
Morozov Alexandr Alexandrovich
Department: CITA
Speciality: Electrinic System
Theme of master's work: Termoanemometr with the unstationary mode of warming-up of sensible element
Leader of work: Kuznecov Dmitri Nicolaivich

Dissertation
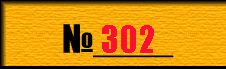
1. REVIEW OF METHODS OF MEASURING OF EXPENSE GAZA. In the spheres of national economy, related to the use and transporting of gases and liquids (by gas, oil, neftepererabatyvayuschey, chemical and t. of d.) the termoanemometricheskie transformers of expense are widely utillized . Termoanemometry possess small inertia, high sensitiveness, exactness, reliability, compactness. Over 20 methods of measuring of expense and large number of their varieties are presently known. Raskhodomery, most widely widespread in industry, on principle actions are divided into the followings basic groups: variable overfall of pressure; flowing around – permanent overfall of pressure; takhometricheskie; electromagnetic; variable level; thermal; vortical; acoustic. In addition, raskhodomery, based on other principles of action is known: resonance, optical, ionization, metochnye and other. However much many of them are in the stage of development and wide application did not get while. Most distribution was got by raskhodometry of variable and permanent overfall of pressure. Difmanometry belong to raskhodometram of variable overfall of pressure, at the use of which the overfall of pressure in a pipeline is created narrowing devices (by diaphragms, nozzles, by the pipe of Venturi etc.). The area of communicating section changes in raskhodometrakh of permanent overfall of pressure, and an overfall before and after it remains unchanging. Such type of raskhodometry executed with the submerged float or piston. The lack of these methods is a necessity for a sverkhchuvstvitel'nom electronic manometer. On occasion, when it is impossible to apply raskhodometr, a flowrate is measured by pressure tubes, hydraulic rotators and anemometers and calculate a flowrate in some his section. A by volume expense is determined, multiplying speed by the area of section. Tachometric flowmeters are widely used in all industries of industry. Principle of their action is based on the use of dependences of rate of movement of bodies – pickoffs, placed in a stream, from the expense of matters, flowings through these flowmeters. From this group of flowmeters most often a turbine is used in practice, ball-shaped and vestibule. For measuring of speed and (or) expense of conducting matter can electromagnetic flowmeters will be used. In basis of work of electromagnetic flowmeters dependence is fixed E.M.F., induciruemoy in an electro-conducting environment, locomotive in the electromagnetic field. Structurally a transformer of electromagnetic flowmeter is an area of pipeline, executed from nemagnitnogo material two electrodes are mounted in which. In the place of location of electrodes the magnetic system or poles of magnet take place out of pipeline . The basic lack of these devices is impossibility of measuring of expense of neprovodyaschikh environments. If it is necessary to measure the expense of muddy liquids, limewater, diffusive juice, susla-samoteka and t. of p., the flowmeters of variable level are usually used. Principle of action of devices is based on dependence of level of liquid in a vessel from an expense at free expiration it through the calibrated opening (crack) in a day or lateral wall of vessel. Presently developed and vortical flowmeters have very wide prospects of application, principle of action of which is based on dependence on the expense of frequency of pressure of environment fluctuations, arising up in a stream in the process of vikhreobrazovaniya. All greater distribution is got by acoustic flowmeters. Principle of action of such raskhodometrov is based on dependence of acoustic effect in the stream of matter from his speed. Possibility of their application is instrumental in wide distribution of acoustic flowmeters for measuring of charges of muddy and aggressive environments, bezinercionnost', contact free of measurings, absence of locomotive parts in a stream, absence of losses of pressure in pipelines and ets Thermal flowmeters are very perspective. Principle of their action is based on the use of dependence of effect of the thermal affecting stream of matter from the mass expense of this matter. A calorimetry distinguish, flowmeters of thermal layer and termoanemometricheskie flowmeters. Calorimetry flowmeters are based on heating or cooling of stream an extraneous energy source, creating the difference of temperatures in a stream. Flowmeters of thermal layer, differences of temperatures based on creation both-side boundary layer. It is accepted to distinguish Termoanemometry on the row of signs, characterizing the thermal mode of