Abstract
Сontents
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Theoretical aspects of product quality management in the enterprise
- 3. Analysis of the activities of the enterprise branch No. 3 «MMZ» CJSC «VNESHTORSERVICE»
- 4. Development of recommendations for the implementation of Lean manufacturing technology at the enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
One of the most important factors in the growth of production efficiency is the improvement in the quality of products or services provided. Improving the quality of manufactured products is currently regarded as a decisive condition for its competitiveness in the domestic and foreign markets.
Lean manufacturing is a way of organizing production, which includes the optimization of production processes, focusing on customer needs, improving quality and saving up to 10% of the company's annual turnover by reducing costs.
Purpose of the study - development of recommendations for the implementation of lean production at Branch No. 3 "MMZ" of CJSC "Vneshtorgservis".
Research objectives:
- Analyze the theoretical and methodological aspects of product quality management at the enterprise.
- Investigate the activities and financial condition of the enterprise Branch No. 3 "MMZ" ZAO "Vneshtorgservis".
- Develop recommendations for the implementation of lean manufacturing at the enterprise of Branch No. 3 "MMZ" of CJSC "Vneshtorgservis".
Object of study: Branch No. 3 "MMZ" CJSC "Vneshtorgservis".
Subject of study:approaches to improve the efficiency of the enterprise by improving product quality management based on lean manufacturing methods.
1. Relevance of the topic
In a market economy, the problem of ensuring the quality of products of an enterprise - manufacturers is fundamental, many scientists study it and develop new systems and technologies.
One of the most important factors in the growth of production efficiency is the improvement in the quality of products or services provided. Improving the quality of manufactured products is currently regarded as a decisive condition for its competitiveness in the domestic and foreign markets. The competitiveness of products largely determines the prestige of the country and is a decisive factor in increasing its national wealth.
The growth of the technical level and quality of products is currently the most characteristic feature of the work of enterprises in industrialized countries. In conditions of prevailing non-price competition and a saturated market, it is the high quality of products that is the main success factor.
The quality of manufactured products can rightfully be attributed to the most important criteria for the activity of any enterprise. It is the improvement of product quality that determines the degree of survival of the company in market conditions, the pace of scientific and technological progress, the growth of production efficiency, the savings of all types of resources used in the enterprise.
An increase in the production of high-quality products by enterprises should ultimately lead to the intensification of the economy, an increase in the living standards of the population, and an increase in the competitiveness of goods in the markets. Modern enterprises need to learn how to more effectively use economic, organizational and legal levers of influence on the process of forming, ensuring and maintaining the required level of quality at all stages of the product life cycle.
One of the ways to improve the quality of products at the enterprise is the concept of lean manufacturing, which is gaining popularity among the countries of the world every year. This concept helps to optimize costs, increase the productivity of available resources, as well as improve the quality of products.
Lean manufacturing methods are very effective for processes that do not create value. Therefore, today the development of new and improvement of existing methods of cost optimization, as well as approaches to the formation of information on costs for the purpose of making informed management decisions, is of particular relevance.
2. Theoretical aspects of product quality management in the enterprise
One of the most important factors in the growth of production efficiency is the improvement in the quality of products or services provided. Improving the quality of manufactured products is currently regarded as a decisive condition for its competitiveness in the domestic and foreign markets.
Quality management is not just a functional area of the organization, but its strategic direction, business philosophy. Quality management is directly related to the degree of customer satisfaction with the products produced, and therefore has a direct impact on the profitability of the company and its market success. The goal of product quality management is to improve the process and successfully complete it.
The goals should correspond to the functions and principles of management (scheme 1), which are formulated in MS ISO 9001:2015 series. The implementation of these principles by the organization will indicate that the organization can create an effective process-oriented management system.
