| DonNTU | Master's DonNTU Portal | ENG | RUS |
| Autobiography | Report about the search | |
| Library | Behind polar circle | Links |
| Dychno M.  giveman@mail.ru giveman@mail.ru |
Abstract on the theme of master's work:"Research of methods of searching gross errors in measurings at equalization of networks of survey foundation of topographical surveys."Scientific adviser: Head of Department, professor, doctor of the technical sciences., Mogilny Sergey |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The presence of gross errors in the geodesic measurings always entailed some temporal and financial expenses. Therefore, detecting measuring, which containing an error, is very important and remains actual to present today. In addition, at present computer-aided systems and technologies of geodesic information collection and storage develop very swift rates. The following aims and tasks follow from the theme of my work: 1) to learn and analyse the existent methods for searching gross errors as it applies to the survey ground networks of topographical surveys; 2) to define by experimental way on how many reliably one or another method is able to detect gross errors; 3) to analyse the obtained results. 2 methods for searching gross errors are briefly produced below: 1th method. An overlay method of charts We will consider a method, which was offered by Dyakov B.N. and Rodionova Y.V. in the article [1]. If some measuring contains the gross error lj, then amendments in all measurings because of this error will be
where g i,j , — are elements of j column of G-matrix. To select the outlier, it is enough to count up mean quadratic deviation of amendments Vi for all n measurings from the samples of vi,j, namely
After testing of all measurings if measuring have minimal sign of then this measuring is outlier [1].
Kougiya V.A. made a conclusion that for measuring, which containing a gross error, attitude of amendment toward admittance vi/mvi has a maximal value. In order that, to find mean quadratic deviation of amendment mvi we use the cross-correlation matrix of amendments:
Supposing measurings independent, write down:
Put the last expression in (1) and replace the random errors of measurings with their means, equal to the zero. We will get the mean of the vector of amendments:
Attitude of the mean of i-that amendment toward admittance will be:
where ri,h is a correlation coefficient to i-that and h-that amendments, constant Modules of correlation coefficients less than or equal to unit for all values of i. Consequently, for measuring, which containing a gross error, attitude of amendment toward admittance has a maximal value and can serve as a indication to exclude this measuring [2]. At first both methods were tested on motion (fig. 1). For research we must make or model a few such networks. It is necessary to add to every measuring a random error, and to one of measurings - outlier. A simulation technique can help herein. Mathcad was used here.
Fig. 1 Linear-angular motion of free form (Animation is done with Microsoft GIF Animator: 10 frames, 5 circles repeating, size 45,1 Kb) Table 1 - Testing of overlay method of charts
Table 2 - Testing of method “amendment/admittance”
The program, which realizing the method of detecting gross errors, which offered by Kougiya, was also written in the environment Delphi. In this case I used results from software product «MGSETI» as basic data. In this case as an analysable geodesic network was chosen a build net (fig. 2).
Рисунок 2 - Схема строительной сетки Program was tested 10 times.
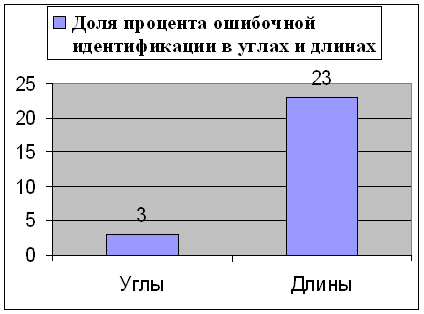
It is possible to draw conclusion from here, that method of detecting gross error on amendments from equalization, which offered by professor Kougiya Vilio by Alexander, in 20-30 from 100 cases not right identifies measuring, which containing a gross error. ВЫВОДЫ.Analysing results, it is possible to do the following conclusions: 1) an overlay method of charts gave unsatisfactory results: 15% the correctly found misses, but it is impossible to trust, because failing can be contained not in a method, but in his programmatic realization, that's why further researches are needed; 2) method of professor Kougiya a «amendment/admittance» gave good results: - 93,5% for linear-angular motion on fig.1; - 74% for a build net (fig.2). But it is a very strange fact noticed in second case: wrong authentication of measuring, which containing a gross error, prevails for measurings of lengths. It is represented in diagram.
This phenomenon must be farther probed. Also further researches will consist on the analysis of methods on possibility of detecting a few gross errors. The fair copy of submitted researches will be presented in December, 2008.
Перечень ссылок:1 . Дьяков Б.Н., Родионова Ю.В. Тестирование линейно-угловых ходов на грубые ошибки измерений // Геодезия и картография. – 2003. - №7. – с. 21-24. 2 . Коугия В.А. Сравнение методов обнаружения и идентификации ошибок измерений // Геодезия и картография. – 1998. - №5. – с. 23-27.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
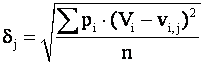 (2)
(2)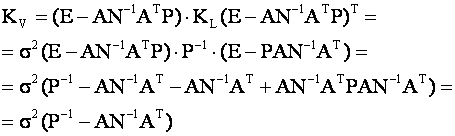
 (4)
(4) 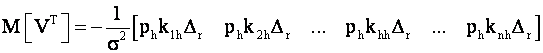 (8)
(8) (9)
(9)