Abstract on the topic of graduation work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 3. Theoretical aspects of the mechanism for making personnel decisions
- 3.1 Mechanism for developing and making personnel decisions
- 3.2 Peculiarities of making personnel decisions at enterprises
- 3.3 Effectiveness of HR solution
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Currently, human resource management is very important for any organization, regardless of its field of activity. Achieving the goals of the organization is possible thanks to the correct selection, placement and professional training of human resources. Human resource management is viewed as an interconnected and strategically grounded organizational decision-making system for labor regulation and labor relations. The quality of decisions made in this regard directly affects the ability of each employee and the organization as a whole to achieve their goals.
Improving the quality of personnel decisions made by managers at all management levels is a significant and important reserve for increasing organizational effectiveness. Making personnel decisions is necessary for the selection, organization, training and development, stimulation and motivation of personnel. At any time, you need to analyze the situation and choose a more suitable solution. This process is the process of developing and making personnel decisions. Therefore, managers must use scientific methods to prepare and make personnel decisions [7].
In conditions of risk and uncertainty, personnel decisions imply the implementation of multidimensional calculations, justification of criteria for assessing alternatives and their priorities, determination of appropriate actions [3].
1. Theme urgency
Currently, human resource management is very important for any organization, regardless of its field of activity. Achieving the goals of the organization is possible thanks to the correct selection, placement and professional training of human resources. Human resource management is viewed as an interconnected and strategically grounded organizational decision-making system for labor regulation and labor relations. The quality of decisions made in this regard directly affects the ability of each employee and the organization as a whole to achieve their goals.
In modern conditions of uncertainty, the goal of personnel work of any organization is the formation of effective and qualified personnel, which determines the accuracy and clarity of decision-making and, as a result, the success of the organization. This result depends on how effectively the personnel decisions are made.
The relevance of the research topic is due to the importance of improving the mechanism for making personnel decisions in the organization.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the study is to reveal the theoretical provisions and develop practical proposals for improving the mechanism for making personnel decisions in conditions of uncertainty.
In accordance with the set goal, the main objectives of the master's work are:
- Disclosure of the essence of the mechanism for the development and adoption of personnel decisions;
- Research of the peculiarities of making personnel decisions in organizations;
- Analysis of the effectiveness of personnel decision making in conditions of uncertainty.
Research object : HR decision making mechanism.
Research subject : theoretical and methodological foundations and practical issues for improving the organizational mechanism for making personnel decisions in conditions of uncertainty.
The methodological and theoretical basis of the study is the works of domestic and foreign authors dedicated to improving the mechanism for making personnel decisions. When implementing the goals and objectives set in the study, various methods, principles, techniques and techniques were used, such as: methods of economic and strategic analysis, generalization, classification, grouping, comparison, modeling of a comprehensive assessment of employee competencies.
3. Theoretical aspects of the mechanism for making personnel decisions
3.1 Mechanism for development and adoption of personnel decisions
Decision making is an objective necessity in any area of management activity. Its effectiveness depends on the quality of management decisions [10]. The level of development of the organization and its further prosperity or survival depends on the strategy and current decisions made by the leaders. This situation also applies to the development and adoption of effective HR decisions.
In modern economic conditions, new opportunities are opening up in the field of personnel decision-making. For example, the forms of employment of workers are becoming more flexible and diversified, the sphere of providing educational services, including on a commercial basis, is expanding, the infrastructure of the labor market is developing, new types of services are emerging in the field of personnel selection and assessment [1]. In this regard, when making personnel decisions, it is necessary to take into account economic, social, national and legal factors. The importance of the strategic aspects of personnel decision making, justification of the economic feasibility of capital investments related to the development of human resources [10] is growing.
In scientific usage, the term decision making
is interpreted by most authors as a complex, multi-stage process. Classical management methods consider personnel decision making as a process consisting of three main stages:
1. Solution preparation;
2. Decision-making;
3. Implementation of the decision.
Each stage includes a series of targeted actions. At the stage of preparing a solution, an analysis of the situation is carried out, including the search, collection and processing of information, as well as the development of a problem to be solved.
At the decision-making stage, alternative decisions and actions are developed and evaluated, the selection criteria for choosing the optimal solution, the selection and adoption of the best decision. At the stage of implementation of the decision, measures are taken to concretize the decision and present it to the executors, control the progress of its implementation, make the necessary adjustments and evaluate the results obtained.
