Abstract on the topic of the final work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Purpose and objectives of the study, planned results
- 3. Research and development overview
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Overview of national sources
- 3.3 Overview of local sources
- 4. Structure of the accounting object of equity
- 5. The state of the problem of the organization of state control and audit of own capital
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
One of the components of the successful activity of any organization is the presence of a balanced set of sources of financing that ensure high competitiveness, trust of economic partners and creditors. In this situation, the development of the institution of corporate property, intensive processes of creation and reorganization of organizations cause increased interest by various market participants in the category of equity capital as a certain indicator of effective activity, financial stability and stability of economic entities.
Equity plays an important role in the activities of economic entities, since it is he who represents the financial basis of its functioning. The condition and structure of equity capital allow you to determine the financial and property status of the organization. Equity capital is formed at the initial stage of the organization's life, during its registration, but throughout the entire period of management, the founders strive to increase their own capital, since this economic category is highly significant. Such economic indicators as financial stability, solvency, efficiency of activity and the level of well-being of the owners of the organization depend on the amount of equity capital.
1. Theme urgency
The low level of informativeness generates caution, and in some cases, unwillingness of potential investors to invest capital due to the uncertainty of the resulting entrepreneurial risk, since the investor is often separated from the capital management process in business organizations compared to private or equity entrepreneurship. In these circumstances, issues related to obtaining complete, transparent, neutral and reliable information about the amount of the organization's own capital become especially relevant. This can be achieved through a qualitatively conducted independent audit in order to improve the efficiency of management decision-making.
In connection with the above, ambiguous approaches to determining the essence of the audit, its weak organizational and methodological support, which is expressed in the dispersion and unsystematic presentation of individual audit evidence, in the study and evaluation of methods of accounting and auditing of equity determine the relevance of the chosen topic of the dissertation research.
In relation to the audit, the choice of the topic is due to the problem of auditing equity transactions on a residual basis, since equity items are relatively non-dynamic (with the exception of retained earnings), but at the same time they are most significant from the point of view of users of accounting statements.
2. Purpose and objectives of the study, planned results
The purpose of the master's thesis is to identify problem areas in the organization of state control and audit of the company's own capital and propose ways to improve it.
In accordance with the set goal , the following tasks were formed:
- to study the theoretical foundations of state control of own capital;
- to consider the methodology of state control of own capital;
- to propose ways to improve the state control of own capital.
The object of the study is the process of organizing state control and audit of the company's equity capital, Branch No. 1 of the State Corporation for the Development and implementation of modern technologies "Donetsk Technologies".
The subject of the study is the organization of state control and audit of the equity capital of the enterprise Branch No. 1 of the State Corporation for the development and implementation of modern technologies "Donetsk Technologies".
The theoretical and methodological basis of the work is the scientific works of researchers dealing with the problems of the organization of state control and audit of equity, regulatory and legislative acts, statistical and accounting reports, and other information obtained from open sources.
The scientific novelty of the obtained results lies in the theoretical substantiation and development of organizational, methodological and practical recommendations for improving state control and audit of the company's own capital.
3. Research and development overview
Equity is one of the most important economic categories. There are no equity accounting standards in the Donetsk People's Republic, however, there are mentions of certain elements in the Accounting Regulations (Standards) 17 "Income Tax" [8], Accounting Regulations (Standards) 1 "General Requirements for Financial Reporting" [6], Accounting Regulations (Standards) 24 "Profit per share" [9] and Accounting Regulations (Standards) 5 "Statement of Equity" [10]. Russian Accounting Standards and International Financial Reporting Standards also do not have a separate standard dedicated to the recognition and reporting of the company's capital and its elements.
