1. Topicality of the work
Ischemic insult is the most frequent form of severe disturbance of cerebral blood circulation (about 80 per cent of cases). Brain infarction is a necrosis area caused by hard and steady disturbance of neuronal structure metabolism as a result of inadequate cerebral blood supply. [1]
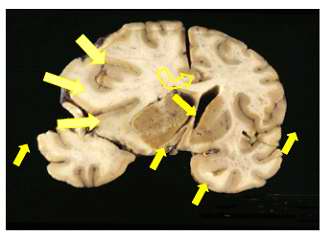
Figure 1 - Ischemic insult
The problem of timely insult diagnostics is very important today and is of interest of physicians of different specialties. The reason is that about six million people in the world are affected by insult every year. Most cases of primary disablement are due to it.[2] That is why the possibility to predict the degree of risk of II development is a matter of particular interest and importance today.
2. Purposes and tasks of the work
The purpose of my Master's work is the prediction of the risk of II development and deriving its formula using Genetic Programming.
The task of the work is the creation of a system capable to predict the risk of II development.
3. Scientific novelty of the work
Prediction systems are widely spread and develop fast today. There is a number of medical projects working up such systems, but in our country such works are not yet widely represented because this line of investigation is just beginning to develop.
Presented in this work is a system of prediction of the risk of II development using Genetic Programming to derive formulas and there is no analogue system today.
4. Theme review
Genetic Programming is used for solving a lot of problems such as symbolic regression, data analysis, optimization and investigation of the behavior of new generations in biological communities. In medicine it is applied to the creation of the prediction systems. [3]
The previous masters of Donetsk National Technical University have already presented prediction systems in their works. But in all those cases neural network Technologies and Genetic Algorithms were used as a mathematical instrument. Genetic Programming, too, was applied to various problems such as creation of data compression subsystem or making up tests for logical organizations. So, there have not yet been any prediction system projects using Genetic Programming in medicine presented in our University.
Investigations into the problems of Genetic Programming are currently carried out in our Faculty. There were made a number of announcements of that theme, particularly by the Professor Skobtsov Y. A. [4].
Prediction systems are widely spread and develop fast today in the world. Oral cancer diagnostics system developed by Simon Kent is a striking example of the usage of Genetic Programming for working out prediction systems. [5, 6]
The results of patients’ questionnaire were used as the input data of the system. But there was much excess information in it that complicated the appraisal of diagnosis. In order to improve that special statements (or predicates) about a patient were made.
The data were exported from the database as differentiated text and were converted into 13 bit fields for every questionnaire. Every bit gave the information about verity or falsity of one of the thirteen statements about a patient.
Terminal set of the task was formed by thirteen bit fields which represented specific way of life and habits of a patient. Functional set of the task was formed by three logic operators: “and”, ”or” and ”no”.
Certain starting parameters such as population size, probability of mutation and crossing etc were accepted to start the Genetic Programming process. First, a learning sample was made. Genetic Programming system was run over several times with various initial populations.
Only those results of the system run were accepted which could appraise correctly big number of positive and negative diagnoses.
5. The Data used in the Master's Work
There is a certain group of the people having a high probability of the insult development. The hazard factors of II are:
a) age (the hazard of the insult development grows three times every ten years of life);
b) sex (victims of the II are mostly men above 55years of age and women above 65);
c) increased arterial pressure (patients with arterial pressure above 160/95 mm Hg have the hazard of the insult four times higher than those with the normal pressure, and if the pressure is more than 200/115 mm Hg then the hazard is ten times higher);
d) atherosclerosis;
e) pancreatic diabetes;
f) smoking;
g) overweight;
h) alcoholism;
i) hypodynamia;
j) lifestyle factors (lack of physical activity, malnutrition, stress factor).
Before the work begins it is necessary to determine a group of patients with the hazard factors and suffering with the II caused by them and a group of patients with the hazard factors but having no II. These shall be the starting data for the work.
In order to solve the task of the work (to predict the risk of II development) it is necessary to collect the data related to II and arrange it correctly. According to that the quantity of patients in the groups is to be as big as possible.
