the period.
- Cash flow for the period.
- The structure of cash flow by type of activity.
Financial ratios are divided into several groups:
- Solvency (liquidity) coefficients.
- Profitability coefficients.
- Turnover coefficients.
- Financial stability coefficients.
- Profitability coefficients.
- Labor efficiency coefficients.
Profitability and profitability indicators are considered separately. This is due to the fact that in the first case, the efficiency of the current (main) activity of the enterprise is analyzed, that is, income and costs associated with their receipt are compared. In the second case, we are talking about the efficiency of the use of capital (assets) as a whole.
Financial ratios do not capture differences in accounting methods, do not reflect the quality of the components. Finally, they are static. It is necessary to understand the limitations that their use imposes and treat them as an analysis tool.
In the process of analysis, the level and dynamics of relative indicators of financial condition are studied. Absolute indicators calculated on the basis of financial statements (net assets, own working capital, etc.) also play an important role in the analysis.
In turn, on the part of the state (the fulfillment of tax obligations by the enterprise), the answer to the question of whether the enterprise is capable of paying taxes is important. Therefore , from the point of view of the tax authorities , the financial situation is characterized by the following indicators:
1) balance sheet profit;
2) return on assets = book profit as a percentage of the value of assets;
3) profitability of sales = balance sheet profit as a percentage of sales revenue;
4) balance sheet profit per 1 ruble of funds for labor remuneration.
Since the interests of management, owners, creditors or potential investors lie in different planes, it is recommended to include different indicators depending on who the information is being prepared for in the analysis system.
To obtain a holistic assessment of the enterprise, various volume indicators and financial coefficients are combined (taking into account the weight and significance of each of them) into complex (composite) indicators of financial condition.
When assessing the financial condition of an enterprise based on a system of indicators, it becomes inevitable to compare the actual level of indicators with their normative values. The importance of having normative values of indicators is due to the tasks of analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise. In particular, the regulations make it possible to:
a) to assess the stability of the financial condition of the analyzed enterprise; — to identify the nature of changes in the financial condition of the enterprise as a result of the implementation of a certain volume of transactions in the course of economic activity;
b) establish a list and the size of the influence of factors on the values of indicators of the financial condition of the enterprise obtained as a result of economic activity that differ from the normative values;
c) develop, if necessary, measures to adjust, change the financial condition of the enterprise. In the economic literature, two approaches to the establishment of normative values of indicators are proposed.
The most common currently is the use of standards established by the experimental statistical method. It is based on observations of trends in the financial ratios of successfully operating enterprises. The purpose of using this method is to establish standard values of indicators, the achievement of which guarantees the stability of any company's financial condition.
The experimental statistical method is also used in determining the standards of indicators of enterprises by industry. Standards in this situation can be established on the basis of statistical processing of an extensive range of data from domestic and foreign companies in the relevant industries. However, this method does not in all cases allow us to identify reserves for improving the financial condition of the enterprise and the efficiency of the use of property.
Another approach to the establishment of normative values is the use of an analytical and computational method. It provides for a preliminary study of the economic processes of the property structure established at the enterprise and its sources of efficiency in the use of capital advanced into the property. With this method, the financial condition of the enterprise subject to rationing is divided into its constituent structural elements, a thorough analysis of the actual values of these elements is carried out, then on the basis of this analysis, an appropriate calculation of the normative value of generalizing and particular indicators characterizing liquidity, solvency, financial stability and efficiency of the use of the enterprise's property is made. Its essence is to calculate the normative values of indicators based on technical and economic calculations.
To make the most effective management decisions aimed at improving the financial condition of an industrial enterprise, an appropriate information base is needed. Financial accounting data form the basis of information support for financial condition analysis. On the basis of these data, a generalized analysis of the financial condition is carried out, and forecast estimates of the values of the main financial indicators are developed [24, с.192].
All data sources for assessing the financial and economic activities of the company are divided into:
- planning and regulatory;
- accounting;
- off-the-books.
Planning and regulatory sources include all types of plans (prospective, current, operational, etc.), as well as regulatory materials, estimates, prices, tariff rates, price tags, etc. Planned data are usually used as a comparison base when assessing the actual state of affairs.
