Onischenko
Oksana
Faculty :
electrotechnical
Speciality :
electric systems of electroconsumption
Theme of master's work :
"Substation 110/35/10 kV vitality estimation which supplies industrial enterprises with electric energy"
Scientific adviser :
prof., d.s.t. Aleksandr Kovalev
kovaliov_alex@ukr.net
ADSTRACT
Introduction
The notion of survivability was first formulated by Russian admiral Stepan Osipovitch Makarov to denote the ability of a vessel to continue the battle in case of damage in different parts [1].
Survivability in power engineering denotes the property of an object to withstand the disturbance preventing triggering cascade of failures leading to disruption in electricity supply for consumers [2].
The impetus for evaluation methods development of power supply systems security and prediction of cascade failures in power systems (PS) was given by blackout failure on November 9, 1965 in the US. As a result around 30 million people were left without electricity for more than 10 hours. The damage made by the failure amounted to more than 100 million dollars. The series of similar minor failures (from the point of view of Economics) ended up on July 13, 1977 with blackout in New York. New York remained collapsed within 25 hours. The consequent damage comprised more than 1 billion dollars [3].
26 years later, on August 14, 2003 at 16:11 p.m. local time due to the damage of Niagara-Mohok power line there was a blackout in eastern part of North America, i.e. 50 million people were left without electricity [4].
In every case we can say that the power system lost its survivability.
Survivability of the electrical power system (EPS) depends on its structure, configuration, reliability of electric equipment, relay protection and emergency automation, as well as the level of proficiency of maintenance staff, stability factor, power reserve, etc [6].
When operating EPS cascade effect appears as a result of sequence of failures in several switches due to transition of through current.
Cascade failures were observed at 25 EPS and 2 OPS on the territory of the former USSR. 75 cascade failures were registered within 5 years. 81% of cascade failures occur because of faulty lines or malfunctioning of a number of protection switching units [7].
90% of national economy loss accounts for cascade failures [8].
The depth of cascade failure shows the level of disruption of power system in case of failure and disturbance [9].
Topicality
Currently, elemental methods have become widely spread for evaluation of reliability of power supply system schemes (PSS). These methods imply that PSS consists of separate independent (in terms of reliability) elements, excluding functional interdependence parameter of some elements and devices [10-14].
The substation under consideration includes the following elements: transmission lines, transformers, switches, separators, isolators, buses.
We understand circuit nodes of the scheme as physical points of PSS, connected to at least three directions for power transmission, i.е. collecting bus or distributor sections, etc.[12].
Thesis results
Mathematical model for reliability of the system disabling switch in dynamic mode has been worked out on the basis of homogeneous Markovian processes with discrete number of states and continuous time.
It is supposed that switch failure to trip occurs in case of concurrency in time and space of two random events: short-circuit (S/C) in the protection operation zone; failure to trip the switch.
The probability of finding system in each of the four possible states can be figured out from the system of equations:
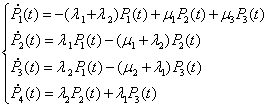 (1)
(1)
Taking into account that
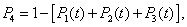 (2)
(2)
Linear differential equation system (1) takes on form:
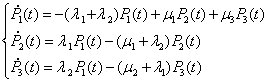 (3)
(3)
The system of equations (3) is solved under initial conditions:
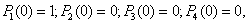 resulting from the following suppositions:
resulting from the following suppositions:
there is no S/C in the net under consideration at the moment, protection switching unit is in the standby mode.
Using direct Laplace transformation in the system of equations (3) with consideration to initial conditions we get
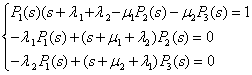 (4)
(4)
Solution (4) in relation to unknown functions upon simplification makes:
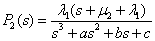 , (5)
, (5)
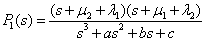 , (6)
, (6)
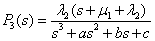 , (7)
, (7)
where, 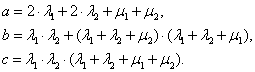
The probability of no-failure operation of protection switching unit taking into account only failures to trip can be figured out from the expression [17]:
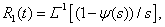 (8)
(8)
where
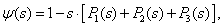 (9)
(9)
where 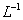 - is the symbol of Laplace inversion.
- is the symbol of Laplace inversion.