3.1 Overview of international sources
To clarify the essence of equity, we will give a number of interpretations. Table 3.1 shows the systematization of views from the standpoint of economic theory on the concept of "capital". [4]
Table 3.1 - Systematization of views on the concept of "capital" from the standpoint of economic theory [4]
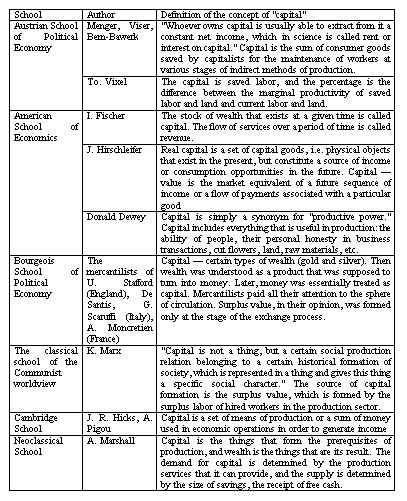
According to the National Accounting Standard 1, equity is the part of an enterprise's assets remaining after deducting its liabilities [6]
The principles of International Financial Reporting Standards define capital as net assets, namely as "the residual interest in the assets of an organization after deducting all its liabilities." [5]
Thus, despite the difference and originality of individual formulations, there are no significant differences in the views of scientists on the issue of the content of equity capital. One way or another, they define equity as the owners' share in the assets of the organization.
3.2 Overview of national sources
In their article, Pos A.Yu. and Piskunova N.V. (Donetsk National University) examined the main approaches to determining the essence of the concept of "equity" as an accounting category, based on a review of the literature, the author's definition of this definition is justified. The idea of the most typical components of equity in foreign countries has been formed. [7]
Chubar Ya.D. and Bessarabov V.O. (Donetsk National University of Economics and Trade named after Mikhail Tugan-Baranovsky) in their work identified a number of problems associated with the ambiguous interpretation of the concept of "equity" in the special economic literature. They justified the need to improve the definition of equity as an object of accounting in modern business conditions of enterprises. Equity is the total value of assets minus liabilities, which combines authorized, additional, reserve capital and retained earnings created using invested and accumulated economic resources, and ensures the effective functioning of the enterprise, as well as profit maximization. [11]
3.3 Overview of local sources
At Donetsk National Technical University (Department of Accounting and Auditing), the peculiarities and problems of accounting and auditing of equity were widely covered.
The article by Bychkova E.V. and Boretskaya K.E. allows us to delve into the history of the emergence of the category "capital". Also, this study showed that the principles of organization and accounting, the procedure for disclosure of information in financial statements and the structure of equity are greatly influenced by the choice of a theoretical conceptual basis for the representation of capital.
Equity accounting is an important area in the accounting system of an industrial enterprise and requires special attention. Qualitative regulatory regulation will allow at the enterprise level to identify bottlenecks in the organization of capital assessment, as well as to determine the directions of its rationing. [1]
Equity capital cannot be considered separately from the rest of the organization's activities. This statement is confirmed by the study of Prof. Gavrilenko V.A. and Leonova L.A. In their article, they justified the need to improve the accounting of transactions with fixed assets. Identified shortcomings in accounting for such operations with fixed assets as: capital repairs; markdown, revaluation, sale and liquidation, which lead to distortion of their book value and equity in general. A new approach is proposed in accounting for the listed operations with fixed assets. [2]
4. Structure of the accounting object of equity
The structure of equity is represented by the following categories corresponding to the Balance Sheet items.
The article "Authorized capital" contains the total value of assets fixed in the constituent documents, which are the contribution of owners (participants) to the capital of the enterprise.
The article "Share capital" provides the amount of share contributions of members of unions and other enterprises provided for in the constituent documents.
In the article "Additional invested capital", joint-stock companies show the amount by which the value of the sale of issued shares exceeds their nominal value. Other enterprises reflect in this article the amount of capital invested by the founders in excess of the authorized capital.
The article "Other additional capital" reflects the amount of additional valuation of non-current assets, the value of non-current assets received by the enterprise free of charge from other legal entities or individuals, and other types of additional capital.
The article "Reserve capital" provides the amount of reserves created in accordance with current legislation or constituent documents at the expense of retained earnings of the enterprise.
The article "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" reflects either the amount of retained earnings or the amount of uncovered loss. The amount of uncovered loss is shown in parentheses and is deducted when determining the total equity.
The article "Unpaid capital" reflects the amount of debt owed by owners (participants) on contributions to the authorized capital. This amount is given in parentheses and is deducted when determining the total equity.
In the article "Withdrawn capital", business companies reflect the actual cost of shares of their own issue or shares purchased by the company from its participants.[3]
A qualitative understanding of the structure of the facility will make it possible to improve state control and audit of the company's own capital.