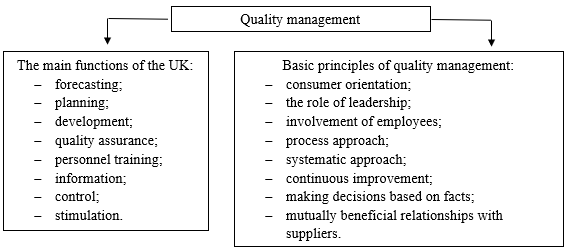
Scheme 1 – Main functions and principles of quality management
The well-known scientist Williams Edwards Deming, who proposed the following approach to the study of quality control, studied the principles listed above. This approach became known as the "Deming cycle", or PDCA, in which he identified four main stages - "plan, implement, check, act" [1].
This cycle is often referred to as the PDCA (Plan-Do-Control-Act) cycle. Deming preferred to call it the PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) cycle, but that name never caught on. [2].
Any quality management system is based on the application of progressive quality management methods. A method is a set of rational actions that must be taken to solve a specific problem or achieve a specific goal [3]. The main methods of product quality management are presented as follows (tab. 2). They are actively used in modern enterprises. Lean manufacturing is gaining popularity.
| Method name | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Six Sigma Method | An approach to improving the production process by finding and eliminating the causes of errors or defects in business processes, focusing on critical output parameters for the consumer. |
| Lean manufacturing | It is an approach to managing an organization aimed at improving the quality of work by reducing waste. This approach extends to all aspects of activity - from design and production, to product marketing. |
| Balanced Scorecard | A system of strategic management of a company based on measuring and evaluating its effectiveness on a set of optimally selected indicators that reflect all aspects of the organization's activities, both financial and non-financial. |
| Reengineering | Radical rethinking and redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic, incremental improvements in key modern company performance indicators such as cost, quality, service and pace. |
| Self-assessment | A comprehensive and systematic review of the company's principles of operation and the results it achieves, carried out considering the business development model that the company implements. |
The use of these methods will help not only improve the functioning of the quality management system, but will also help to increase the efficiency of enterprises, and, consequently, reduce various types of losses.
The most urgent problem of enterprises is the search for ways of economic growth, taking into account national characteristics. According to the theory of the American economist and historian, Walt W. Rostow, the way out of a state of underdevelopment can be described by a series of steps or stages through which any country must pass. This conclusion was obtained as a result of studying the economic history of developed countries that have passed through the stage of a breakthrough towards self-sustaining growth. As for other countries, they are at the stages of either a traditional society or the maturation of the prerequisites for a breakthrough. One of the main conditions is the mobilization of domestic and foreign investments to accelerate economic growth [4].
The key goal of lean manufacturing is to move towards lean and efficient manufacturing with a culture of continuous improvement. Accordingly, lean production acts as the most successful combination of advanced management ideas of recent decades, which is the result of systematization of the experience of organizing the production process of the world's leading companies, such as Toyota, General Electric, Ford. In general, lean manufacturing is a management technology, the basis of which is to reduce costs, increase efficiency and increase customer satisfaction. [5].
The principles and tools of «lean manufacturing» are designed to be implemented in the production systems of commercial enterprises, the main goal of which is to minimize costs and maximize profits. [6]. It is undoubtedly important to introduce this concept in an enterprise, but one should also be able to evaluate the effect obtained from the implementation.
For «lean production» the most significant are the performance and efficiency indicators, for their calculation indicators can be used that can be classified according to three criteria:
- External manifestation, that is, the value for the consumer of the results of the enterprise.
- Internal manifestation, that is, due to which direction of activity «thrift» is ensured.
- The specific lean manufacturing tool used.
Indicators of the external manifestation of the results of the enterprise, and the priorities for their improvement, of course, are achieved by "internal quality" or in accordance with the classification. Indicators of internal manifestation are classified into four groups of features: system-wide significance; the share of costs for creating the value of the product in its production; share of logistics costs; the level of «freezing» of capital [7].