The general scheme of the personnel decision-making procedure can be presented as follows:
1. Diagnostics of the personnel problem, that is, awareness of the need to make a decision and analysis of the situation where the problem arises (assessment of the time and resources available to the decision-making manager, analysis of personnel information (Fig. 1), identification of external and internal problems, their ranking;

Figure 1 – Analysis of personnel information (animation: 9 frames, 15 repetition cycles, 125 kilobytes)
2. Determination of criteria for evaluating the decision;
3. Prioritization (significance of criteria);
4. Finding possible alternatives to solve the problem;
5. Assessment of alternatives;
6. Choosing the best solution;
7. Implementation of the solution and evaluation of the results obtained.
Based on this scheme, we will consider in more detail the stages of decision-making associated with making personnel decisions:
1. The process of making any personnel decision begins with the need to analyze the situation of the problem and the reasons for its occurrence. The identification and presentation of issues provides preliminary information for assessing the time available for decision making and the amount of resources required. An important aspect of analyzing the situation of the problem is the classification of the problem into external and internal. The end result at this stage is the identification and ranking of the so-called basic, cardinal problems, which should be tackled first of all [1].
The first stage of personnel decision-making should end with the setting of a number of tasks, namely: what personnel problems should be resolved; how much time should be allocated to solve the problem; and what forces and means will be used to solve the problem.
2. At the second stage of personnel decision-making, criteria are established for assessing various options for solving the assigned tasks. Since the best decisions are usually made on an alternative basis, it is important to define the criteria for choosing the best option. According to the number of criteria for evaluating alternatives, single and multi-criteria decision-making problems are distinguished. It may happen that there is only one option, for example, that the decision is an act provided for by the Labor Code or other laws. With regard to the selection criteria for personnel decisions, the multi-criteria approach is in most cases dominant [5].
3. At the third stage, it is necessary to select from the total number of selected criteria those that will be priority under the existing conditions.
4. In the fourth step, the main task is to identify available solutions to the problem. When choosing a solution to a problem, it is important to be able to analyze all the different possibilities available. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the conditions that impose restrictions on the adoption of personnel decisions, such as legal norms, the lack of adequate financial resources in the organization, the lack of qualified specialists in the labor market.
5. The fifth step is to analyze the collected information and evaluate various options based on previously selected criteria. Many of the alternative solutions are easy to find because they are usually known from previous experience, are standard, and easily fit within the criterion boundaries of the best solution. However, new, unique problems often arise that do not fit into the usual framework. In this case, you need to get creative. All proposed alternatives should be compared or evaluated with each other in order to select the best alternatives. The assessment included identifying the negative and positive aspects of the considered alternatives and establishing the degree of compromise between them. For this, you can use quantitative and qualitative changes.
6. At the final stage of decision-making, the final decision is made – this is the decision that best meets the previously selected criteria and ensures the achievement of the desired result. Risks and constraints need to be identified and minimized.
7. Finally, the seventh stage is the implementation of the solution and the evaluation of the results obtained. To solve a problem or take advantage of existing opportunities, a solution must be implemented. Only after making a decision on its implementation will its true value and quality be revealed. The task of the manager at this stage is to organize the implementation of the decision, including the development of an implementation plan, bringing the plan and the decision itself to the attention of the executors, as well as monitoring the implementation of work. The solution implementation plan should include a list of works, implementation timeframes, a list of executors and required resources. Even a good solution is not always automatically recognized by all participants, so there may be a need for explanatory work. In the process of implementing the solution, it is necessary to monitor the progress of the work and the results obtained.
Any successful management decision, including personnel, must meet the following requirements:
• comprehensive validity;
• reality;
• timeliness;
• profitability (achieving the best end result at the lowest cost).
The growing desire of entrepreneurs to survive in conditions of fierce competition, to provide a stable prospect for the development of productive forces, the need for the introduction of new equipment and technologies, innovative processes, is becoming increasingly important, which necessitates the future development and constant improvement of human resources. At the same time, the issues of planning human resources are becoming most relevant. In practice, special attention is paid to the formation of new labor motivations and morality, the willingness to share innovative risks with entrepreneurs, as well as the long-term development of personnel to perform qualified types of work and adaptation to changing production conditions. The issue of making operational decisions, recruiting, evaluating and motivating personnel remains important. However, they are filled with new content and are closely related to the overall development strategy of the company. All the variety of personnel decisions (Fig. 2) can be conditionally classified according to the following criteria:
• strategic focus;
• functional orientation;
• production focus;
• the nature of the authority and responsibility for making and implementing personnel decisions;
• the nature of the contractual relationship with employees.
