Actuality and motivation
Today, in the time of competition and globalization, the issue of security policy is extremely acute, so putting money in information systems (IS) is fully justified.
Information protection is a process that requires constant attention of the specialists in IS as well as the top management of the company.
The development of the model estimating losses is a challenge, because it connects the task of increasing profits
to the issue of information security that should reduce the losses associated with the problems of protection of the main information
properties (availability, integrity, confidentiality).
Many people think that the main problem is the communication between IS professionals who think in terms of technical
tasks and managers whose main concern is financial prosperity. However, it is often hard for IS
professionals to assess the amount of money to spend to ensure the better protection of the company’s systems and yet not to spend the money in vain.
If an IS expert knows how much money the company may lose because of implementation of the threats,
what places in the system are most vulnerable, what measures should be taken to improve security without spending extra money and all of above is well
documented, the task to convince the management to pay attention and allocate resources for IS becomes much more feasible [1].
Aims
A key word in information security is "information" and its value from a financial point of view.
The main aim of my work is to estimate the financial losses from the realized threats in the company.
The goal is to create a program that can do mathematical computations and analyze the results that are score states of the system. The purpose is to
minimize losses and to develop maximum possible level of protection for information in pre-arranged funding.
Scientific innovation
Scientific innovation of my master's work is systematizing the existing methods
of assessing losses, creation of a mathematical model based on chosen method, the practical implementation, testing in the company and
analysis of the results, to find out advantages and disadvantages of created model.
Expected practical results
The purpose of the work is to identify vulnerabilities in IS and create software product for the calculation of losses, which includes:
– development of a model for estimating of losses;
– analysis of realized threats;
– data collection on idle time, number of failures, time to troubleshoot, salaries of the staff and other factors affecting the formation of losses;
– creating a report on financial losses based on proposed model.
Exsistent methods
There are several methods of estimating loss that are the part of an information security systems, some of them deal with expected loss, others do with real.
– One of the simplest methods of valuation is to use a qualitative ranking for high, medium and low loss [2].
– "Total Cost of Ownership" (TCO) – a technique which include connection of risks and losses [3].
– "Cost Benefit Analysis" (CBA) - method is based on the analysis of estimates of gains and losses for the optimal variant [5].
– Semantic threat model – a technique that builds a semantic hierarchical network based on well-defined linkages between resources, evaluates the potential and actual losses from the realized risks given resources [4].
– Analytical methods for threat and damage.
– Expert methods.
– The model of estimating losses to threaten the availability, integrity and confidentiality of information which was proposed by Grezdov G. G.
Threat and vulnerabilities in information systems
Threat to security in information systems (IS) – a potentially possible event,
process or phenomenon that can lead to the destruction, loss of integrity confidentiality or availability of information.
The threats can be premedicated and unpremedicated [6].
The key moment in development of the model is realizing the reasons of losses. The vulnerability of computer systems (networks) – is any of its characteristic using which the offender may lead to the realization of threat.
The path of the model is presented in the figure [7].
Valuable information and its protection
The protection of the information requires information to preserve such qualities as confidentiality, integrity and accessibility while being processed by IS.
One method of assessing values is to determine the consequences after loss or modification.
In my work I use the mathematical basis for calculating estimates of losses of availability, integrity and confidentiality that was proposed by Grezdov G. G.
Approach to estimating availability losses
The threat of accessibility is a limited access to resources, or its absence.
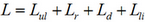 (1)
(1)where Lul – losses from untimely delivery of access;
Lr – losses associated with the restoration of availability;
Ld – losses associated with suspesion of work;
Lli – losses associated with the loss of income [9].
Losses associated with the restoration of availability are extended:
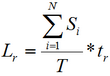 (2)
(2)where Si — salary per month the employee who recovers the attacked system;
N — a number of the employees who recover the attacked system;
tr — recovery time efficiency;
Т — work period of the system during month [9].
losses associated with the restoration of availability are extended:
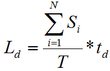 (3)
(3)where Si — salary per month employee of the attacked system;
N — number of employees who work on the attacked system;
td — downtime;
Т — work period of the system during month [9].
Losses associated with the loss of income are extended:
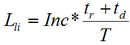 (4)
(4) where Inc – annual income from the attacked system;
tr — recovery time efficiency;
td — downtime;
Т — work period of the system during the year[9].
Approach to estimating integrity losses
Integrity means that data is complete and unchanged. Data may be subjected intentionally and unintentionally.
