|
|
|


Abstract
Content
- The list of reductions.
- Magnetic suspension of the vehicle.
- Block diagram of a control system of electromagnetic suspension of HSST.
- The brief description of the made work.
- The brief analysis of the received results.
- The conclusion.
The list of reductions.
HSST – high-speed social transport;
CDS – continuous dynamic system;
DDS – discrete dynamic system;
MS – magnetic suspension;
EM – an electromagnet;
EMS – electromagnetic suspension;
EDS – electrodynamic suspension;
SCS – suspension on constant magnets;
CMS – combined magnetic suspension;
FR – ferro-rail;
CS – a control system;
PEE – a power executive element;
LE – the linear engine;
PAP – a package of applied programs.
Magnetic suspension of the vehicle.
The system electromagnetic suspension is based on effect of a magnetic attraction of an electromagnet to ferro-rail. Force of an attraction to FR which is called the elevating force FÏ, should counterbalance all loadings FÝ acting on vehicle, including force of weight of vehicle.
while EM is moving lengthways the ferro-rail the vortical currents in it create a magnetic stream, that disables the basic magnetic stream. Arising force FÂ can be spread out on brake FÒ , directed against movement of vehicle , and the repellent force FÎÒ directed against elevating force FÏ. With growth of the speed of the vehicle, the influence of vortical currents can reach essential size and consequently should be considered at calculation and designing of electromagnet and ferro-rail. The diagram of interaction of forces in system EMS is shown on fig. 1 a, at motionless vehicle, and on fig. 1, b, at movement. Indemnification of repellent force FÎÒ is carried out automatically by a control system of MS by corresponding increase of the current strength in winding of EM, and brake force FÒ – corresponding increase of traction effort of the linear engine.
Two stabilizing systems are generally required for deduction of vehicle above way structure: in vertical and horizontal planes. Most simply it is reached by using of two independent systems of EMS. One of them carries out magnetic suspension of vehicle in a vertical plane, and another is directing. The basic constructive scheme of such vehicle is shown on fig. 2.

Figure 1 – the Diagram of interaction of forces of EMS

Figure 2 – the Constructive scheme of vehicle with separate system of suspension and direction:
1 – LE; 2 – direction EM; 3 – suspension EM
To content
Block diagram of a control system of electromagnetic suspension of HSST.
In the given work widespread enough block diagram of a control system electromagnetic of suspension of HSST is used.
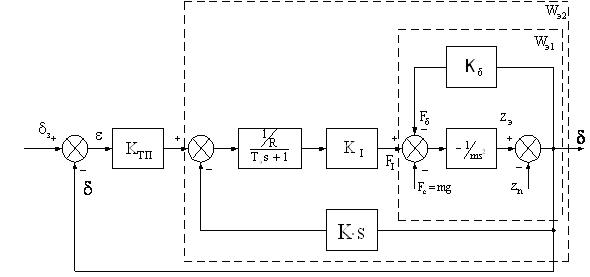
Figure 3 – the Block diagram of system of automatic control of a backlash
On fig. 3 following designations are used:
 – an air backlash between poles of electromagnets and ferro-rail; – an air backlash between poles of electromagnets and ferro-rail;
 – a signal of a mismatch; – a signal of a mismatch;
 – coordinate of the electromagnet; – coordinate of the electromagnet;
 – coordinate of the way; – coordinate of the way;
Òý – a constant of time of an electromagnet (EM);
R – field resistance of EM;
m – weight of the vehicle;
Kòï – gain constant of the thyristor valve;
 – gain constants accordingly from a current and a backlash to force; – gain constants accordingly from a current and a backlash to force;
K – gain constant from speed of change of a backlash to EMF of induction.
To content
The brief description of the made work.
The transfer function of investigated system is defined using the block diagram above , the system of the differential equations that describe behavior of system and representation of system in space of conditions is carried out on its basis.
Further synthesis of a modal regulator has been made for system of automatic control, with preliminary transformation our continuous dynamic systems (CDS) in discrete (DDS). Synthesis of a modal regulator is made using the Akkerman’s method on the basis of a choice of a desirable arrangement of poles of the loop system.
After reception of a vector of factors of a feedback of a modal regulator. The Akkerman’s method is used to synthesize the observer of a condition of the lowered order for investigated system. Having received factors of a feedback of the observer of the lowered order we synthesize a dynamic regulator, using also the received factors of a feedback of a modal regulator and the observer of the lowered order.
Further research of optimum control of the system of EMS of HSST is made. So we synthesize an optimum regulator for DDS of EMS on the basis of Lyapunov's second method.
To content
The brief analysis of the received results.
Analyzing the transitive characteristics, received at virtual synthesis of dynamic and optimum regulators with use of a package of applied programs MatLab, it is possible to draw conclusions, that in system with a dynamic regulator a little overcontrol is observed. It is the negative factor that influences comfort of a trip in the vehicle of HSST. The optimum regulator in turn allows to achieve full absence of overcontrol, however the speed of such regulator in comparison with dynamic considerably decreases.
On the basis of the received results it is possible to draw a conclusion, that it is more preferable for the system to use an optimum regulator for maintenance of greater comfortableness of transportations but if control speed is accepted to a basis to the detriment of comfort the dynamic regulator is better to use.
To content
The conclusion.
During the research the system of by a backlash of magnetic suspension of high-speed social transport automatic control has been investigated. Problems and prospects of development and perfection of transport system have been studied. Pros and cons of introduction the system of HSST in world transport are studied.
Also the equations of a condition and the equation of an output of dynamic system of electromagnetic suspension in the continuous and discrete forms have been received. The problem of synthesis of a dynamic regulator on the basis of desirable accommodation of poles of the loop system using Akkerman’s method is solved.
Synthesis of algorithm of optimum control by square-law criterion of quality by Lyapunov's second method is made and the decision of Rikkati’s matrix equation is received. Expressions for the minimal value of criterion of an optimality and algorithm of the optimum operating influence delivering a minimum to set criterion of quality are resulted.
Experimental modelling of the investigated DDS with reception of transients in the nominal and indignant operating modes is lead.
The received experimental results completely confirm the basic theoretical positions of the given work.
Since the master’s work is not finished yet, it is supposed in the future to synthesis and research the robust control systems of ENS of HSST, and also to lead the comparative analysis of all investigated systems of automatic control of EMS of HSST, with the purpose of definition of the most effective regulator.
To content


|










