Donetsk National Technical University (DNTU)

Moskaliuk Yelena Nikolayevna
 lady_love@land.ru
lady_love@land.ru
The Faculty of Computer Information Technology and Automation (CITA)
Speciality: Automated Control Systems (ACS)
Subject: "Designing a Computerized Optimization Subsystem of the Work of a Chemical Reactor (examplified by ammonia production)"
Supervisor: assistant professor of the ACS department Volodyn Nikolai Alexandrovich
| Biography |
| Dissertation |
| Library |
| Search data |
| Links |
| Individual task |
Dissertation
- Urgency.
- The review of the executed works.
- The list of problems solved in work.
- Automatic control of the unit of synthesis.
- Statement of a problem.
- Own development.
- Experimental researches.
- The review of results and conclusions.
- Prospects of the further researches.
- The list of the literature.
Now the basic intermediate product for reception of huge number various nitrogenated connections is ammonia, and its synthesis from hydrogen and nitrogen – a unique large-scale method of manufacture of this major product.
Production of ammonia – the fully-automated process. Management of the unit is concentrated in one central item of management with application of the computer. The uniform energotechnological circuit connects the block of synthesis of ammonia with the previous stages of process.
In a column of synthesis a plenty of heat which is used on heating of the feedwater directed for reception pair by pressure Ìpascal is allocated.
The number of the researches, putting the purpose the decision of problems of optimum control of process of synthesis of ammonia, last years has considerably increased. Generalization of the lead researches shows, that in working units most expediently introduction of optimum control by a temperature mode of a column of synthesis of ammonia.
The review of the executed works
The huge amount of works is devoted to problems of optimization. In particular huge amount of books of Kafarova V.V. in the field of modelling chemical processes, optimization heat-chemical processes, etc. There is an opportunity of development of a technique of the decision of the nonlinear differential equations with the help of Simulink, a package Matlab by the example of modelling chemical reactors.
Also it is possible to note, that there is a software (CR (catalytic Reactor) version 2000.9, Windows 9x/2000; DesK (Descriptive kinetics), version 2.0, Windows 9x/2000/NT; ForK (Formal kinetics) version 1.62, Windows 9x/2000/NT and so on) which basically is intended for the decision of the basic problems kinetics of reactions, modelling of carrying out of reactions.
The list of problems solved in work
The purpose of the given work is the decision of a problem of management in temperature of reaction by adjustment of a stream of heat on an external surface of walls of a reactor.
This problem is solved with use of extreme methods for problems of optimization.
Automatic control of the unit of synthesis
The circuit of the unit computer-controlled is shown by process of synthesis of ammonia on fig. At such management of the unit the following parameters of process are automatically adjusted: temperature in columns of synthesis; levels of liquid ammonia in a separator and condensation column; temperature of the gas leaving the ammoniac condenser; structure of circulating gas under the contents of inert impurity; delivery of liquid ammonia from rectifier on a warehouse; pressure in rectifier.
The general principle of action of system can be explained by the example of automatic control of temperature in a column of synthesis.
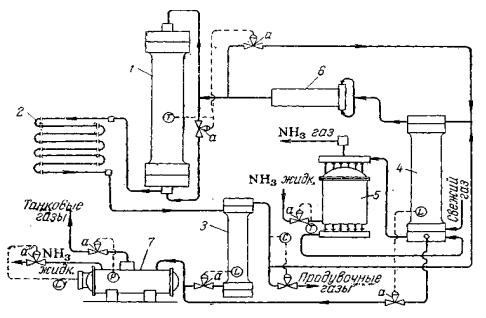
Fig. The unit of synthesis of ammonia computer-controlled:
1 – column of synthesis; 2 – the water condenser; 3 – a separator of liquid ammonia;4 – condensation column; 5 – the evaporator; 6 – the centrifugal circulating compressor; 7 – rectifier; 8 – the regulating valve; T – measuring instruments of temperature; L – measuring instruments of a level; P – a measuring instrument of pressure; C – a regulator of structure.