Loss of integrity can be calculated by the formula:
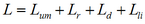 (5)
(5)where Lum — loss from unauthorized modification of information.
Size of losses will depend on the importance of information whiich integrity is compromised;
Lr — losses associated with the restoration of availability, Ld as in formula (1).
Lli — losses associated with the loss of income [9].
Losses associated with the restoration of integrity are extended:
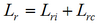 (6)
(6)where Lri — losses associated with the restoration of information; Lrc — losses associated with the replacement of damaged components. They are fixed material costs [9].
Losses associated with the restoration of information are extended:
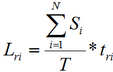 (7)
(7)where Si, N as in formula (3);
tri — time required to recover information on the attacked system;
Т — work period of the system during month [9].
Losses associated with downtime attacked system are calculated according to formula 2.
Losses associated with the loss of income are extended:.
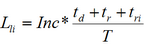 (8)
(8)where Inc — annual income from the attacked system;
td, tr as in formula (4);
tri as in formula (7);
Т — work period of the system during the year [9].
Approach to estimating confidential losses
Confidential information is a kind of information that needs to be protected from disclosure.
Otherwise, its owner will have losses that may be associated with the financial aspect, loss of reputation, competitiveness, etc.
Therefore, confidential information means that it is disclosed only to a limited number of employees while the rest do not have an access to it [10].
The most convenient method for the calculation of the losses is an expert evaluation. The essence of this method is that a group of specialists in this field analyze the loss based on the significance of the information. Because of the breach in several groups of properties, the evaluation of losses may be different depending on the type of properties that were threatened. The mathematical representation of the formulas is presented in Figure 1.
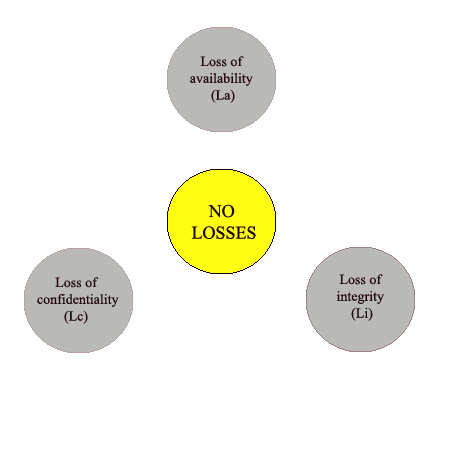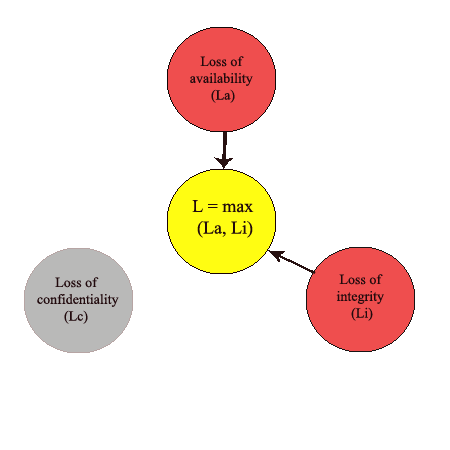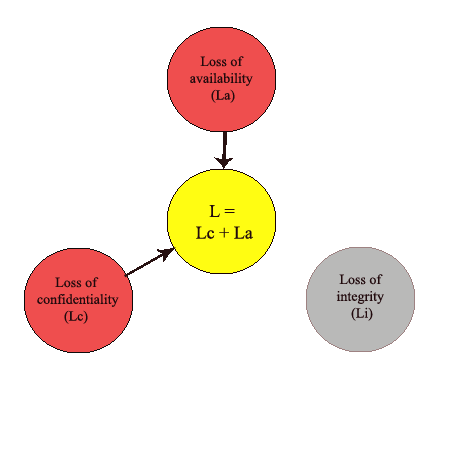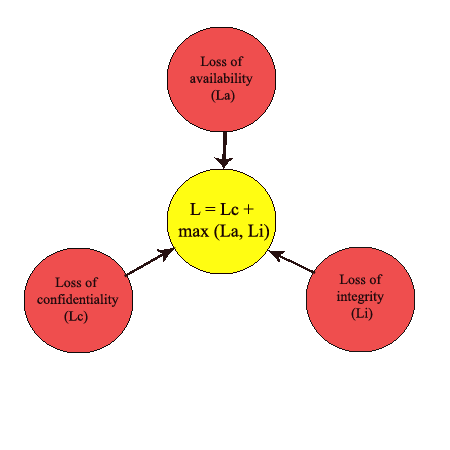
Figure 1 — Evaluation of losses, which break some properties of information
(animation: volume - 30,3 КB; size- 450x450; number of shots - 5; number of repetition cycles - infinitely; delay between shots - 1,2 мs)
Conclusions and a list of the main results
We can use the insurance information risk enterprise for improving the model.