Non‒accounting sources of information are documents that regulate the activities of an economic entity, as well as data characterizing the external environment of the company's functioning and data from special surveys. Unrecorded sources of information include: materials of external and internal audit; materials of inspections of tax authorities; explanatory and memos of middle managers of enterprise management; materials obtained as a result of personal contacts with performers; materials published in the press, etc.
This also includes any other information that may be useful to a specialist when making managerial decisions. Sources of non-accounting information are information published in the media (newspapers, magazines, television), the Internet, stock bulletins, statistical collections, etc.
Accounting sources of financial analysis have five types of accounting data. Let's depict them in Figure 1.5.
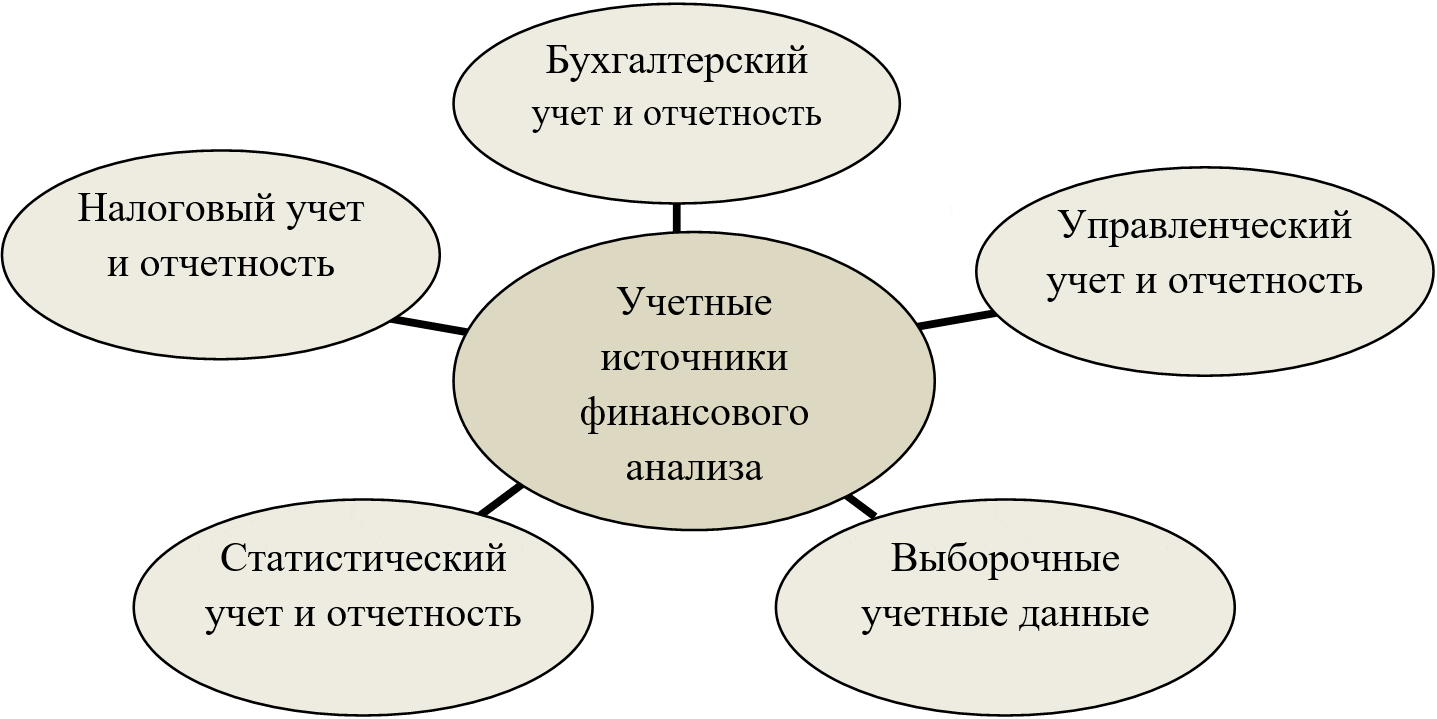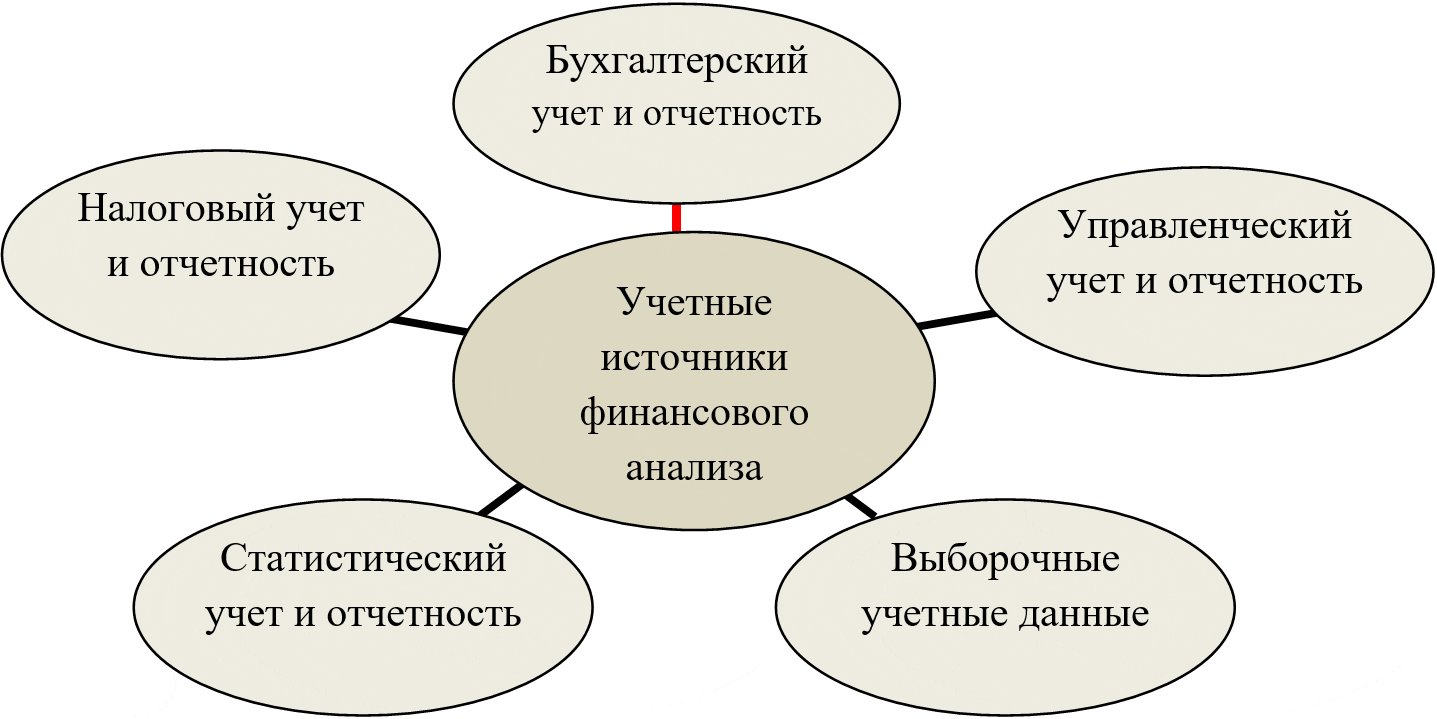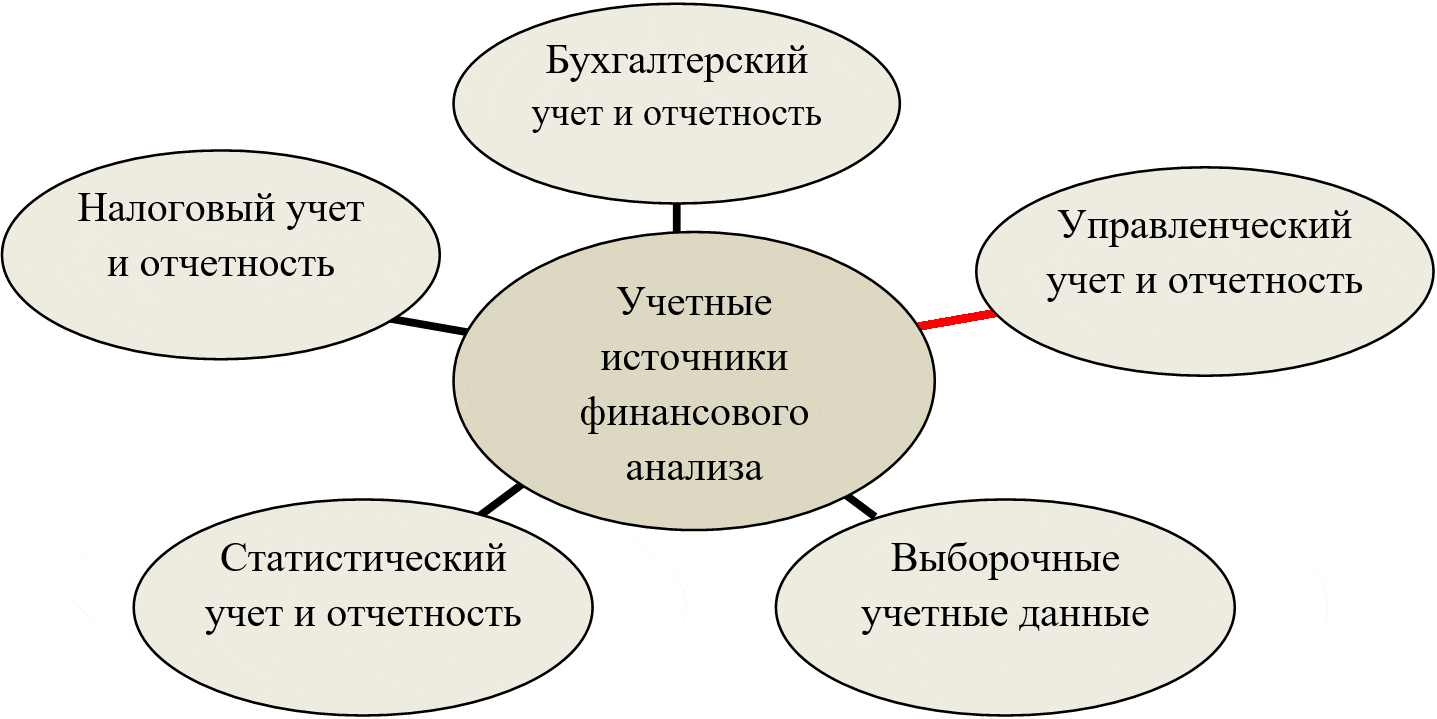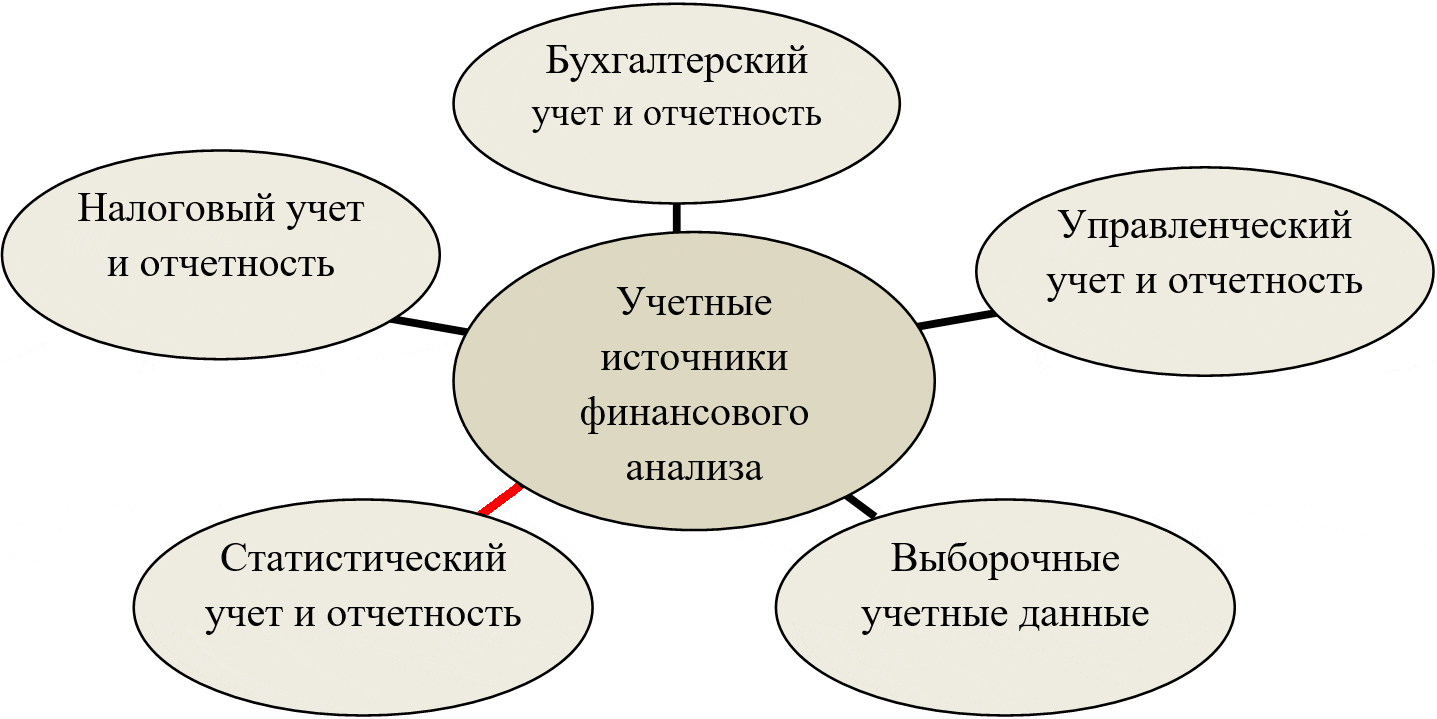