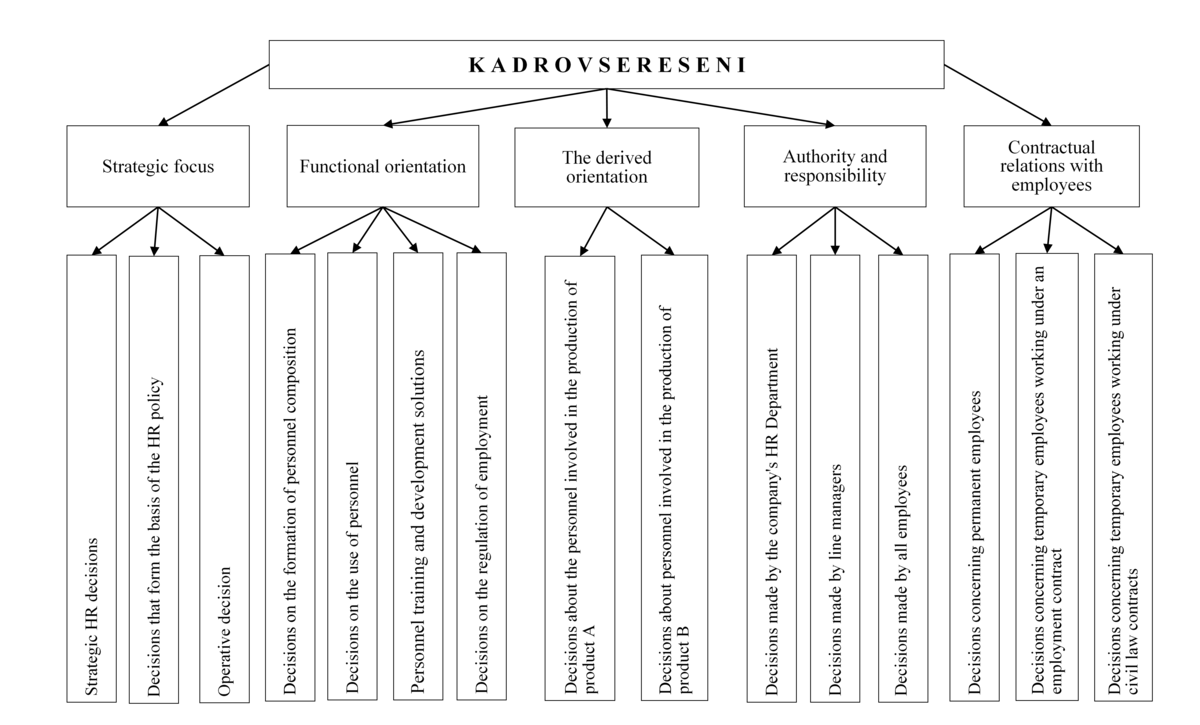
Figure 2 – Classification of HR decisions
Therefore, based on various personnel decisions, we can conclude that to justify them, it is necessary to take into account a wide range of factors and conditions – economic, social, legal, national. All these factors are closely interrelated.
3.2 Peculiarities of making personnel decisions at the enterprise
In management, personnel decision making is a systematic process that largely affects the employees of an organization and is an essential part of the daily work of a manager of any level and official rank [6].
In the process of forming personnel decisions, special methods, justification of approaches, experience, intuition and experimentation are widely used. The development of solution options is carried out in accordance with the decision tree
method. With its help, options for solutions are considered:
• possible;
• acceptable;
• preferred.
Of these, a group of preferred alternatives is singled out, from which the final decision will be made. It is important that decisions are made in a timely manner during the economic and incentive cycles, taking into account the state of the managed object, which will further create conditions for motivating employees and increasing business activity.
For the effective use of human resources, a two-stage model for the preparation and adoption of personnel decisions has been developed. It allows you to manage processes within the organization and influence the work motivation of employees, make timely personnel decisions for the effective use of business potential.
Modeling of the preparation and decision-making process is carried out in full accordance with the developed HR strategy of the organization. The essence of the personnel strategy is as follows. In the near future, a number of structural, financial, organizational and personnel changes should be implemented, such as:
• financial recovery of the enterprise;
• reorganization of the enterprise;
• effective use of human resources;
• improvement of methods of organization and production management.