Each of the classification features is evaluated by a number of particular indicators. Of course, the proposed groups and indicators included in them do not claim to be complete, universal, and even more so mandatory for use. This should be determined by the enterprise itself, again taking into account the specifics and features of the products and processes being carried out. When forming the proposed indicators, on the one hand, the ideological approaches used in «lean production» (combating all types of losses) were taken into account, and, on the other hand, it was taken into account that with the least number of indicators, a sufficiently reasonable management decision could be made. internal improvements [8].
Having studied the main aspects of «lean production», we can draw the following conclusions (tab. 2) [9].
| № | Name of value | Essence of value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Safety | Considered from the point of view of the priority of the life and health of personnel, safety concerns the production processes and other organizational processes. |
| 2 | Value for the consumer | Identifying customer requirements for products and services in a timely manner, monitoring changing customer needs and creating value they are willing to pay for. |
| 3 | Customer focus | Measures to retain existing customers and identify their new needs, attracting new customers. |
| 4 | Loss reduction | The elimination of losses is considered as the main condition for the competitiveness of the organization, and therefore the head of the organization must involve all staff in reducing all types of losses. |
| 5 | The value of time | Excess time that is spent on the performance of work or the provision of services subsequently turns into significant losses. |
| 6 | Respect for the person | Human resources are one of the main sources of value creation for the consumer, only the staff provides success to the consumer. |
Lean manufacturing is now universally recognized as the most efficient, reliable and low-cost way for companies to get out of the crisis and increase their competitiveness on a global scale.
3. Analysis of the activities of the enterprise branch No. 3 «MMZ» CJSC «VNESHTORSERVICE»
The metallurgical plant was founded in 1898 by the French joint-stock company «General Society of iron-smelting, iron-working and steelworks «Russia» for the production of sheet and long products. »
In recent years, the plant has changed forms of ownership from state to rental and vice versa, it was a plant then a combine and vice versa.
Since March 28, 2017, Makeevka Metallurgical Plant has been Branch No. 3 of CJSC Vneshtorgservis (hereinafter Branch No. 3 MMZ of CJSC Vneshtogrservis).
The main activity is the production of rolled metal and rail fastenings, blanks, processing of ferrous metal scrap: wire rod, angles, channels, reinforcing bars, round bars, PK terminal [10].
The main workshops and equipment of the enterprise consists of a rolling shop, which includes a billet acceptance, processing and shipment section, a continuous low-section mill 150, a continuous section mill 390, a section for shipment and finishing of finished rolled products, a rolling section, a section for the production of rail fasteners, a section POS, fire cutting departments, press departments.
It is important for any business to really see the levers that it can manage - the company's internal resources, as well as to understand the factors that are outside the impact zone - external threats. Simply understanding these points already saves budget and time.
To begin with, let's build a general matrix that includes the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, as well as opportunities and threats from the external environment (tab. 3).
Table 3 - SWOT-analysis of the enterprise «MMZ» CJSC «Vneshtorgservis».
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|
|
|---|---|
| Opportunities | Threats |
|
|
Thanks to SWOT analysis, you can design a strategy for an enterprise, services and its products. This algorithm can also be applied for personal introspection of the enterprise and its professional growth. You can also highlight the competitive advantages of the environment of competitors.
In table. 1 we see the levers that we can manage - the internal resources of the enterprise, and also understand the factors that are outside the zone of influence, that is, external threats to the enterprise. Simply understanding these points can significantly save the company not only the budget, but also time, which is a very important factor.
4. Development of recommendations for the implementation of Lean manufacturing technology at the enterprise
The system of lean manufacturing is extremely specific. In order to rebuild production, you first need to put things in order in the existing system, eliminating the most obvious "leaks", that is, minimizing hidden losses, nullifying unhelpful actions. Thus, efficiency will increase and management will improve in other areas. Therefore, it is necessary first of all to determine the main types of possible losses in production.
The company recommends the use of two lean manufacturing tools - the 5S system and Kanban.
By implementing the 5S system in fact, when changing the workplace, you can get several types of results:
- First, you can reduce the time of production operations (for example, the time it takes to make a part).