transformer: to the method of heating of pickoff (to the line, indirect, continuous, impulsive); to the sort of current, feed-in a bridge (permanent, variable); to the features of electric chart and ets. Termoanemometricheskiy a method is based on dependence of heat emission of the heated pickoff on a flowrate. In general case heat emission depends on many factors, namely – from a flowrate, physical properties of gas (to the closeness, heat conductivity, heat capacity and viscidity), difference of temperatures of pickoff and gas, and also from configuration of transformer. Cooling of pickoff a gas stream results in diminishing of his temperature, change of electric resistances and Dzhouleva of teplovydeleniya. Measuring a pickoff on CHE and current in his chain, it is possible, at the known physical properties of material of pickoff and conformities to law of heat exchange, to define a local flowrate. Termoanemometricheskiy a method possesses the row of dignities: a high sensitiveness provides possibility of measuring in the wide range of speeds of streams; the miniature sizes of pickoff provide possibility of measuring of quickly changing local speeds; independence of testimonies from the closeness of gas (mass speed is measured); presence of electric output signal with a level, not requiring the additional strengthening; measurings charts PIP maximum simple; measuring is carried out comparatively simply. To the number the lacks of method belong: necessity of the individual calibrating each PIP, conditioned impossibility of making of identical transformers on electric and structural parameters; nestabil'nost' of calibration description, conditioned the structural changes of material of pickoff, caused heating, dynamic loadings, contamination; substantial temperature dependence of testimonies of thermoanemometer, obuslavlivayuschaya necessity of implementation of calibrating at the different temperatures of gas. Office hours THAT. Depending on the thermal mode CHE distinguish termoanemometry of direct-current and stationary temperature. Considerably the best dynamic and static descriptions are possessed by termoanemometry of stationary temperature. They are executed on the reserved measuring chart (ris.1) and work on compensative principle. Warmed-up termorezistor of Rw makes a bridge chart with the permanent resistors of R1-r3. In obedience to the law of Dzhoulya-lenca thermal power of F1, selected a pickoff in time unit, is determined expression I – is a current through the filament of thermoanemometer.. In the set mode of operations of thermoanemometer the power of F1 transformed in a heat will be equal to the power of F2 dispersed in a stream : Thus due to maintenance of certain size of current of I0 is a bridge chart able, near to balanced, and signal of rassoglasovaniya ? on a measuring diagonal appears very small. Change mass speed ?? stream does cause the change of heat emission of F1, and also temperatures of Tw, resistances of Rw and signal of rassoglasovaniya ?. Change ? through a strengthener manages the size of the electric power of F2 selected on a filament by the change of current of I0 of feed of bridge. Does the current of I1, passing on a filament, change until balance of powers of F2 and F1 will not come and the sizes of resistance of Rw and temperatures of Tw of filament will appear near enough to the former values at which signal ? will become very insignificant.  picture1 - Chart of compensative principle. Thus, the temperature of filament of Tw will be supported in sort permanent. The data-out of chart is a general current of I0 or tension of feed of bridge of E, I1 simply related to the current. The model type of family of calibrating plots of thermoanemometer at the different temperatures of gas of Tg is resulted on ris.2. We will mark that with the change of temperature of stream there is vertical displacement of calibration description, therefore at measurings in neizotermicheskikh streams it is necessary to carry out temperature indemnification of testimonies TA.  picture 2 - Family of calibrating plots of thermoanemometer. 2. SENSIBLE ELEMENTS Types of pickoffs THAT. Charts, descriptions and application domains THAT different type largely determined properties of pickoffs, reactive directly on the change of gas-dynamic property. The wire apply, pellicle and semiconductor CHE. On ris.3 the constructions of wire transformers, intended for measuring of one or two komponent of speed of flat stream and his temperature are resulted. Wire CHE very nenadezhny from fragility of wire the diameter of which makes units of micrometres. A their application domain is limited, mainly, by experimental researches of dynamic descriptions of gas streams.  