Figure 1.5 - Accounting sources of financial analysis
From Figure 1.5, we see that the sources of accounting are data containing accounting, operational and statistical accounting documents and all types of reporting, including primary accounting documentation.
The most complete information system of the enterprise that records almost all business transactions is the accounting system.
The main task of accounting statements is to identify all the facts that may affect the users' assessment of information about the state of ownership, financial situation and financial results of the company. Accounting and reporting plays a leading role in the information support of financial analysis.
Due to the fact that the national peculiarities of doing business in a particular country may differ significantly from other states, and accounting statements are the only available and indicative source of information, almost all scientists and practitioners say that it is necessary to establish a number of fundamental recommendations for its formation and interpretation.
A certain unity of accounting and reporting principles is achieved by introducing the so-called International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which are developed by the Committee on International Financial Reporting Standards (IASB).
These standards have been adopted in almost all economically developed countries. It is expected that adherence to the uniform accounting rules, calculation of financial results and preparation of accounting and financial statements recommended by IFRS will ensure sufficient clarity of reporting data, their presentation and unambiguous interpretation in the international context [25, p. 68].
In modern conditions, uniform accounting forms have been established for all enterprises and commercial organizations that are close to international standards, which creates conditions for the unification of analytical work.
Accounting statements of organizations, with the exception of reports of budget organizations, consist of: balance sheet; profit and loss statement; appendices to them provided for by regulations; audit opinion on the reliability of accounting statements; explanatory note. A comprehensive analysis of accounting statements allows us to identify the main trends in the property and financial condition of enterprises and take the necessary measures to improve it.
Selective accounting data helps to detail the reporting indicators and make the analysis more in-depth and representative. They should be considered as a source of accounting nature, since the necessary data are taken from the general ledger and registers of synthetic and analytical accounting.
Financial analysis is not only the main source of informative data, but also allows you to establish the advantages and disadvantages of the current system of analytical information.
An indispensable condition for a complete qualitative analysis of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise is the ability to read and analyze financial statements.
The relationship of financial analysis with its informative base lies in the fact that in the process of analysis, control is exercised over the information itself, which serves as the basis for conducting analytical work.