Using (5,6,7) and (9), we get
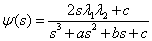 (10)
(10)
Mean time before the first failure of protection switching unit 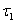 , and dispersion
, and dispersion 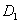 is figured out from the expressions [18]:
is figured out from the expressions [18]:
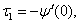 (11)
(11)
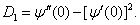 (12)
(12)
Using (10,11,12), we get:
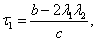 (13)
(13)
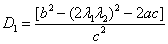 (14)
(14)
Using expression (5,6,7) with regard to Laplace inversion, we get:
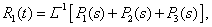 (15)
(15)
Placing into the formula (15) the meanings 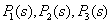 from (5,6,7):
from (5,6,7):
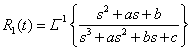 (16)
(16)
Conclusions
1. Regulations and suppositions have been worked out, allowing to present switching unit failures as the process of concurrence in time and space of two regular homogeneous Markovian processes with different frequency and continuity of existence.
2. On the basis of the theory of regular homogenous Markovian processes new mathematical model of protection switching unit is suggested. It takes into account both failure to trip in dynamic mode (relay protection, breaking actuator, switch drive), and also diagnostics terms Θ of the switching sistem.
3. In case the condition (26) is fulfilled the difference between precise and approximate meanings 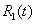 and
and 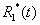 in time interval
in time interval 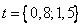 of the year does not exceed 1%.
of the year does not exceed 1%.
4. Logbook compiling procedure explaining the reasons for failures of load nodes of 110/10 kV substation is suggested.
5. Minimal stress relay reliability procedure and its effects on load nodes operation reliability have been worked out.
References
1. Марков С.О. Разброс элементов, составляющих боевую силу судов. Морской сборник, 1894, № 6. - 106 с.
2. Надежность схем энергетики. Терминология. М.: Наука, 1980.
3. Prevention of power failures Vol.
3. Studies of the task groups on the northeast power interruption. A report to the federal power commission. June 1967, 142 p.
4. Горохов К. Америке утроили темную. Комсомольская правда в Украине. 16 августа 2003 года.
5. Руденко Ю.Н., Ушаков И.А. Надежность систем энергетики. М.: Наука, 1986. – 176 с.
6. Китушин В.Д. Определение характеристик отказов системы при цепочечном развитии аварий. – Изв. АН СССР. Энергетика и транспорт, 1977, № 6. стр. 20-30.
7. Гук Ю.Б. Анализ надежности электроэнергетических установок – Л.: Энергоатомиздат, 1984. – 176 с.
8. Гук Ю.Б. Анализ надежности электроэнергетических установок – Л.: Энергоатомиздат, Ленинградское отделение, 1988. – 224 с.
9. Розанов М.Н. Надежность электроэнергетических систем – М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1984 - 176 с.
10. Рябинин И.А. Основы теории и расчета надежности судовых электроэнергетических систем.-2-е изд. - Л.: Судостроение, 1971.-456 с.
11. Нечипоренко В.И. Структурный анализ систем (эффективность и надежность). - М.: Сов. радио, 1977. - 216 с.
12. Фокин Ю.А., Харченко А.М. Расчет надежности систем электроснабжения. – Электричество, 1982, №8, с. 5-10.
13. Константинов Б.А., Лосев Э.А. Логико-аналитический метод расчета надежности восстанавливаемых систем электроснабжения. – Электричество, 1971, № 12, с. 21-25.
14. Белоусенко И.В., Ершов М.С., Ковалев А.П., Якимишина В.В., Шевченко О.А. О раcчете надежности систем электроснабжения газовых промыслов. – Электричество, 2004, №3, С. 23-28.
15. Синьчугов Ф.И. Основные положения расчета надежности электроэнергетических систем. – Электричество, 1980, № 4, с. 12-16.
16. Лосев Э.А. Отклик на статью Ф.И. Синьчугова. – Электричество, 1981, № 9, с. 72-73.
17. Сандлел Дж. Техника надежности систем. Перевод с английского – Наука, 1966. – 300 с.
18. Креденцер Б.П. Прогнозирование надежности систем с временной избыточностью. – К.: Наукова думка, 1978. – 240 с.
19. Бронштейн И.Н., Семендяев К.А. Справочник по математике для инженеров и учащихся вузов. – М.: Наука, 1986. – 554 с.