picture 3 - Constructions of wire transformers Pellicle transformers are much more reliable. They consist of thin tape, executed from platinum or nickel, inflicted on podlozhku from glass or quartz. Tokopodvodami are either platinum electrodes, podlozhki placed inward or silver napylennye explorers, located to on formative podlozhki. On ris.4 the most widespread types of pellicle transformers, used at measurings of descriptions of turbulence are resulted.  picture 4 - Types of pellicle transformers Substantial failing wire and pellicle CHE is strong temporal nestabil'nost' of calibration description, conditioned a direct contact with a gas stream and contamination, that requires their careful permanent calibrating. 3. PRINCIPLE OF DECISION OF TASKS OF HEAT CONDUCTIVITY AND HEAT EXCHANGE. We will consider the general view of calibration dependence THAT, establishing a connection of output signal from a flowrate. From three types of heat exchange (heat conductivity, convection, caloradiance) basic role in the heat exchange of pickoff a convection and heat conductivity of fastening armature play with the stream of gas.Obviously, that a konvektivnaya heat transfer is useful, while heat conductivity of fastening armature – concomitant, deteriorative metrology descriptions of primary transformer. A konvektivnyy heat exchange depends on nature of origin and mode of stream, family and physical properties of working environment, form and size of body. Is intensity of konvektivnogo heat exchange characterized the coefficient of heat emission ?, which is determined on the formula of N'yutona-rikhmana In obedience to this law the thermal stream of W is proportional the surface of heat exchange of S and differences of temperatures of surface and gas (Tf – Tg). The coefficient of heat emission is determined as an amount of warmth, given in time unit unit of surface at the difference of temperatures between a surface and liquid, equal to one degree: The processes of heat emission are indissolubly related to the terms of motion of gas. As is generally known, there are two basic modes of flow: laminarnyy and turbulent. At the laminarnom mode even, stream temper has a flow. At turbulent is motion of neuporyadochennoe, vortical. The change of the mode of motion takes place at some «stalling» speed which in every case is different. The theoretical raising of task of heat conductivity with the forced convection even at certain limitations results in the decision of the difficult system of joint equalizations in partials in relation to a temperature and speed at the proper scope terms. Kingom was first put and decided task of heat exchange for a neogranichennogo cylinder. As a result expression for the amount of heat of F is got on unit of length of cylindrical wire in time unit [28]:  Tw, Tg is a temperature of wire and gas; d is a diameter of wire; ?g it is heat gas conductivity; ?, sg is a closeness and specific heat capacity of gas; ? it is gas speed. Determining in termoanemometrii is dependence of number of Nussel'ta on the number of Reynolds (in the criteria of similarity). Presentation of dependence in the numbers of similarity allows the results of separate experiments to diffuse on all similar to it processes. Expression (5) in a dimensionless kind is written down as follows: Nu, Re – accordingly numbers of Nussel'ta and Reynolds; And and In are dimensionless coefficients. The number of Nussel'ta is characterized by intensity of konvektivnogo teploobmena The number of Reynolds is determined by hydromechanical similarity of flows of teplonositeley: Plenty of criterion correlations is conditioned the presence of large number of constructions of transformers, different quality of experiment and different methods of processing of data. However taken all of them, in the total, are to generally accepted for wire and pellicle THAT to expression of kind We will paint the number of Nussel'ta, will get 4. METHOD OF MEASURING OF EXPENSE ON SPEED IN ONE POINT OF CROSS-SECTIONAL OF PIPELINE. GOST 8.361-79 sets the rules of measuring of expense for pipes by a diameter from 300 mm by determination of flowrate in characteristic points. There are 3 methods of measuring of expense on speed in one point of cross-sectional: 1. A method of the direct measuring of middle speed is in the place of its existence. 2. Method of measuring of high speed along the axis of round pipe with subsequent determination on it of middle speed. 