 |
 |
| |
 |
 |
 |
ABSTRACT OF MASTER'S WORKof Karaganova Elenaon the topic:"Recirńulation of top gas with the purpose of reduction of emissions of carbon dioxide"Scientific advisor: Kochura Vladimyr |
In the prime price of cast-iron about 50% expenses on its smelting are related to the expensive fuel - coke. Suggestion on injection of different types of fuels in the high furnaces with the purpose of its economy practically realized from 50-th years of XX century. A prevailing value was purchased by natural gas and pulverized coal. Injection of pulverized coal gives a considerable economic effect, but requires realization of expensive projects on the reconstruction of existing and creation of new equipment.
Ukraine used cheap natural gas of the Russian and Turkmenian deposits, that stipulated development and general application of technology of the blast-furnace melting with injection exactly it. However, presently prices grew substantially on it, and the folded structure of fuel balance of metallurgical enterprises with the use of natural gas as a substitute of coke became ineffective. Blast-furnace gas can be the alternative substitute of coke in the blast-furnace melting.
There was developed and tested the technology with injection in high furnace of hot restoration gases (HRG) and cold technological oxygen with the complete exception of the ordinary heated atmospheric blowing. For a receipt HRG apply own top gas in the process of his recycling. Main advantage of this technology consists of that it allows practically fully to utilize chemical energy of carbon of scarce coke and maximally to enrich ore-hearth gases repairers.
The flowsheet of process foresees pressing of the top gas cleared from a dust, deleting from it of dioxide of carbon, warming and serve of gas in the furnace of high furnace through tuyere devices. Through the same devices cold pressed technological oxygen is given. The gas cleaning from a dust is carried out by ordinary devices, serve is carried out by gas compressors. Deleting of CO2 from top gas is made by one of methods, mastered and widely applied in industry. For heating of gas utilize the regenerative vehicles of type of stoves.
A flowsheet foresees a CO2 utilizing, abstracted from top gas for the further use as a liquid or hard product. Calculations and workings show that such technology will provide the decline of expense of coke to 280-300 kg/t of cast-iron and increase of the productivity of stove on 25-30%.
The chart of work of blast furnace is presented on a picture 1.
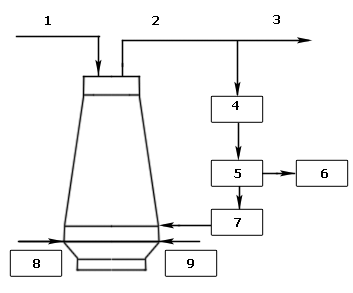
1 – coke
2 – top gas
3 – gas for users
4 – gas cleaning from a dust
5 – cleaning from CO2
6 – CO2 for the use
7 – gas heater
8 – pulverized coal
9 – cold blowing
Picture 1 – The chart of work of blast furnace on the method of Shar-DIN
Calculations show that realization of this chart in the conditions of blast-furnace workshop of "Azovstal'" will allow on the base of present resources of oxygen to give up application of natural gas (0,6 billion m3), reduce the annual necessity of coke on 430 thousand t, to economize 450 thousand t of conditional fuel; to promote the productivity of workshop on 40 thousand t, to improve quality of cast-iron on maintenance sulphure and silicon.
Mastering of the described technology in the blast-furnace workshop of "Azovstal" will be accompanied also by a production 4,1 million t of CO2 in the gaseous, liquid and hard state. Substantial part – 20...40 % of this new product can find application on a metallurgical combine.
The serious problems of this variant is absence of industrial eqipment for the production of cleaned top gas in mass amounts in the conditions of blast-furnace workshop, additional capital costs on realization of variant, operating costs, nessesary at the production of cleaned top gas.
On the whole it is obviously, that the variant of technology is very perspective foremost due to that provides, similarly as well as heating of blowing or improvement of preparation of iron-ore raw material, absolute decline of expense of fuel on an ironmaking. Therefore indicated variant needs deep theoretical, economic and project working as it applies to a large blast-furnace workshop.