The objectivity of the reflection of economic processes is the most important requirement for information obtained from accounting and reporting data. Due to the transparency of reporting, the results of the analysis fully and reliably reveal the picture of the financial situation of the organization, contributing to the correct management decision-making in order to strengthen the financial position of the enterprise.
List of sources
- A.N.Litvinenko Economic and national security: the problem of correlating concepts // Scientific and Technical Bulletin of St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University. Economic sciences. 2013. №3 (173).
- A.N.Lyashenko, Specific properties of financial security of the enterprise (Text)/ A.N. Lyashenko // Project management and production development. - 2012. - No. 4. – pp. 1-7
- N.V.Manokhina Economic security: A textbook / N.V. Manokhina, M.V. Popov, N.P. Kolyadin, I.E. Zhadan. – M.: SIC INFRAM, 2016. – 320 p.
- M.O.Musataeva Sources, types and factors of threats to economic security, the creation of an economic security service // Scientific and methodological electronic journal Concept. – 2015. – Vol. 23. – pp. 26-30.
- On state supervision in the sphere of economic activity: Law of the DPR No. 76-IHC of August 21, 2015 – Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. – System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- On Industrial safety of hazardous production facilities: DNR Law No. 54-IHC of June 05, 2015 – Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. – System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- On information and information technologies: DNR Law No. 71-IHC of August 07, 2015 – Donetsk : [B.I.], 2015. – Systems. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- On remuneration: DPR Law No. 19-IHC of March 06, 2015 – Donetsk : [B.I.], 2015. – System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- About vacations: Law of the DPR No. 16-IHC of June 06, 2015 – Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. – System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- On labor protection: Law of the DPR No. 31-IHC of April 03, 2015 – Donetsk : [B. I.], 2015. – System. Requirements: Acrobat Reader. – Title. With a title. The screen.
- E.L.leynikov Economic and national security / E.L. Oleynikov. – M.: Exam, 2014. – 182 p.
- R.S.Papekhin / Factors of financial stability and security of the enterprise: abstract of the dis. ... Candidate of Economic Sciences/; [Place of protection: Volgogr. State. Un-t]. – Volgograd, 2017. – 21 s
- I.M.Podvolodina, Voronin V. P., Approaches to the assessment of economic security of enterprises // Vestnik VGUIT. – 2017. – No. 4. – pp. 47-49.
- M.L.Pyatov Development of elements of the accounting policy of the organization // Accounting, - 2017. – No. 5. – pp. 15-18.
- N.I.Reverchuk / The influence of marketing security on the business reputation of an enterprise /// Reverchuk N.I. Dzyamulich E.C / Universum: Economics and jurisprudence. 2014. №5 (6).
- G.V.Savitskaya Analysis of economic activity of enterprises – Mn.: Novoe znanie, 2015 – 85 p.
- Modern methods of managing the economic security of organizations / V. P. Mac-Mac ; M-vo of education of the Moscow region, Academy of Social Sciences. Upr., Kaf. Obshch. Management. – Moscow : ASOU, 2015. - 175
- O.N.Sorokina Essential characteristics of financial security of the enterprise // Almanac of modern science and education. - 2015. – No. 6. – pp. 224-225.
- A.V.Sorokov Economic security: actual problems of modernity // "Legal initiative" – 2016. – No.9. – p. 45.
- L.A.Trofimova Economic indicators used to assess the effectiveness of the enterprise // Auditor. – 2016. – No. 9. – p. 12.
- O.A.Firsova Economic security of the enterprise / Publisher Litagent "MABIV", 2017. – 220 p.
- A.D.Sheremet, Finance of enterprises: textbook/ A.D. Sheremet, R.S. Saifulin. – M.: INFRA–M, 2015. – 589s.
- V.V.Shlykov Complex provision of economic security of the enterprise / V.V. Shlykov. – St. Petersburg: Aleteya, 2019. – 237 p.
- Economic security: textbook for universities / under the general editorship of L.P. Goncharenko, F.V. Akulinina. – M. : Yurayt Publishing House, 2015. – 478 p. – Series : Specialist