Electromotive force, arising in the thermocouple (sensor), it is proportional to temperature which is counted on a scale of the measuring device. The rejection of temperature from set will be transformed by the special device to a pulse of pressure of air, bringing in action system of regulation. The more the rejection, the is stronger the influence transmitted by a regulator to controls.
At rise in temperature the gate of cold by-pass opens, at decrease it is covered. If this reception of regulation does not result in rise in temperature at closed by-pass, regulation is made by change of volumetric speed. Thus the regulator starts to submit a signal on opening of the gate "long by-pass" owing to what the amount of the gas submitted in a column by the circulating compressor decreases.
Productivity of columns in many respects depends on a design of their nozzles which perfection is estimated by simplicity and reliability of work, and also an opportunity of creation of an optimum temperature mode of synthesis of ammonia. In an ideal case distribution of temperatures on height of a layer of the catalyst should correspond to an optimum temperature curve. For maintenance of an optimum mode the parity of the sizes preliminary heat exchanger and catalyst boxes should be correctly determined and heat removal from a zone of reaction is organized so that the opportunity as à overheating, and overcoolings of the catalyst was excluded.
To increase in a degree of use of gas in modern systems of synthesis À. apply repeated circulation of a nitric and hydrogen mix – a circular ammoniac cycle (see picture).
Fresh gas (nitric and hydrogen mix) and not reacted, so-called circulating gases act all over again in the filter where they are cleared of extraneous impurity, then in intertrumpet space condensation columns, giving heat to the gas moving on tubes of a column. Further gases pass through the evaporator in which there is their further cooling and condensation À., keen on circulating gases. The cooled mix of gases and constructed À. from the evaporator go to a dividing part (separator) condensation columns where liquid À. it is separated and as the ready product is deduced on a pipe in the tank. Gaseous À., leaving the evaporator, passing liquid trap, it is released from drops liquid À. and goes to shop of processing or in a refrigerating machinery on liquation. Gases, released from À., from a separator act in a column of synthesis. The column of synthesis inside has catalyst box with a tubular or half-internal nozzle and heat exchanger. Gases, passing through a column of synthesis, react among themselves; the gas mix leaving a column contains % A. Then these gases act in the condenser where occurs liquation A. Liquid À. is separated in a separator and acts in the tank, and not reacted gases move the circulating pump in the filter for mixture with a fresh àçîòî-hydrogen mix.
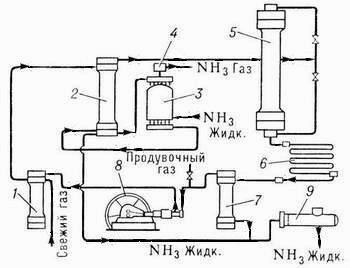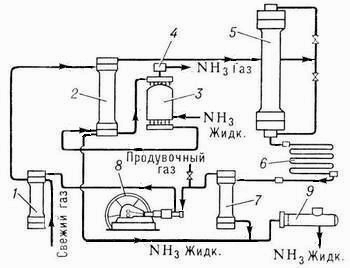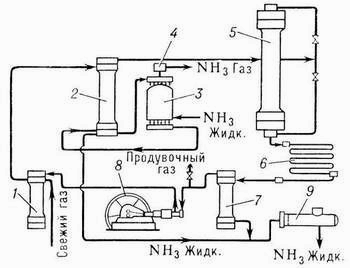
Fig. 2. The unit of synthesis of ammonia (the technological circuit)
Let there is a unit of synthesis of ammonia. Reaction in it proceeds with absorption of heat. All process should satisfy to an extreme temperature mode of reaction on an internal surface of walls of a reactor. Management in temperature of reaction we shall carry out adjustment of a stream of heat on an external surface of walls. Thus process of a heat transfer will be written down as:
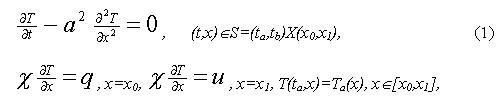
where a, c – factors temperature- and heat conductivities accordingly, Òà – reference temperature of walls.
A degree of a deviation of temperature Ò(t,x0) of reaction from the set extreme temperature we shall estimate by functional