In the presence of appropriate staffing, it is possible to solve the set strategic tasks. The orientation towards the employee as a subject of management does not mean the destruction of the traditionally accepted hierarchy, the rigid classical management structure. This is a two-stage decision-making model. This model of training and making personnel decisions with their subsequent assessment and the employee's reaction allows diagnosing and shaping motivation and regulating the degree of concentration of the employee's internal business potential. The essence of the two-stage personnel and individual decision-making is to minimize differences in expectations and harmonize the interests of the employee and the organization, which, in principle, can be considered a way to reduce risk when making personnel decisions. The two-stage model is that along with personnel decisions, individual decisions are made. HR decisions are decisions made by the organization between the responsible person (the subject of management) and the employee (the subject of management). Individual decisions are decisions made by the employee himself (the subject of management). When making personnel decisions, it is necessary to anticipate and take into account possible options for individual decisions, which will significantly improve the quality of personnel decisions and ensure that the difference between the expectations of employees and the organization is minimized. After making a decision, an employee who is an object of management may be in the following states: stability and growth, job satisfaction, job dissatisfaction, a desire to study the labor market, a crisis, the search for a way out of the crisis, consciously, when the satisfaction of both parties is achieved, that is, interests are coordinated organization and employee, the efficiency of the employee and the organization as a whole increases.
External conditions (independent variables) affect personnel decisions:
• legislative and regulatory framework;
• the state of the labor market;
• effective use of human resources;
• tax policy;
• inflation rate;
• migration policy;
• social partnership (the atmosphere in the organization depends on it);
• education system (linked to the professional development system);
• health care system (as part of the social package);
• national characteristics (the mentality of the staff depends on this).
When making personnel decisions, it is important to fulfill the requirements that directly affect the quality of decisions made:
– goals and objectives of personnel work should be clearly defined and not contradict each other;
– Personnel decision makers should be able to fully identify all possible solutions to the problem and assess its advantages and disadvantages;
– the criteria for the effectiveness of the solution and its priorities should be quantifiable as possible, which facilitates the assessment of various options and the choice of alternative solutions;
– assessments and their priorities should be relatively constant. If the decision time is too long, it is important to timely adjust the set of key criteria and re-evaluate priorities;
– decision-makers must have the appropriate knowledge and skills to make optimal management decisions and assess their economic and social consequences [4].
A managerial personnel decision is an act of purposeful impact on personnel, which is based on the analysis of reliable personal data characterizing a specific personnel problem, defines a goal and contains a program to achieve it [8].
In managing an organization, personnel decisions are made by managers of all levels and are quite complex, since not only one person is involved in decision-making, but also a specific unit and the organization as a whole. Organization of personnel decision making consists of several stages (Table 1).
Table 1. Stages of personnel decision making [2]
The progress of the implementation of the personnel decision plan should be constantly monitored, the outlined changes in conditions or attitudes during the implementation of the plan should be analyzed. If the results of the analysis make you seriously think about the possible development of the personnel situation and there are doubts about the correctness of the goals, then it is necessary to rethink and change the strategy of the organization as a whole and the style of work of the manager in particular [2].
3.3 Effectiveness of the HR solution
Every leader must make effective and optimal management decisions. Effectiveness refers to the degree to which actual results are aligned with the goals set. For the validity of the decision, there are ways to convey it to a specific performer. Control is an objective necessity, because even optimal plans will not be fulfilled if they are not communicated to the executor, and they are not constantly monitored. In this regard, the assessment and control of personnel decisions can increase their effectiveness in the organization.
The effectiveness of personnel decisions is understood as the efficiency of using the resources obtained in the preparation and implementation of personnel decisions in the organization. Resources can be finances, materials, workers' health, work organization, etc. There are organizational, economic, psychological, legal, ethical, technological and social efficiency of management decisions.
Organizational effectiveness of management decisions is understood as the fact that organizational goals are achieved with fewer employees or less time. Organizational goals are associated with the implementation of the following human needs: the organization's needs for life and safety, management, stability, order. Organizational efficiency and the quality of management decisions are inextricably linked.
The economic efficiency of managerial decisions is the ratio of the value of the surplus product obtained during the implementation of a specific managerial decision to the cost of making and implementing managerial decisions.
The social benefits of management decisions are that social goals are achieved for more people and society in less time, fewer employees, and lower financial costs. Social goals satisfy the following human needs: the need for information, knowledge, creativity, self-expression, communication and relaxation.
Technological efficiency of management decisions lies in the fact that the achievement of certain results (industrial, national or world level of production technology) are achieved by reducing the time frame or reducing financial costs.
The psychological effectiveness of management decisions lies in the fact that psychological goals are achieved in a shorter period of time for more employees or groups of the population, fewer employees, or at lower financial costs. Psychological goals achieve the following human needs: the need for love, family and free time.
The legal consequences of management decisions refer to the extent to which the legal objectives of an organization and staff have been achieved in a shorter period of time, with fewer staff, or at a lower cost. Legal purposes satisfy the following human needs: safety, order.
The environmental efficiency of management decisions is that the environmental goals of the organization and personnel are achieved in less time, with fewer employees or at lower financial costs. Environmental goals satisfy the following human needs: the need for safety, health, sustainable organization of life and physiological needs.