5. The state of the problem of the organization of state control and audit of own capital
To create a comprehensive information and methodological support for the audit, a model of the information base for the audit of equity capital has been developed, including objects and elements (generalized and private). The list of objects of equity capital audit is presented in an enlarged form by authorized, additional, reserve capital and retained earnings; potential capital in the form of targeted financing should be allocated separately. Generalized audit elements are indicators formed in accordance with the current procedure for the formation (calculation) and changes in the value of individual components of equity. Private elements are essentially already indivisible indicators or separate transactions reflected in primary documents and on accounting accounts, which are the reference units in the totality of objects and elements of the audit.
For a comprehensive audit of operations with equity and minimization of information risk in management decision-making, it is recommended to conduct an audit in three consecutive stages (fig. 5.1).
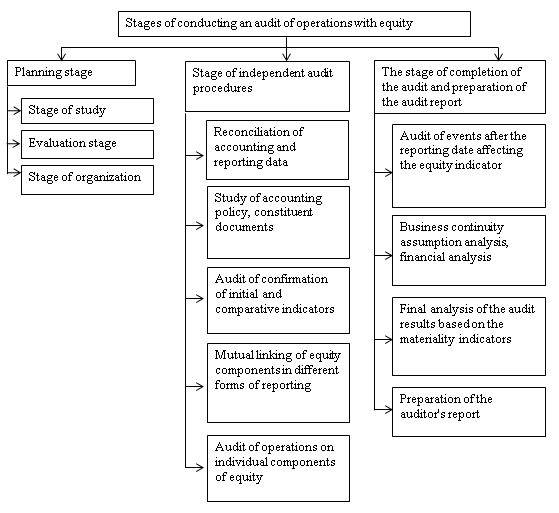
Figure 5.1 – Diagram of the stages of conducting an audit of operations with equity
The methodology for calculating the materiality level is based on an inductive method of determining it, combining an analysis of the risk level of the internal control system for each element (article) of the reporting, the impact of the element (article) on the entire reporting and the auditor's assessment of the significance for potential users of the reporting of each element (article). The essence of the inductive approach in the proposed methodology consists in the initial determination of the magnitude of the materiality levels of all items of the balance sheet and profit and loss statement, and then in the assessment of the overall (aggregated) level of materiality, based on the impact of each level of materiality.
To reduce audit risk, the absolute value of the materiality level for significant items is reduced by 1.5 times compared to the generally established procedure. With regard to the audit of individual components of equity, it can be noted that in this methodology for calculating the level of materiality, equity items will be significant in the following cases:
- with an initiative external audit in the interests of potential investors, creditors - all articles of equity;
- in case of an initiative internal audit in the interests of the management of the organization, its owners - all articles of equity;
- in case of mandatory audit - for organizations in the form of an open joint stock company - authorized capital, retained earnings (uncovered loss) of the reporting period;
- with mandatory audit - for organizations of all organizational and legal forms, newly formed or at the stage of reorganization - all articles of the section "Capital and reserves";
- for non-profit organizations - articles of targeted financing.
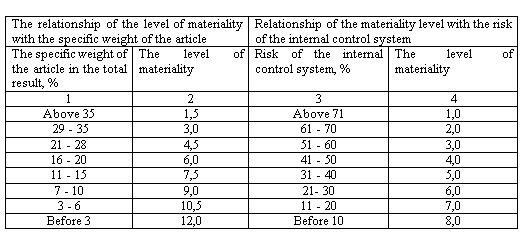
To account for the relationship between the level of materiality of the accounting reporting item with the risk of the internal control system for this article and the specific weight of the article in the total result, an algorithm is laid down in the developed form (table 5.1). Its essence boils down to the fact that for those reporting items that are characterized by a high risk of the internal control system and a significant share in the total, the level of materiality (materiality) for such items is reduced in order to have reasonable confidence in the absence of distortions in them.