The aggregate loss (L *)is calculated as follows:
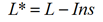 (9)
(9)
where L - total losses due to violations of several informational categories;
Ins - total income from insurance, which is calculated by the formula:
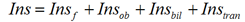 (10)
(10)where
Insf - income from insurance of information security
Insob - income from insurance on information security;
Insbil - income from insurance for buildings where objects of protection are located;
Instran — income from insurance on recourses of information transmission [13].
Estimated model of losses helps calculate the real costs of upgrading and buying new software that allows companies to avoid most of the threats.
Analysis shows that one of the suitable ways to optimize the costs of defense, minimize funding and get the best result is to develop a model estimating the loss.
The advantages of the use of this model, an estimate of losses should include:
• convenience of calculation, all the indicators used in the formulas are public data;
• visibility, concrete indicators losses enable a realistic assessment of the concept of "lost income";
• easy user training methods work with the model;
• ability to use in any enterprise;
• monitoring system for modifying vital information and creating a plan as quickly as possible to restore it.
References
1. IT-портал Ixbt. [Electronic resourse]: http://www.ixbt.com/cm/informationsystem-risks012004.shtml – Современные методы и средства анализа и контроля рисков информационных систем компаний. И. Медведовский.
2. Домарев, В. В. Защита информации и безопасность компьютерных систем, К.: Издательство «ДиаСофт», 1999. – 480с.
3. TRN.com.ua: Тренинговый портал Украины. [Electronic resourse]: http://www.trn.com.ua/articles/2081/ – Экономика информационной безопасности. С. В. Карпенко.
4. Low Cost Online Data Recovery Service [Electronic resourse]: Information Risk Management – Information Risk Management.
5. Michael E. Whitman, Herbert J. Mattord, Herbert J. Mattord. Management of Information Security. First edition ISBN-10: 0619216271 ISBN-13: 9780619216276. 272 pages, 2006.
6. ProGrammer: Сайт о программировании, математике и моделировании. [Electronic resourse]: http://progrm.ru/?p=300 – Семантическая модель угроз.
7. IT-портал CITForum. [Electronic resourse]: http://citforum.ru/security/articles/threats/ – Как определить источники угроз? С. Вихорев, Р. Кобцев. Открытые системы No.7-8/2002.
8. DLtens. [Electronic resourse]: http://www.dltens.ru/audit-it-infrastructury.html – Аудит IT-инфраструктуры предприятия: цели, задачи, реализация. Р. И. Мамонтов.
9. Компьютерная документация от А до Я. [Electronic resourse]: http://www.compdoc.ru/secur/xacer/netcrit/ – Аудит IT-инфраструктуры предприятия: цели, задачи, реализация. А. В. Лукацкий.
10. Тимошенко, А. А. Защита информации в специализированных информационно-телекоммуникационных системах – Текст лекции, Киев, 2010.
11. Грездов, Г. Г. Способ решения задачи формирования комплексной системы защиты информации для автоматизированных систем 1 и 2 класса [Текст] / Г. Г. Грездов // (Препринт/ НАН Украины. Отделение гибридных управляющих систем в энергетике ИПМЭ им. Г. П. Пухова НАН Украины; № 01/2005 ) – Киев : ЧП Нестреровой, 2005. – С. 66.
12. Защита информации и Информационная безопасность [Electronic resourse]: www/ URL: http://www.zashita-informacii.ru/ – Угроза доступности. Угроза конфиденциальности.
13. «Амулет» [Electronic resourse]: http://www.amulet-group.ru/page.htm?id=30 – Страхование информационных рисков как метод защиты информации. Д. Дьяконов.
14. Information Security Management [Electronic resourse]: http://www.netbotz.com/library/ISO_17799.pdf – Information Security Management: Understanding ISO 17799. Tom Carlson.
15. Privacy / Data Protection Project [Electronic resourse]: http://privacy.med.miami.edu/glossary/xd_iso_27002_index.htm – ISO Code of Practice for Information Security Management (ISO 17799, 27002).
Comment
When writing this abstract the master’s qualification work is not completed. Date of final completion of work: December, 1, 2011. Full text of the work and materials on a work theme can be received from the author or his scientific supervisor after that date.