The ethical effectiveness of management decisions lies in the fact that the ethical goals of the organization and personnel are achieved in less time, with fewer employees or less financial costs. Moral goals achieve the satisfaction of the needs and interests of a person in accordance with the ethical norms of behavior of other people.
All proposed types of effectiveness of managerial decisions should be considered on the basis of close relationship and interdependence. The assessment of management decisions is based on certain principles:
1) the complexity of assessing the effectiveness of the solution;
2) the objectivity of the assessment of the decision;
3) obligatory assessment;
4) consistency of the assessment methodology and the nature of the managed object;
5) comparability of indicators for evaluating various management decisions;
6) taking into account the individual characteristics of the organization of the management situation when creating a model for assessing the effectiveness of management decisions.
In most cases, efficiency is assessed at a qualitative level and is expressed by the dynamics of quantitative and qualitative indicators: production, turnover, production and working costs, profits and other factors reflecting the overall performance of the organizational team.
Conclusion
The transition to market relations, the priority of issues of quality of products and services provided, as well as ensuring their competitiveness have increased the importance of a creative attitude to work and high professionalism. This encourages the search for new forms of management, to develop the potential abilities of personnel, to provide motivation for the labor process. Human resource management is one of the most important areas of the organization's activities and is considered the main criterion for its economic success.
At all stages of management, there is a need to make decisions. Making decisions on personnel management is classified as making personnel decisions. Features of personnel decisions are manifested in the following:
– are of an individual, personal nature, must take into account the personality characteristics of the subject of management;
– should be taken taking into account the fulfillment of the requirements of psychophysiology, technical aesthetics of labor, safety, environmental protection conditions;
– are accepted taking into account the controllability standards;
– must be taken in accordance with the norms of state law and the regulations of the enterprise;
– are aimed at increasing the efficiency of employees, taking into account the provision of job satisfaction for the sustainable development of the enterprise;
– are often intuitive in nature, based on the rationale and experience of the leader;
– are characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and risk;
– have a significant impact on the efficiency of the enterprise, play a decisive role in ensuring its competitiveness.
The control process can be represented as the following sequence:
• setting goals and identifying problems;
• development and decision making;
• organization and control of the implementation of the decision.
The mechanism for making personnel decisions involves performing multivariate calculations, justifying criteria for evaluating various alternatives, their priorities, determining actions and constantly improving it.
References
- Голубков, Е. П. Технология принятия управленческих решений / Е. П. Голубков. – Москва : Издательство «Дело и Сервис», 2005. – 554 с.
- Злобина, Н. В. Управленческие решения : учеб. пособие / Н. В. Злобина. – Тамбов : Изд-во Тамб. гос. техн. ун-та, 2007. – 80 с.
- Кибанов, А. Я. Оценка результатов труда персонала и результатов деятельности подразделений службы управления персоналом : учебно-практическое пособие / А. Я. Кибанов. – Москва : Проспект, 2015. – 72 с.
- Орлов, А. И. Принятие решений. Теория и методы разработки управленческих решений : учеб. пособие / А. И. Орлов. – Москва : Март, 2011. – 495 с.
- Смирнов, Э. А. Разработка управленческих решений : учебник / Э. А. Смирнов. – Москва : ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, 2010. – 271 с.
- Тронин, Ю. Н. Управленческие решения : учеб. пособие / Ю. Н. Тронин. – Москва : ЮНИТИ, 2012. – 309 с.
- Юкаева, В. С. Управленческие решения : учеб. пособие / В. С. Юкаева. – 4-е изд. – Москва : Дашков и Ко, 2009, – 322 с.
- Кибанов, А. Я. Управление персоналом организации : стратегия, маркетинг, интернационализация: учеб. пособие / А. Я. Кибанов, И. Б. Дуракова. – Москва : ИНФРА-М, 2009. – 301 с.
- Гильдингерш, М. Г., Добрусина М. Е. Концептуальные подходы к формированию профессиональной мобильности рабочей силы / М. Г. Гильдингерш, М. Е. Добрусина // Вестник Томского государственного университета. – 2013. – №377. – С. 102–105.
- Добрусина, М. Е., Завьялова Г. Н., Тулупова О. Н. и др. Государственно-частное партнерство как инновационная форма развития российского здравоохранения / М. Е. Добрусина, Г. Н. Завьялова, О. Н. Тулупова и др. // Вестник Томского государственного университета. – Экономика. – 2011. – № 1 (13). – С. 142–147.
- Добрусина, М. Е. Успешный пример последипломной подготовки / М. Е. Добрусина // Человек и труд. – 2007. – № 7. – С. 76–77.