3. A method of measuring of local speed is in the arbitrary point of section, correlation of local and middle speed is known in which. At implementation of measurings the followings terms must be observed: – a stream in a pipeline must be formed and turbulent, and motion – set; – the area of measuring section during all period of measurings must remain permanent; – on walls a pipe must not be deposits and growths of measureable environment or products of corrosion; – a measureable environment must be odnofaznoy or on the physical properties near to odnofaznoy; – at measuring of expense the number of Stroke must not exceed 0,25. At determination of expense this method it is necessary to measure a primary transformer local speed in one point of cross-sectional of pipe and area of this cross-sectional. Expense of Q, m3/s determine on a formula At measuring of flowrate on the axis of pipe value of coefficient to To? depends on hydraulic descriptions of pipes (roughnesses of surface, numbers of Reynolds – Re) and it must be preliminary determined experimentally for every measuring section. At measuring in points middle speed coefficient to To? remains permanent and equal to unit in all range of turbulent flow. The points of middle speed at the developed turbulent flow of measureable environment are located in the distance (0,242?0,013) r from the internal surface of wall of pipe, where r is an internal radius of pipe in a measuring section (pic.5). 5. ALTERNATIVE METHODS OF MEASURING OF EXPENSE GAZA. Based it is possible to draw conclusion on the collected material, that by the basic lack of termoanemometrov built on classic charts (thermoanemometer of direct-current, thermoanemometer of stationary temperature) there is strong dependence of testimonies of device on the temperature of the controlled environment. Therefore calibrating of these devices is executed at different temperatures, and, consequently, there is a labour intensive process and related to the heavy temporal tolls. Perspective in that behalf are THAT with, so urgent, by the nestacionarnym mode of warming-up of termochuvstvitel'nogo element (TCHE). Their principle of action is based on dependence permanent time of TCHE from a flowrate gas (liquids). From some data this dependence is the very weak function of temperature. However method of measurings of gas speed, based on dependence of TPV CHE on a flowrate gas while did not find wide distribution because of complication of his hardware representation. Presently due to successes in development of microelectronics and microprocessor technique realization of this method of measurings became the real and accessible. We will consider some variants of construction THAT by the nestacionarnym mode of warming-up of TCHA on the basis of thermoanemometer of stationary temperature. The flow diagram of measuring device is presented on a picture 5. A measuring device works in two modes: mode of large currents (mode of thermoanemometer of stationary temperature) and mode of small current (mode of thermometer). For switching of the modes the block of commutation of the modes is used. The mode of thermoanemometer is used for the warming-up of CHE to the set temperature, mode of thermometer – for measurings of current temperature of CHE. The method of measuring of TPV consists in realization of next actions (ris.6) of measuring of current temperature of SE: 1) ITA is translated in the mode of thermoanemometer of stationary temperature and CHE warmed up to the set temperature of Tw; 2) ITA is commuted in the mode of thermometer and taken off transitional description of cooling-down of SE; complex microprocessor treatment of the got results is executed with the purpose of determination of TPV SE.  picture 5 - Flow diagram TA.  picture 6 - Diagrams, explaining work TA. Variants of construction of analog part THAT, plugging in itself the thermoanemometer of stationary temperature, thermometer and block of commutation of the modes, presented on pictures 7 and 8. The first variant differs simplicity of realization as contains an only one operating strengthener (OU), and for commutation of the modes of termoanemometr/termometr the unique key of S1 is used.  picture7 -Analog part of ITA on the base of bridge chart of thermoanemometer of stationary temperature 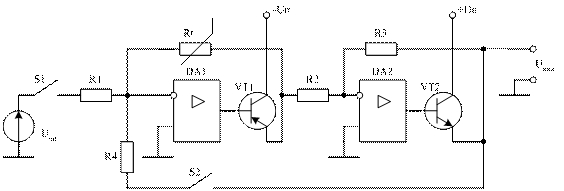 picture 8 - Improved analog part of ITA on two operating strengtheners In SKTB «Turbulence» the pre-production model of ITA was made with analog part built on the chart of ris.8. For commutation of the modes of termoanemometr/termometr the switchboard of analog signals Kr590kn4 is used miniature termistor of firm Epcos is used the .v role of CHE in a glass shell. On ris.9 calibration dependences of ITA are presented got experimentally on air in the aerodynamic stand of Ads200/250 in the range of speeds a from 1 to 15 m/s at temperatures 20 ? and 45 ?. The results of experimental researches well combine a mate with results. designs and confirm that TPV CHE poorly depends on the temperature of gas.  picture 9 - Experimental calibration descriptions of experimental ITA As turned out, this chart did not possess sufficient pomekhozaschischennost'yu, that results in the gallops of calibration description on the initial stage. |
DonNTU |
Master's personal portal DonNTU |
Dissertation | library | links |
Serch report | Individual work