Table 5.1 – Algorithm for linking the materiality level of an article with the specific weight of the article and the risks of the control system
To calculate the level of materiality for the reporting item , the program contains the formula:
- for meaningful articles:
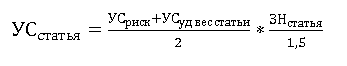
- for insignificant articles:
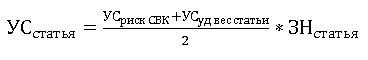
where УСстатья - the level of materiality under the accounting reporting item,
УСриск СВК - the risk factor of the internal control system affecting the indicator of the level of materiality under the reporting item
УСуд вес статьи - the factor of the specific weight of the accounting reporting item that affects the indicator of the level of materiality
ЗНстатья - the value of the accounting reporting item as of the end of the reporting period (for balance sheet indicators), as of the reporting period (for profit and loss statement indicators), for which the level of materiality is assessed.
In the context of the use of automated accounting information processing processes, the form of the MS Excel office application, which technically implements the described methodology for calculating the level of materiality, allows, in addition to the main functional load, to perform a number of applied tasks solved during the audit of equity:
- provides mutual linking of equity components reflected in different forms of reporting;
- performs an analysis of the financial and economic activities of the audited entity, as well as an analysis of compliance with the established requirements for net assets.
The proposed methodology for calculating the level of materiality allows us to take into account the variety of business conditions of the audited entities, eliminates individualism, unreasonableness and bias, ensures uniformity of calculation principles, simplicity and clarity in conclusions that may affect the decisions of users of reporting.
In relation to the described methodology for calculating the level of materiality, a mechanism for assessing the impact of the set of identified distortions on the modification of the auditor's report is proposed (fig. 5.2).
The essence of the proposed mechanism for applying the materiality level in assessing the audit results is to study the relationship between the totality of the identified distortions with the indicator of the aggregated level of materiality in the accounting statements as a whole and the indicators of materiality for individual reporting items.

Figure 5.2 – Application of the materiality level in the evaluation of audit results (animation: 7 frames, no repetitions limited, size 55.8 kilobytes)
Symbols:
- |ОТКЛс|- the totality of the identified distortions under the article;
- ПДОс – maximum permissible error under the reporting article;
- УСс – indicator of the level of materiality for the accounting reporting item;
- Уса – an aggregated indicator of materiality in the accounting statements as a whole.
The demand for the indicator of the organization's own capital is due to the wide possibilities of using and interpreting the results obtained during the analysis of economic activity. It is possible not to question the reliability of equity indicators generated programmatically. However, this does not solve the problem of forming high-quality information.
Reporting indicators may meet the criteria of reliability, but at the same time do not have the property of usefulness to users. In this regard, ways are proposed to increase the analytical value of the results of the audit of equity, from the standpoint of international and Russian standards, which consist in carrying out the following adjustments of individual components of equity:
- the heterogeneity of additional capital in accounting statements, the specifics of the formation of its individual components and the possibility of their use make it necessary to analyze the state and changes in additional capital in the context of such components. The allocation of the invested part from the additional capital (issue income and exchange differences resulting from contributions to the authorized capital in foreign currency) and the accumulated part (the results of revaluations of fixed assets) will allow special attention to be paid to the analysis of information accumulated in the form of an increase in the value of property during revaluation, which serves as an additional characteristic to the value of fixed assets of the organization, being a criterion for the validity of this value;
- additional costs directly related to capital transactions that could have been avoided in the absence of such transactions are accounted for in IFRS as a decrease in equity. There are no instructions in the national standards regarding the accounting of costs associated with the issue of securities. In practice, such costs are usually expensed in the income statement. In this regard, it seems appropriate to make adjustments to the indicators of retained earnings (uncovered loss) of the reporting period and additional capital in terms of issue income in cases of issue costs;
- the indicator of retained earnings in the current form of the balance sheet does not quite clearly reflect the characteristics of the financial result for the reporting periods. If an uncovered loss of the reporting year occurs and there is a balance of retained earnings of previous years, the amount of the loss in the balance sheet is covered by the profits of previous years. Due to the opacity of the retained earnings indicator, owners are deprived of the opportunity to make a decision on covering losses from other sources.