The problem of optimum control of the given reactor of synthesis of ammonia it is formulated as follows. It is necessary to find the stream of heat u(t) delivering a minimum to functional J.
Following to the gradient approach to problems of optimization of systems with the distributed parameters the gradient of functional (2) can be found:

where f(t,x) – multiplier of Lagrang satisfying the connected problem:
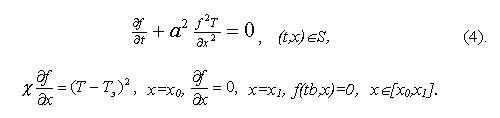
On the basis of a gradient (3) the directed iterative correction of management is organized:

where k – number of iteration, a – parameter of a step of gradient descent.

For the decision of the direct and connected problem we shall take advantage of a method of prorace. For construction certainly – difference analogue of the differential equation (1) it is used Krank-Nicholson's widely known, absolutely steady circuit:
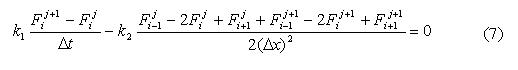
We shall write down the previous equation in the initial kind convenient for the decision by a method of chaser:
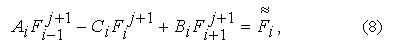
For the Decision of system of the algebraic equations (8) we shall search as a parity:

Where factors 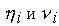 are defined from recurrent parities:
are defined from recurrent parities:
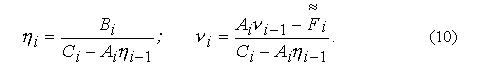
For the equations (8) boundary conditions enter the name in a general view:
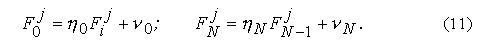
Thus, knowing 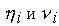 and applying formulas of direct prorace (10), we determine all proracing factors
and applying formulas of direct prorace (10), we determine all proracing factors 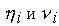 . Boundary value it is determined from a parity
. Boundary value it is determined from a parity

Formulas (9) and (12) represent formulas of the return prorace, allowing to define values Fji at all values i.
Thus, it is possible to present the general integrated algorithm of a task in view of optimization:

As own development it is possible to note master's thesis which is at a stage of performance.
Experimental researches in the given work were not carried out for the following reasons. First, results are not received yet, second, the material resources is necessary for carrying out of these researches.
The review of results and conclusions
At the given stage of performance of work end results are not achieved, so final conclusions to make it is impossible. It is possible to assume only, that the technique of the decision of a task in view is original, that should lead to desirable result.
Prospects of the further researches
Recognizing that ammonia is very important raw material, and process of its reception is fully-automated, in connection with development of technical equipment there is a necessity of modernization of this process. Thus, any offers connected to optimization of work of reactors will be actual, and varied variables by optimization heat-exchange apparatus and systems are the mass charge of a cold stream, final temperatures of streams, quantity of the heat transmitted in the device or in system as a whole.
1. Volodin N.A., Tolstykh V.K. On application of the gradient method of optimization to the problem of heat control of the reactor. // Magazine Automatics, 1993., ¹1, p. 40-44.
2. Kyznetsov L.D., Dmitrenko L.M., Rabina P.D., Sokolinski U.A. Synthes of ammonia. M.: Chemistry, 1982.
3. Demidovich B.P., Maron I.A.Numerical methods of the analysis. M.: the Science, 1967.
4. Ogurtsov A.P., Nedopekin F.V., Tolstykh V.K., Volodin N.A.Direct optimization thermalphysic processes. - Donetsk: publishing house "Southeast", 1997.