- Secondly, it is possible to reduce the time for performing non-production or auxiliary operations (for example, preparation for work, changeover, cleaning the workplace).
- Thirdly, the level of rejects can be reduced (for example, by reducing the number of errors when choosing a tool or part).
- Fourth, work safety can be improved.
The direct economic effect can be calculated quite rarely, because. even if it is possible to reduce the time of performing the main production operations, that is, as a result of improving the organization of the workplace, to produce more parts or finished products, the enterprise will not necessarily receive additional profit from this. Perhaps the company can only sell a certain amount of products, and then the production of additional units of products will not bring profit, but only increase the stock of finished products, which will also need to be done with.
A reasonable assessment of the potential result can only be given by having a ready-made example with similar initial conditions in front of you - too many factors affect the final result. The same proposals can be accepted and rejected by different people and different teams, depending on how objectively or subjectively the actual result is evaluated.
Let's calculate the economic efficiency of using the Kanban tool in Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis» to justify the feasibility of implementing the proposed measures (tab. 4).
| Accountable figures | Calculation method | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing the labor intensity of production as a result of the introduction kanban tool | ΔТgen. = ∑Nyear (tth1 - tth2), Nyear – annual output in physical terms; Tth1, tth2 – the norm of time for the manufacture of a unit of production (hours). | ΔТgen = 477938 • (0,0481 - 0,0291) = 9080,822 n/h |
| Relative (conditional) release number of workers by reducing labor intensity | ΔR = (ΔТgen / (F half a year • К a.n)), F half a year. – annual useful working time fund of the 1st worker (hour); К a.n – coefficient of fulfillment of production norms. | ΔR = (9080,822 / (1769 • 1)) = 5,13 |
| Reduced labor intensity production unit products, % | а = 100(1 - (tth1 / tth2)), а – reduction in labor intensity, % | а = 100 • (1 - 0,70) = 30% |
| Performance Boost labor (production) on the basis of reducing labor intensity, % | ΔPB = ((100 • а) / (100 - а)) | ΔPB = 1352 - 70 = 19,31% |
| Relative (conditional) release of numbers workers by increasing use of basic workers | ΔR = Rorig (1 - (F half b. imp. / F half a. imp)) , Rorig – initial population personnel; Fhalf. – useful fund of working time of one worker before the introduction of organizational and technical measures and after. | ΔR = 1981 • (1 - (1544 / 1581)) = 46,4 |
| Performance Boost labor as a result of savings in the number of employees | ΔPB = ((ΔR • 100) / (Rorig - ΔR)) | ΔPB = ((46,4 • 100) / (1981 – 46,4)) = 2,46% |
The data in table 4 show that as a result of the introduction of the Kanban system, there is an increase in labor productivity as a result of saving the number of employees by 2.46%; the labor intensity of production of a unit of production decreased by 30%; the relative (conditional) release of the number of workers by reducing labor intensity amounted to 5 people, by increasing the use of the main workers - 46 people. Thus, the introduction of the proposed recommendations, namely the Kanban system, into the activities of Branch No. 3 "MMZ" of CJSC "Vneshtorgservis" is expedient, which is justified by the results of calculating the economic efficiency. And the 5S system will serve as an additional improvement in combination with the Kanban system.
To calculate the economic efficiency from the introduction of lean manufacturing tools, we will use statistics on the metallurgical industry [12]. According to the improvement observed from 10 to 30%. Considering the factors that affect the activities of the enterprise and possible threats, the strengths and weaknesses of Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis», we will take 12% and calculate all the main indicators of the enterprise, analyze the result of changes in the situation at the enterprise after the introduction of lean production.