Thus, the distribution of profit (loss) on the indicators of previous years and the reporting period will contribute to a more reliable presentation of the generated indicators, as well as provide users with information for making decisions on the possible distribution of their own sources. [12]
Conclusion
The State Corporation for the development and implementation of modern Technologies "Donetsk Technologies" has various enterprises in its composition by type of activity: from the production of high-quality products to the provision of services in the field of hotel management. The proposed methodology for conducting an audit of equity capital can "adapt" to various enterprises, increasing the efficiency of the audit, which is relevant for this enterprise. The use of a unified methodology for conducting an audit of equity for a state corporation, taking into account the special impact of the type of activity of the branch, improves the quality of the audit. The methodology for determining the level of materiality in the conditions of automated data processing can be performed on the basis of the MS Excel office application.
The proposed methodology for calculating the level of materiality allows us to take into account the variety of business conditions of the audited entities, eliminates individualism, unreasonableness and bias, ensures uniformity of calculation principles, simplicity and clarity in conclusions that may affect the decisions of users of reporting.
To increase the usefulness of reporting indicators for users, it is necessary to make adjustments to individual components of equity at the level of accounting standards.
References
- Бычкова Е.В., Борецкая К.Е. Проблемы организации учета собственного капитала промышленного предприятия / Е.В. Бычкова, К.Е. Борецкая // Механизм реализации стратегии социально-экономического развития государства - 2020 [Электронный ресурс]: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=46124982.
- Гавриленко В.А., Леонова Л.А. Особенности реформирования учета операций с основными средствами и его влияние на собственный капитал / В.А. Гавриленко, Л.А. Леонова // Вестник Института экономических исследований – 2017. [Электронный ресурс]: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-reformirovaniya-ucheta-operatsiy-s-osnovnymi-sredstvami-i-ego-vliyaniya-na-sobstvennyy-kapital.
- Закон Донецкой Народной Республики «О государственном надзоре в сфере хозяйственной деятельности» №I-307П-НС от 21.08.2015 г. [Электронный ресурс]: https://dnrsovet.su/zakonodatelnaya-deyatelnost/prinyatye/zakony/zakon-donetskoj-narodnoj-respubliki-o-gosudarstvennom-nadzore-v-sfere-hozyajstvennoj-deyatelnosti/.
- Евстафьева Е.М. Эволюция развития категории «Собственный капитал» / Е.М. Евстафьева // Учет и статистика – 2009. [Электронный ресурс]: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/evolyutsiya-razvitiya-kategorii-sobstvennyy-kapital.
- Международный Стандарт Финансовой Отчетности (IAS) 12 «Налог на прибыль» № 160н от 25.11.2011 г. [Электронный ресурс]: https://minfin.gov.ru/common/upload/library/2017/01/main/MSFO_IAS_12.pdf.
- Национальное Положение Стандарт Бухгалтерского Учета 1 «Общие требования к финансовой отчетности» № 73 от 07.02.2013 г. [Электронный ресурс]:https://kodeksy.com.ua/ka/buh/psbu/1.htm.
- Пось А.Ю., Пискунова Н.В. Основные подходы к определению «собственный капитал» как учетной категории / А.Ю. Пось, Н.В. Пискунова // Финансы, учет, банки – 2018 . [Электронный ресурс]: http://donnu.ru/public/journals/files/Сборник%20ФУБ_2018%20-%203.pdf.
- Положение Стандарт Бухгалтерского Учета 17 «Налог на прибыль» № 353 от 28.12.2000 г. [Электронный ресурс]: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0047-01#Text.
- Положение Стандарт Бухгалтерского Учета 24 «Прибыль на акцию» №344 от 16.17.2001 г. [Электронный ресурс]: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0647-01#Text.
- Положение Стандарт Бухгалтерского Учета 5 «Отчет о собственном капитале» №391 от 21.07.1999 г. [Электронный ресурс]: https://kodeksy.com.ua/ka/buh/psbu/5.htm .
- Чубарь Я.Д., Бессарабов В.О. Сущность собственного капитала предприятия как объекта бухгалтерского учета/ Я.Д. Чубарь, В.О. Бессарабов // Актуальные проблемы экономики и управления: теория и практика – 2017. [Электронный ресурс]: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=29151151.
- Шириков С.И. Организация аудита собственного капитала хозяйствующих субъектов: теория и практика / С.И. Шириков // Автореферат – 2008. [Электронный ресурс]: https://economy-lib.com/disser/261633/a?#.