20. Ковалев А.П., Шевченко А.В., Белоусенко И.В. Оценка пожарной безопасности передвижных трансформаторных подстанций 110/35/6 кВ// Промышленная энергетика . – 1991 - № 6. с. 28-31

The notion of survivability was first formulated by Russian admiral Stepan Osipovitch Makarov to denote the ability of a vessel to continue the battle in case of damage in different parts [1].
Survivability in power engineering denotes the property of an object to withstand the disturbance preventing triggering cascade of failures leading to disruption in electricity supply for consumers [2].
The impetus for evaluation methods development of power supply systems security and prediction of cascade failures in power systems (PS) was given by blackout failure on November 9, 1965 in the US. As a result around 30 million people were left without electricity for more than 10 hours. The damage made by the failure amounted to more than 100 million dollars. The series of similar minor failures (from the point of view of Economics) ended up on July 13, 1977 with blackout in New York. New York remained collapsed within 25 hours. The consequent damage comprised more than 1 billion dollars [3].
26 years later, on August 14, 2003 at 16:11 p.m. local time due to the damage of Niagara-Mohok power line there was a blackout in eastern part of North America, i.e. 50 million people were left without electricity [4].
In every case we can say that the power system lost its survivability.
Survivability of the electrical power system (EPS) depends on its structure, configuration, reliability of electric equipment, relay protection and emergency automation, as well as the level of proficiency of maintenance staff, stability factor, power reserve, etc [6].
When operating EPS cascade effect appears as a result of sequence of failures in several switches due to transition of through current.
Cascade failures were observed at 25 EPS and 2 OPS on the territory of the former USSR. 75 cascade failures were registered within 5 years. 81% of cascade failures occur because of faulty lines or malfunctioning of a number of protection switching units [7].
90% of national economy loss accounts for cascade failures [8].
The depth of cascade failure shows the level of disruption of power system in case of failure and disturbance [9].
Currently, elemental methods have become widely spread for evaluation of reliability of power supply system schemes (PSS). These methods imply that PSS consists of separate independent (in terms of reliability) elements, excluding functional interdependence parameter of some elements and devices [10-14].
The substation under consideration includes the following elements: transmission lines, transformers, switches, separators, isolators, buses.
We understand circuit nodes of the scheme as physical points of PSS, connected to at least three directions for power transmission, i.е. collecting bus or distributor sections, etc.[12].
Mathematical model for reliability of the system disabling switch in dynamic mode has been worked out on the basis of homogeneous Markovian processes with discrete number of states and continuous time.
It is supposed that switch failure to trip occurs in case of concurrency in time and space of two random events: short-circuit (S/C) in the protection operation zone; failure to trip the switch.
The probability of finding system in each of the four possible states can be figured out from the system of equations:
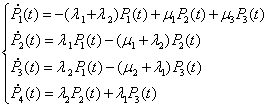 (1)
(1)
Taking into account that
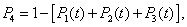 (2)
(2)
Linear differential equation system (1) takes on form:
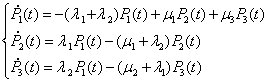 (3)
(3)
The system of equations (3) is solved under initial conditions:
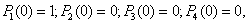 resulting from the following suppositions:
resulting from the following suppositions:
there is no S/C in the net under consideration at the moment, protection switching unit is in the standby mode.
Using direct Laplace transformation in the system of equations (3) with consideration to initial conditions we get
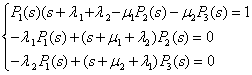 (4)
(4)
Solution (4) in relation to unknown functions upon simplification makes:
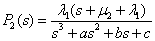 , (5)
, (5)
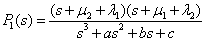 , (6)
, (6)
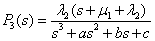 , (7)
, (7)
where, 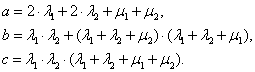
The probability of no-failure operation of protection switching unit taking into account only failures to trip can be figured out from the expression [17]:
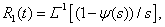 (8)
(8)
where
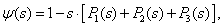 (9)
(9)
where 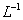 - is the symbol of Laplace inversion.
- is the symbol of Laplace inversion.