Let us determine the overall economic effect that will be reflected in the main indicators of the enterprise after the introduction of lean production tools (pic. 5).
| № | Name of indicator | Values | Percent change, % | |
| No events | With events | |||
| 1 | Headcount, persons | 1981 | 1743 | -12 |
| 2 | General labor costs, man-hour | 1581 | 1391 | -12 |
| 3 | Unproductive losses, including, man-hour: | 46,4 | 40,8 | -12,1 |
| 3.1 | from overproduction | 12,4 | 10,9 | -12,1 |
| 3.2 | elimination of defects | 18,7 | 16,5 | -11,8 |
| 3.3 | from expectations | 15,3 | 13,5 | -11,8 |
| 4 | Unscheduled downtime, hour: | 519,12 | 456,8 | -12 |
| 4.1 | Mill 150 | 254,56 | 224 | -12 |
| 4.2 | Mill 390 | 264,56 | 232,8 | -12 |
| 5 | Production waste, t: | 789,69 | 694,9 | -12 |
| 5.1 | Mill 150 | 364,56 | 320,8 | -12 |
| 5.2 | Mill 360 | 425,13 | 374,1 | -12 |
| 6 | Labor productivity, % | 78 | 87,4 | 12,1 |
| 7 | General indicator of production losses, % | 37 | 32,57 | -12 |
| 8 | Product quality, % | 75 | 84 | 12 |
According to table 5, the following conclusions can be drawn: the headcount will be reduced by 12% due to the introduction of the Kanban system, which will reduce personnel costs; unproductive losses decrease by 12.1%. Unscheduled downtime, which increased over the three year period, will be reduced by 12%, resulting in increased output at both mills. So it should be noted that production waste at two mills 150 and 390 will be reduced by 12%, which contributes to the economical use of resources at the enterprise (tab. 6). Labor productivity will increase by 12.1%. Since the concept of lean manufacturing is aimed at reducing all types of waste, then, in general, this figure will reach 12% in the first year. And the quality of products after the introduction of lean manufacturing technology will increase by 12%.
For the enterprise Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis», two main measures were developed and economically justified:
- The introduction of the 5S system, which will help reduce the number of accidents, improve product quality and reduce the number of defects, create a comfortable psychological climate and stimulate the desire to work, unify and standardize jobs, increase labor productivity by reducing the time it takes to search for items within the workspace.
- Implementation of the Kanban system, which will create a quality product in a timely manner, providing control at every stage of production.
Assessing the economic effect of the implementation, we found that the main indicators of the enterprise will improve by 12%, which will lead to an improvement in its activities and will further improve its work.
Conclusion
Quality management in an enterprise is a management activity to ensure the design, manufacture and sale of goods that have a sufficiently high degree of utility and satisfy consumer needs.
At the present stage of economic development, issues of increasing the efficiency of an enterprise through the use of modern management tools, in particular, the concept of "lean production", are of particular importance.
An effective method of improving quality management at the enterprise Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis» will be the introduction of lean production tools.
The introduction of Lean Production tools is the transition of the enterprise to a new, higher quality level, which involves the involvement of all employees of Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis» in the process. Product quality management of a manufacturing enterprise is an extremely urgent problem for modern enterprises.
Thus, the introduction of the proposed recommendations into the activities of Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis» is expedient, which is justified by the results of calculating the economic efficiency.
A forecast was also made for changes in the main production indicators, taking into account statistical data on the effect that is achieved at the enterprises of the metallurgical industry through the introduction of lean production. Namely, such indicators as the headcount, unscheduled downtime, enterprise waste, non-production losses will be reduced by 12%, which will improve the enterprise's performance and improve product quality.
In general, the introduction of lean manufacturing tools at the enterprise of Branch No. 3 «MMZ» of CJSC «Vneshtorgservis» will lead to its economic efficiency and will contribute to the growth of its competition in the market, by improving the quality of products and the operation of the enterprise as a whole. Not only by reducing unplanned downtime and reducing plant waste, but by reducing other types of waste, such as product transportation, defect handling, waiting times, and so on.
At the time of writing this essay, the master's work has not yet been completed. Final completion of construction: June 2023. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the specified date.
References
- Огвоздин, В. Управление качеством. Основы теории и практики: учеб. пособие / В. Огвоздин; Дело и сервис. – Москва, 2017 г. – 261с.