6. Mathematical Methods used in the Master’s Work
Either Neuron Networks or Genetic Programming can be used as mathematical methods for solving the task of the work (prediction of the degree of risk of II development). But Neuron Networks have a certain disadvantage. Working with this method is like working with a "black box": one can input starting parameters and then get the result without opportunity to observe the process of finding the solution. Genetic Programming has no such disadvantage.
In Genetic Programming, the population consists of programs in proper code that are put to the test by genetic operators in order to find an optimal solution that is the program solving the current task best. The abilities of programs are analyzed regarding fitness function that is defined particularly.
The programs in Genetic Programming are interpreted like trees. Every next generation is the result of the use of genetic operators: crossover, reproduction and mutation.[7, 8]
The mutation operator is of secondary importance compared with the crossover operator. It means that the crossover in classical genetic algorithm is almost always present while the mutation is rather rare.[9]

Animation - Genetic operators (31 frames , 10 iterations )
In Genetic Programming population individuals are interpreted like trees in which functions are internal junctions with input parameters (subtrees) connected to them. The “crossingover” shall be made by putting a subtree of the first “parent” instead of one of the subtrees of the second one. The mutation shall be made by a random modification of a tree junction.
The main steps of Genetic Programming are: [10]:
a) initialization (the selection of a start chromosome population);
b) evaluation of the fitness of the chromosomes in the population;
c) check-up of the algorithm stop condition;
d) selection of the chromosomes;
e) usage of the genetic operators;
f) forming of the new population;
g) selection of “the best” chromosome.
7 Conclusion
Today Genetic Programming is competing with Neuro Networks in diagnostics and has got some advantages.
The development of a forecasting system with the help of Genetic Programming demands to find a criterion function and optimal parameters: the population size, the probabilities of usage of genetic operators of crossover, reproduction, mutation, and to determine the selection method.
My Master’s Work has the purpose to enlarge the area of the usage of Genetic Programming regarding as an example the problem of the prediction of the degree of risk of II development that is very relevant now. The system developed in this work shall be able to predict the degree of risk of II development and to derive its formulas using Genetic Programming.
Literature
- Гусев Е.И. Ишемическая болезнь мозга //Вестник РАМН - 1993. - N7.- С.34-39.
- Валикова Т.А., к.м.н., доцент, Алифирова В.М., д.м.н., профессор - Инсульт, этиология, патогенез, классификация, клинические формы, лечение и профилактика. Source: http://medbookaide.ru/books/fold1002/book1117/p1.php
- Рутковская Н. Д., Пилиньский Д. М., Рутковский М. В. – Нейронные сети, генетические алгоритмы и нечеткие системы – М.- Горячая линия-телеком-2006.
- Скобцов Ю.А., Хмелевой С.В. Генетический подход к задачам прогнозирования // Наукові праці Донецького національного технічного університету, серія: “Обчислювальна техніка та автоматизація” - випуск 90.-Донецьк : ДонНТУ. – 2005.- С.127-136.
- Simon Kent - Diagnosis of Oral Cancer using Genetic Programming.- Technical Report CSTR-96-14 CNES-96-04 - July 1996.
- D. C. Dracopoulos and Simon Kent. Genetic Programming for Prediction and Control. Neural Computing and Applications, 6(4):214-228, 1997.
- Курейчик В.М., Родзин С.И. Эволюционные алгоритмы: генетическое программирование // Известия РАНБ ТиСУ. 2001. №6.
- A.Конушин Введение в генетические методы - Графика и Мультимедиа.
Научно-образовательный сетевой журнал, посвященный компьютерной графике, машинному зрению и обработке изображений. Source: http://cgm.graphicon.ru/content/view/35/66/
- Sean Luke, Lee Spector. A Comparison of Crossover and Mutation in Genetic Programming.
Source: http://cs.gmu.edu/~sean/papers/comparison/comparison.pdf
- Yuri Burger Раздел статьи "Мягкие вычисления" Source: http://www.codenet.ru/progr/alg/Smart/Genetic-Programming.php
|