Using (5,6,7) and (9), we get
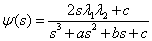 (10)
(10)
Mean time before the first failure of protection switching unit 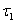 , and dispersion
, and dispersion 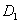 is figured out from the expressions [18]:
is figured out from the expressions [18]:
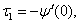 (11)
(11)
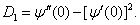 (12)
(12)
Using (10,11,12), we get:
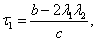 (13)
(13)
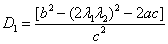 (14)
(14)
Using expression (5,6,7) with regard to Laplace inversion, we get:
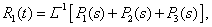 (15)
(15)
Placing into the formula (15) the meanings 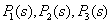 from (5,6,7):
from (5,6,7):
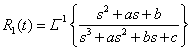 (16)
(16)
1. Regulations and suppositions have been worked out, allowing to present switching unit failures as the process of concurrence in time and space of two regular homogeneous Markovian processes with different frequency and continuity of existence.
2. On the basis of the theory of regular homogenous Markovian processes new mathematical model of protection switching unit is suggested. It takes into account both failure to trip in dynamic mode (relay protection, breaking actuator, switch drive), and also diagnostics terms Θ of the switching sistem.
3. In case the condition (26) is fulfilled the difference between precise and approximate meanings 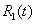 and
and 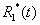 in time interval
in time interval 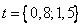 of the year does not exceed 1%.
of the year does not exceed 1%.
4. Logbook compiling procedure explaining the reasons for failures of load nodes of 110/10 kV substation is suggested.
5. Minimal stress relay reliability procedure and its effects on load nodes operation reliability have been worked out.
2. Надежность схем энергетики. Терминология. М.: Наука, 1980.
3. Prevention of power failures Vol.
3. Studies of the task groups on the northeast power interruption. A report to the federal power commission. June 1967, 142 p.
4. Горохов К. Америке утроили темную. Комсомольская правда в Украине. 16 августа 2003 года.
5. Руденко Ю.Н., Ушаков И.А. Надежность систем энергетики. М.: Наука, 1986. – 176 с.
6. Китушин В.Д. Определение характеристик отказов системы при цепочечном развитии аварий. – Изв. АН СССР. Энергетика и транспорт, 1977, № 6. стр. 20-30.
7. Гук Ю.Б. Анализ надежности электроэнергетических установок – Л.: Энергоатомиздат, 1984. – 176 с.
8. Гук Ю.Б. Анализ надежности электроэнергетических установок – Л.: Энергоатомиздат, Ленинградское отделение, 1988. – 224 с.
9. Розанов М.Н. Надежность электроэнергетических систем – М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1984 - 176 с.
10. Рябинин И.А. Основы теории и расчета надежности судовых электроэнергетических систем.-2-е изд. - Л.: Судостроение, 1971.-456 с.
11. Нечипоренко В.И. Структурный анализ систем (эффективность и надежность). - М.: Сов. радио, 1977. - 216 с.
12. Фокин Ю.А., Харченко А.М. Расчет надежности систем электроснабжения. – Электричество, 1982, №8, с. 5-10.
13. Константинов Б.А., Лосев Э.А. Логико-аналитический метод расчета надежности восстанавливаемых систем электроснабжения. – Электричество, 1971, № 12, с. 21-25.
14. Белоусенко И.В., Ершов М.С., Ковалев А.П., Якимишина В.В., Шевченко О.А. О раcчете надежности систем электроснабжения газовых промыслов. – Электричество, 2004, №3, С. 23-28.
15. Синьчугов Ф.И. Основные положения расчета надежности электроэнергетических систем. – Электричество, 1980, № 4, с. 12-16.
16. Лосев Э.А. Отклик на статью Ф.И. Синьчугова. – Электричество, 1981, № 9, с. 72-73.
17. Сандлел Дж. Техника надежности систем. Перевод с английского – Наука, 1966. – 300 с.
18. Креденцер Б.П. Прогнозирование надежности систем с временной избыточностью. – К.: Наукова думка, 1978. – 240 с.
19. Бронштейн И.Н., Семендяев К.А. Справочник по математике для инженеров и учащихся вузов. – М.: Наука, 1986. – 554 с.
20. Ковалев А.П., Шевченко А.В., Белоусенко И.В. Оценка пожарной безопасности передвижных трансформаторных подстанций 110/35/6 кВ// Промышленная энергетика . – 1991 - № 6. с. 28-31

 .ru
.ru  .ua
.ua