- Герасимова, Е.Б. Управление качеством / Е. Б. Герасимова, В. И. Герасимов, А. Ю. Сизикин – Москва: ФОРУМ: ИНФРЛ-М, 2007. – 256c.
- Деминг Э. Выход из кризиса: Новая парадигма управления людьми, системами и процессами / Э. Деминг // Выход из кризиса. – М.: Альпина Паблишер, 2012. – 419 с.
- Вумек, Дж. Бережливое производство: Как избавиться от потерь и добиться процветания вашей компании/ Дж. Вумек, Д. Джонс. – Москва: Альпина Паблишер, 2013. – 720 с.
- Погребняк, С. И. Бережливое производство. Формула эффективности / С. И. Погребняк. – Москва: Триумф, 2013. – 308 с.
- Макеевский металлургический завод ЗАО «Внешторгсервис», филиал №3 [Электронный ресурс]: DNR LIVE Деловой портал. – 2019. – № 000158 – Режим доступа: http://dnr-live.ru/companies/metallurgicheskiy-kompleks/makeevskiy-metallurgicheskiy-zavod-zao-vneshtorgservis-filial-3/. – Загл. с экрана.
- Чечевицына, Л. Н. Анализ финансово-хозяйственной деятельности / Л. Н. Чечевицына, К. В. Чечевицын // Ростов н/Д: Феникс – 2013 – C. 368.
- Николаева, А. Б. Оценка эффективности внедрения бережливого производства на промышленных предприятиях / А. Б. Николаева // Вестник экономики, права и социологии. – 2016. – №4. – С. 69- 72.
- Замбржицкая, Е. С. Оценка качества металлопродукции как элемент анализа конкурентоспособности металлургических предприятий / Е. С. Замбржицкая, А. Н. Шаповалов, Р. Р. Дема, М. В. Харченко // Бюллетень науки и практики. – 2019. – №9. – 262- 269.
- Романюк, Н. В. Особенности внедрения принципов всеобщего управления качеством в деятельности предприятия / Н. В. Романюк, Е. А. Романюк, А. А. Журбинова // Экономика и маркетинг в ХХІ веке: проблемы, опыт, перспективы : Сборник материалов XVII международной научно-практической конференции, посвящается 100-летию ДОННТУ, Донецк, 25–26 ноября 2021 года / Редколлегия: А.А. Кравченко [и др.]. – Донецк: Донецкий национальный технический университет, 2021. – С. 560-565. – EDN IXYYMO.
- Романюк, Н. В. Основные инструменты бережливого производства / Н. В. Романюк, А. А. Журбинова // Стратегия устойчивого развития в антикризисном управлении экономическими системами : Материалы VI Международной научно-практической конференции, Донецк, 08 апреля 2020 года. – Донецк: Донецкий национальный технический университет, 2020. – С. 136-140. – EDN UVAKVR.
- Романюк, Н. В. Анализ эффективности применения технологии бережливого производства на промышленных предприятиях ДНР / Н. В. Романюк, А. А. Журбинова // Экономика и маркетинг в XXI веке: проблемы, опыт, перспективы : Сборник материалов XVI международной научно-практической конференции: посвящается 100-летию ДОННТУ, Донецк, 19–20 ноября 2020 года. – Донецк: Донецкий национальный технический университет, 2020. – С. 96-101. – EDN DTDWDL.
- Романюк, Н. В. Роль человеческого фактора при внедрении концепции бережливого производства на предприятии / Н. В. Романюк, А. А. Журбинова // Стратегия устойчивого развития в антикризисном управлении экономическими системами : Материалы VIІ Международной научно-практической конференции, Донецк, 08 апреля 2021 года / Отв. редакторы О.Н. Шарнопольская, И.А. Кондаурова, Е.Г. Курган. – г. Донецк: Донецкий национальный технический университет, 2021. – С. 198-204. – EDN VNRVJR.
